💻 Educational Technology: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Educational technology (EdTech) refers to the use of technological tools and innovations to enhance teaching, learning, and administration in educational settings. It bridges the gap between traditional education methods and modern advancements, enabling more personalized, accessible, and effective learning experiences. RC passages on EdTech often explore themes such as digital learning platforms, artificial intelligence in education, and the role of technology in addressing educational inequities. Understanding these concepts allows readers to analyze the transformative impact of technology on education.
📋 Overview
This guide will explore the following essential EdTech concepts:
- Definition and Scope of Educational Technology
- Digital Learning Platforms
- Artificial Intelligence in Education
- Gamification in Learning
- Virtual and Augmented Reality in Education
- Accessibility and Inclusion in EdTech
- Learning Analytics
- Challenges in Implementing Educational Technology
- The Role of Teachers in the Digital Age
- Future Trends in Educational Technology
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. Definition and Scope of Educational Technology
Educational technology encompasses the tools, processes, and methodologies used to improve educational outcomes through technology. It includes both hardware, like tablets and interactive whiteboards, and software, such as learning management systems (LMS) and educational apps.
- Key Features:
- Enhances teaching efficiency through automated grading and curriculum management.
- Offers personalized learning paths tailored to individual student needs.
- Facilitates distance learning through online courses and virtual classrooms.
- Examples:
- Google Classroom streamlines communication and assignment management.
- Tablets in classrooms allow interactive learning experiences.
Explained Simply: EdTech is like upgrading a traditional classroom with digital tools to make learning more engaging and effective.
2. Digital Learning Platforms
Digital learning platforms provide online spaces for students and educators to access courses, materials, and assessments. These platforms enable learning beyond physical classrooms.
- Examples of Platforms:
- Khan Academy: Offers free lessons on subjects ranging from math to history.
- Coursera: Provides university-level courses and certifications.
- Features:
- Video tutorials, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums.
- Mobile access allows students to learn anytime, anywhere.
- Benefits:
- Expands access to education for students in remote areas.
- Supports self-paced learning and continuous skill development.
Explained Simply: Digital learning platforms are like virtual classrooms where anyone can learn from anywhere in the world.
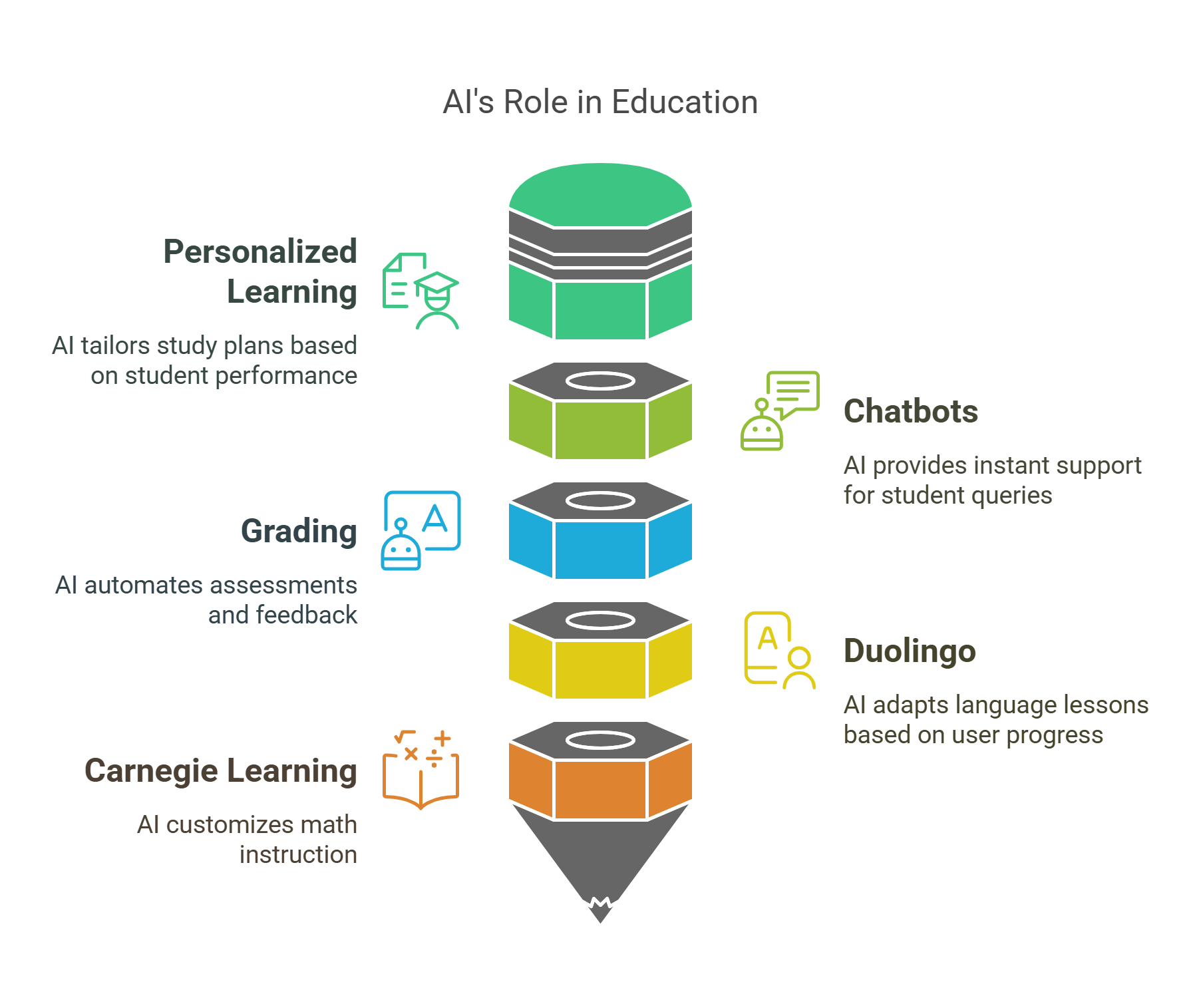
3. Artificial Intelligence in Education
AI in education uses machine learning and natural language processing to create adaptive learning experiences and automate administrative tasks.
- Applications in Learning:
- Personalized Learning: AI algorithms analyze student performance to suggest tailored study plans.
- Chatbots: Provide instant support for student queries.
- Grading: Automates assessments and provides feedback.
- Examples:
- Duolingo’s AI adapts language lessons based on user progress.
- Carnegie Learning uses AI to customize math instruction.
- Impact:
- Saves teachers time for instructional activities.
- Enhances student engagement through interactive tools.
Explained Simply: AI in education is like having a personal tutor and assistant that adapts to your needs and answers your questions instantly.
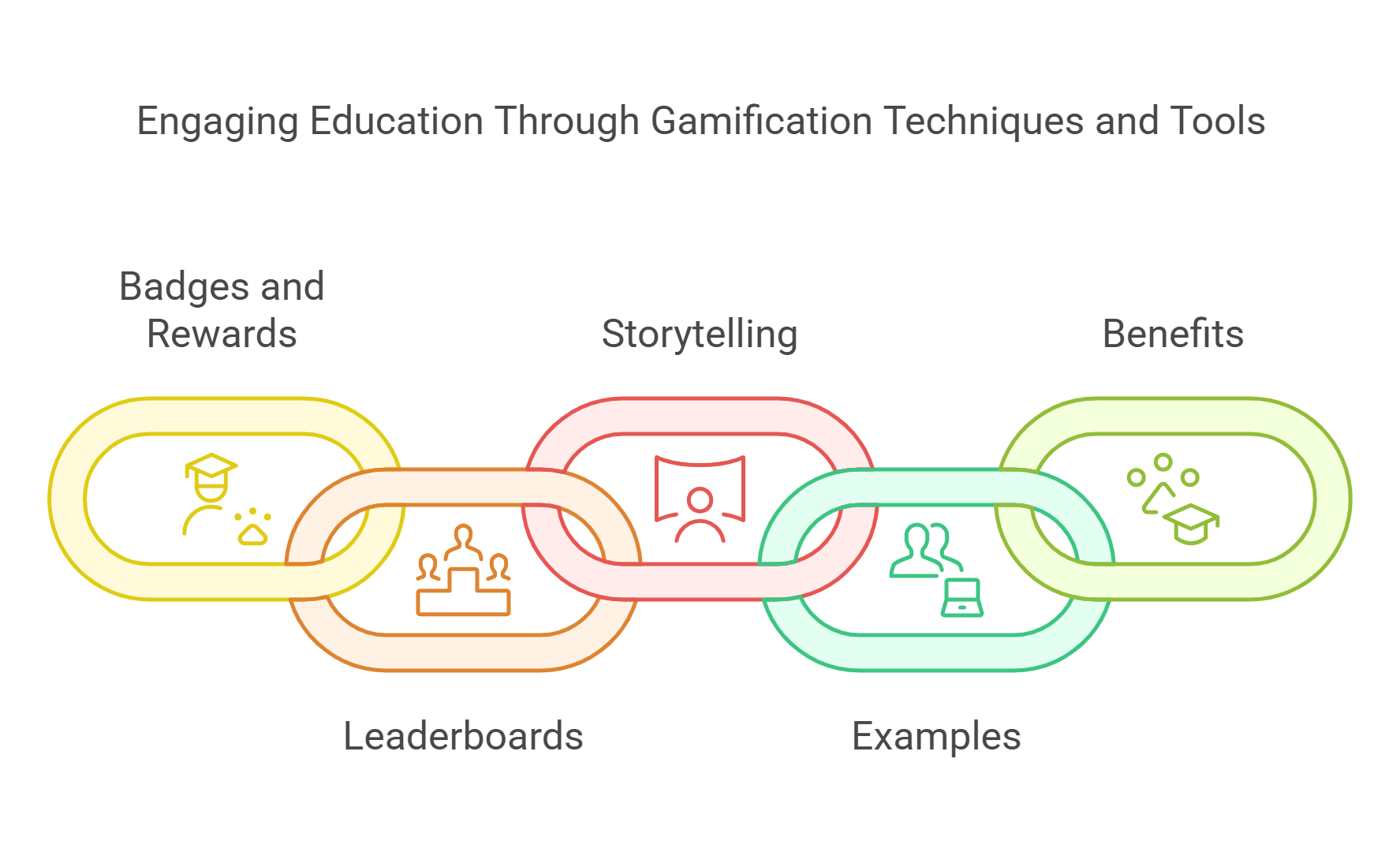
4. Gamification in Learning
Gamification applies game design elements to educational contexts to boost engagement and motivation.
- Key Elements:
- Badges and Rewards: Recognize achievements.
- Leaderboards: Foster healthy competition.
- Storytelling: Makes learning immersive and relatable.
- Examples:
- Kahoot!: Uses quizzes and games to make learning fun.
- Minecraft Education Edition: Teaches coding and problem-solving through a sandbox game environment.
- Benefits:
- Increases student participation.
- Reinforces learning through repetition in a fun format.
Explained Simply: Gamification turns learning into a game, making it exciting and rewarding.
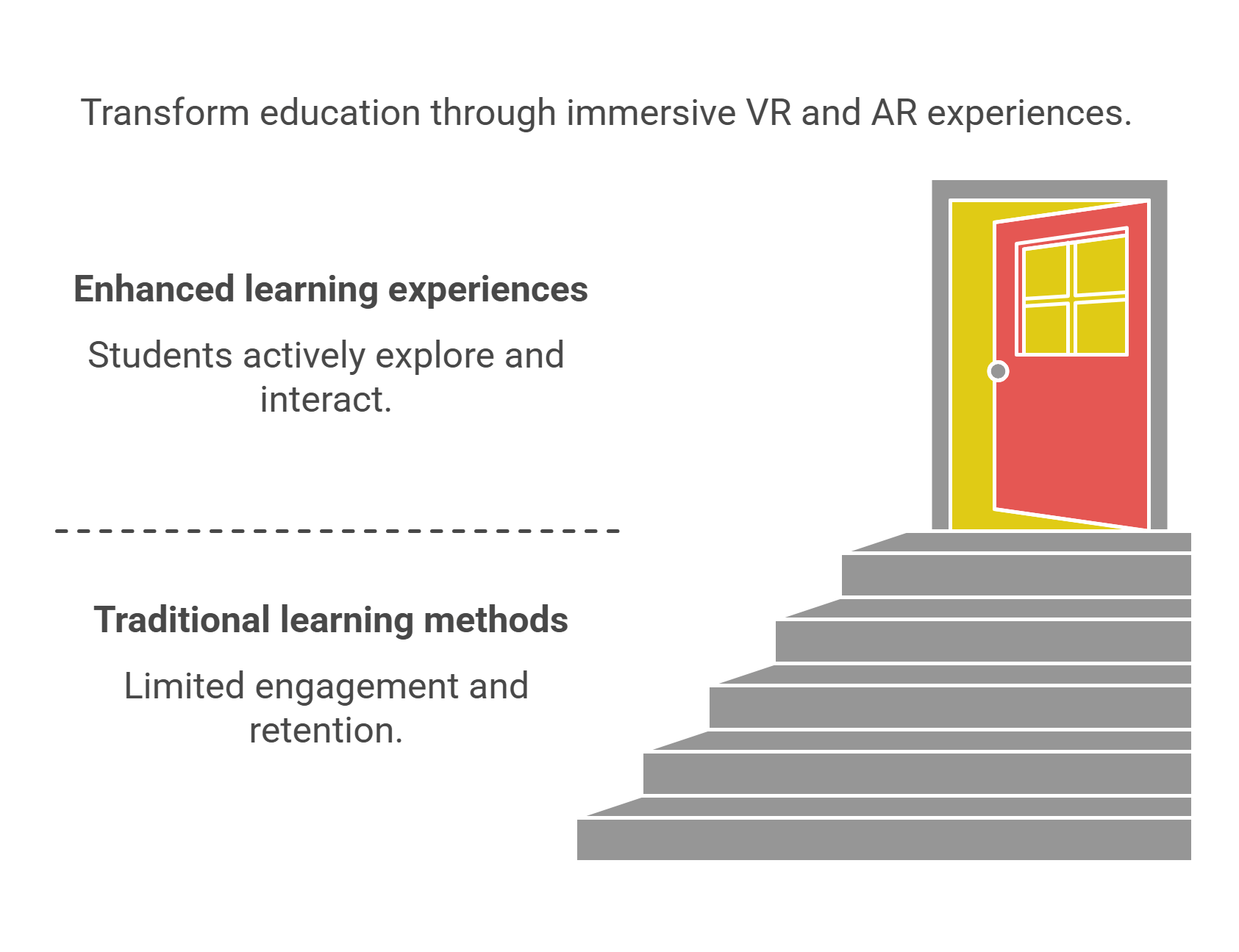
5. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Education
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) create immersive learning environments, allowing students to experience lessons in new and engaging ways.
- Virtual Reality:
- Simulates real-world or imagined scenarios.
- Example: VR field trips let students explore historical sites like ancient Rome.
- Augmented Reality:
- Overlays digital elements onto the real world.
- Example: AR apps like Google Lens provide interactive lessons by enhancing textbooks with 3D visuals.
- Impact:
- Improves retention through experiential learning.
- Makes abstract concepts tangible.
Explained Simply: VR and AR are like magic portals that bring lessons to life, allowing students to explore and interact with their subjects.
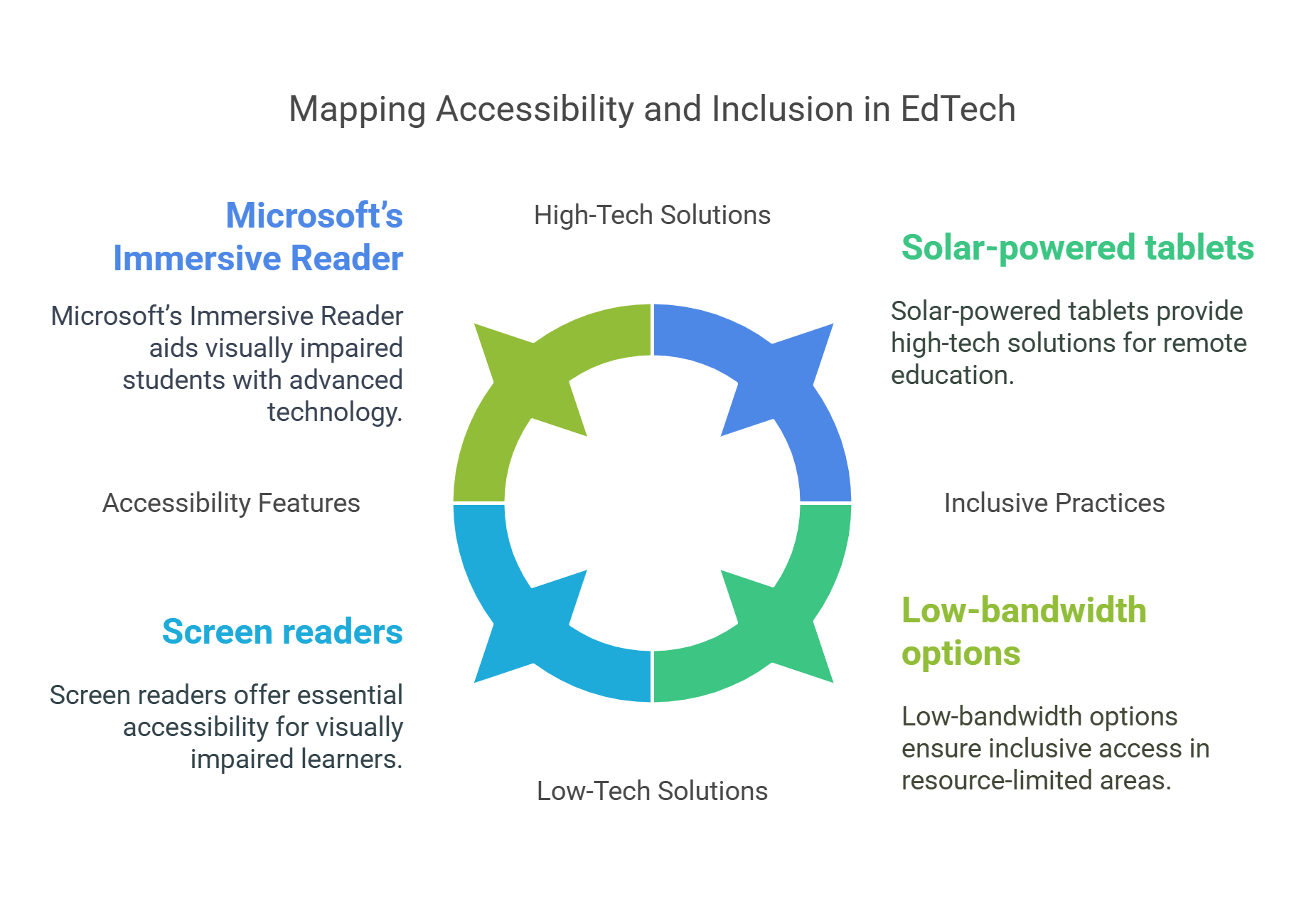
6. Accessibility and Inclusion in EdTech
Accessibility and inclusion ensure that EdTech benefits all learners, including those with disabilities or limited access to resources.
- Accessible Features:
- Screen readers for visually impaired students.
- Closed captions for videos to aid hearing-impaired learners.
- Inclusive Practices:
- Designing platforms that accommodate diverse learning needs.
- Providing low-bandwidth options for students in underserved areas.
- Examples:
- Microsoft’s Immersive Reader assists students with dyslexia.
- Solar-powered tablets bring education to remote villages in Africa.
Explained Simply: Accessibility in EdTech is like building ramps for everyone to climb the steps of education, regardless of their starting point.
7. Learning Analytics
Learning analytics uses data to measure, analyze, and improve student learning outcomes.
- Key Metrics:
- Engagement levels: Tracks participation in lessons and activities.
- Performance trends: Identifies strengths and areas for improvement.
- Applications:
- Early intervention for struggling students.
- Personalized feedback to enhance learning experiences.
- Examples:
- EdTech platforms like Blackboard provide dashboards for tracking student progress.
- Predictive analytics help educators anticipate dropout risks.
Explained Simply: Learning analytics is like a fitness tracker for education, helping students and teachers monitor progress and stay on track.
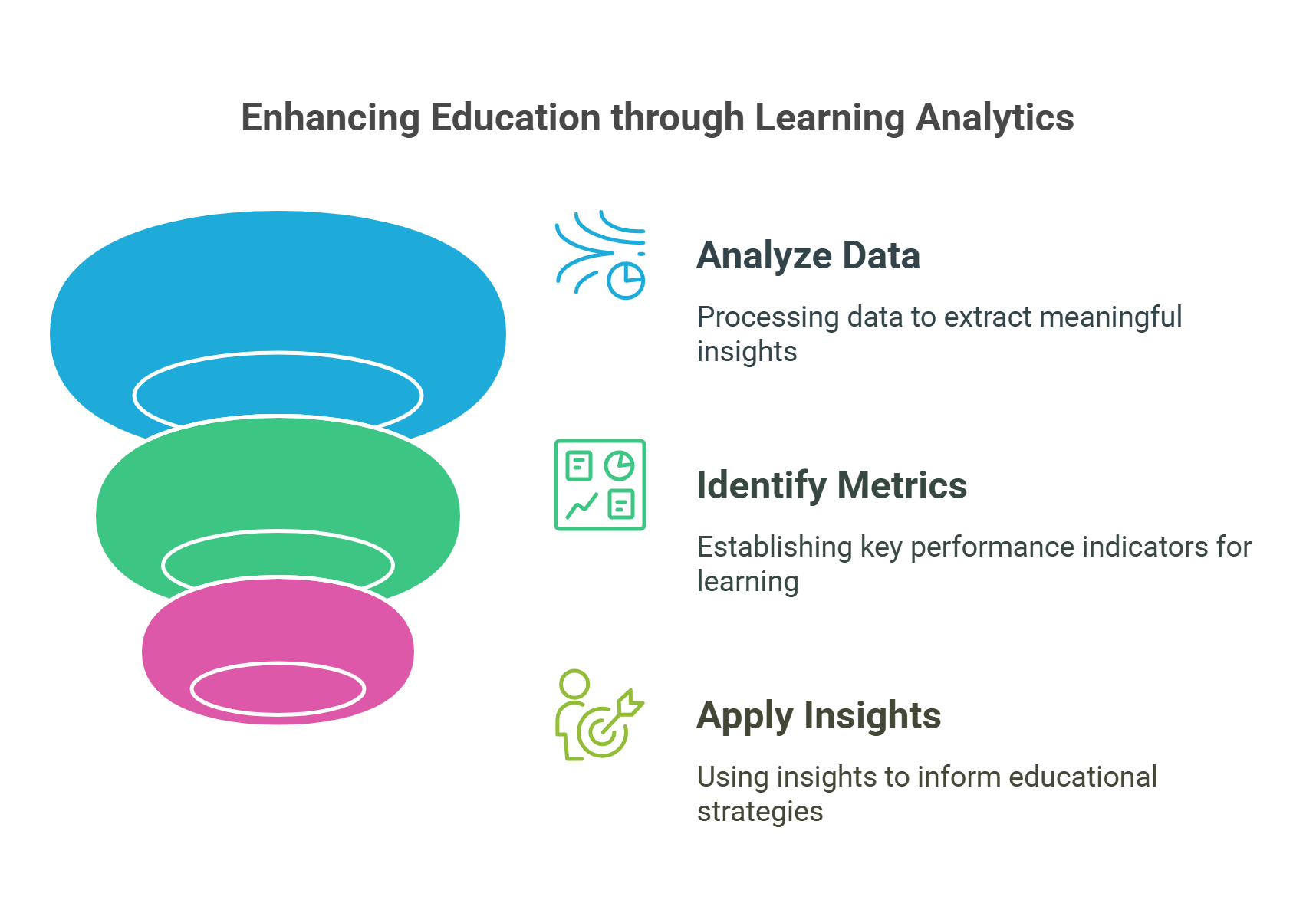
This infographic shows how learning analytics can be used to enhance education by analyzing data, identifying key metrics for learning, and applying insights to inform educational strategies for better student outcomes.
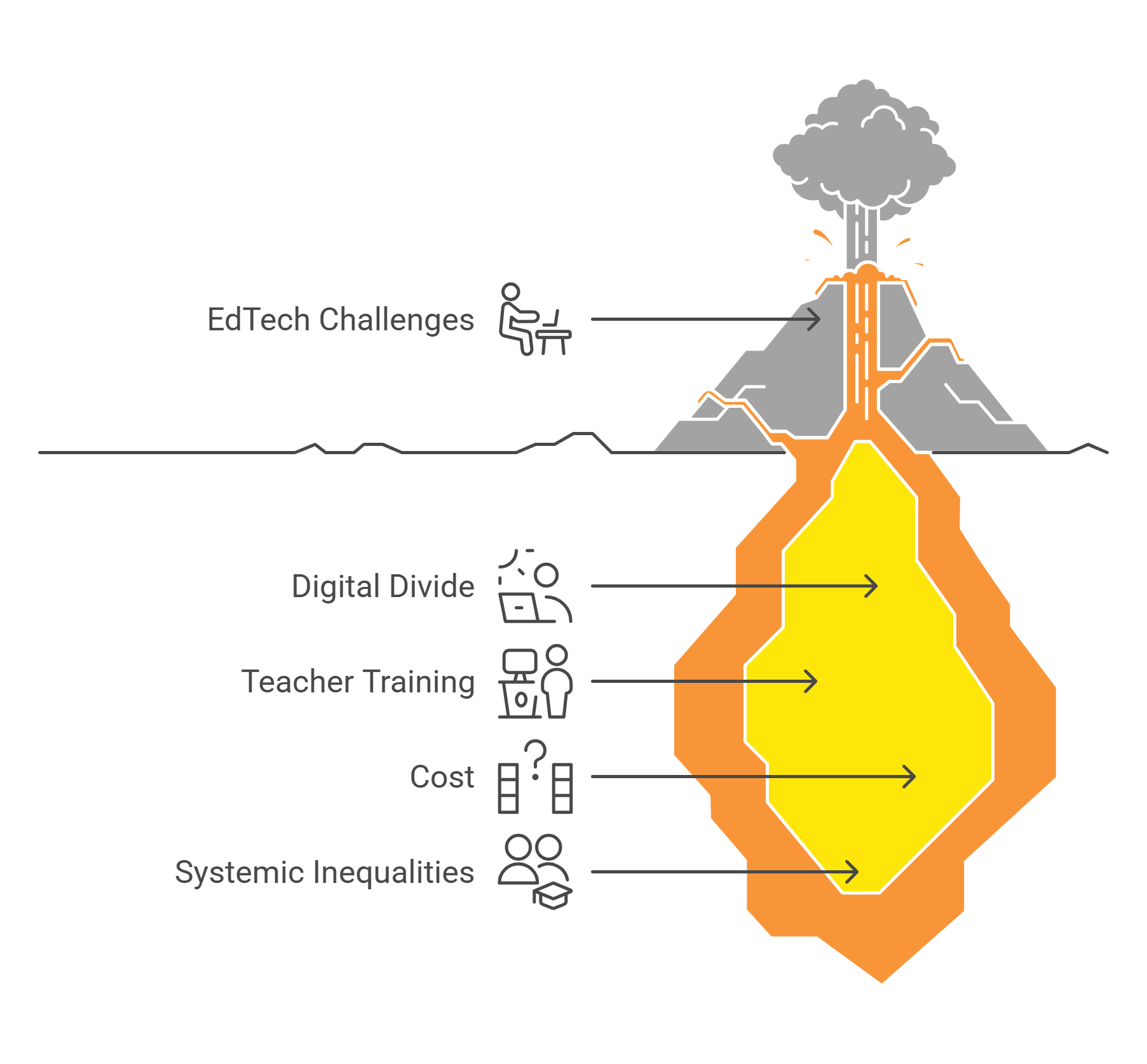
8. Challenges in Implementing Educational Technology
Despite its benefits, integrating EdTech into educational systems faces challenges, including infrastructure, training, and equity issues.
- Key Challenges:
- Digital Divide: Lack of access to devices and internet connectivity.
- Teacher Training: Inadequate preparation for using technology effectively.
- Cost: High initial investment in hardware and software.
- Examples:
- Rural schools struggle with internet connectivity.
- Teachers may lack confidence in using interactive whiteboards or LMS tools.
- Solutions:
- Public-private partnerships to expand access.
- Continuous professional development for educators.
Explained Simply: Implementing EdTech is like upgrading a car—it’s powerful, but only if everyone knows how to drive it and has access to the fuel.
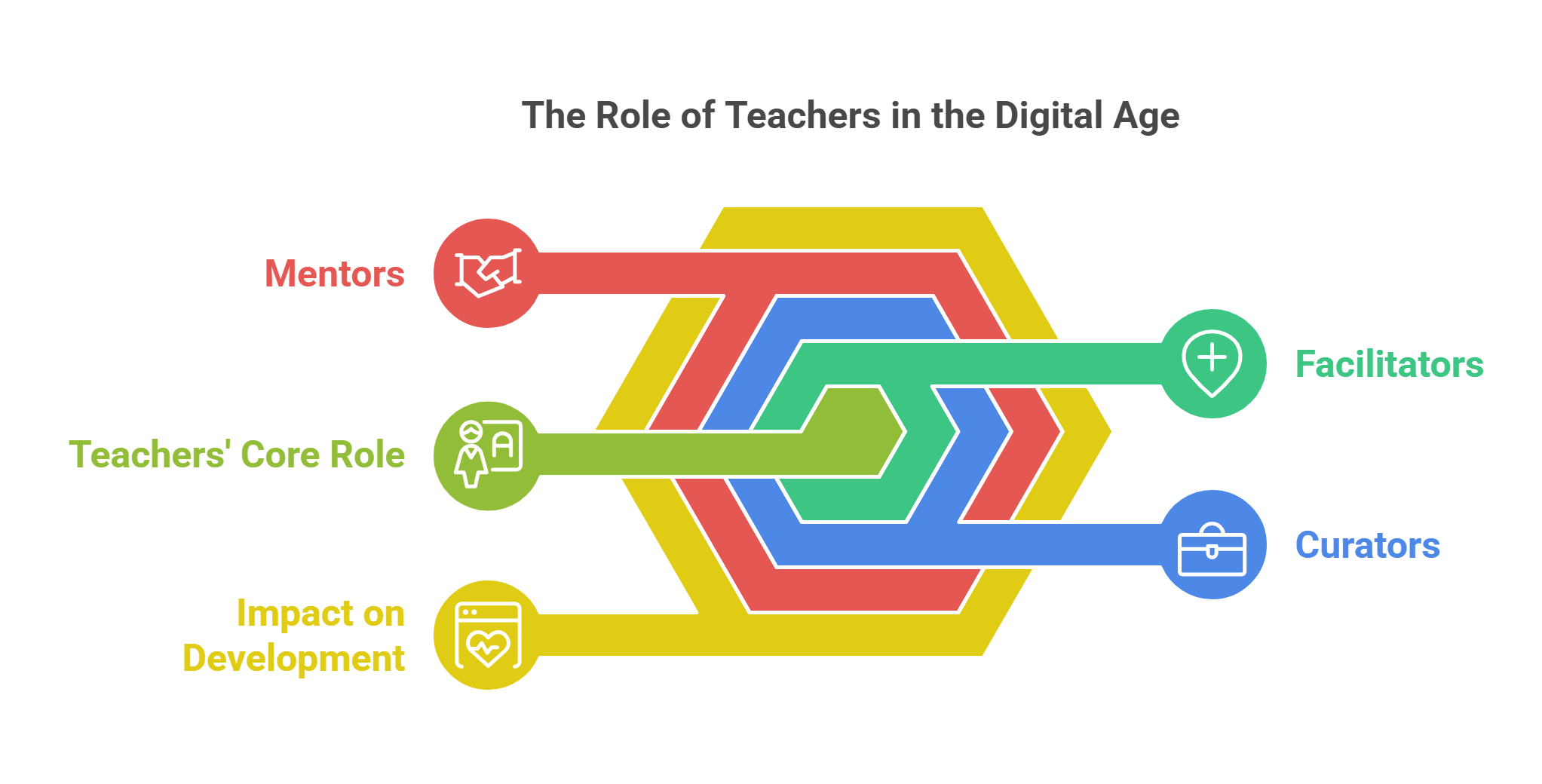
9. The Role of Teachers in the Digital Age
Teachers remain essential in the digital age, guiding students through technology-enhanced learning environments.
- Key Roles:
- Facilitators: Help students navigate online resources.
- Curators: Select the most effective digital tools and content.
- Mentors: Provide personalized support and motivation.
- Examples:
- Flipped classrooms allow teachers to spend more time on interactive problem-solving during class.
- Teachers use platforms like Seesaw to share student progress with parents.
- Impact: Human interaction remains crucial for emotional and social development.
Explained Simply: Teachers in the digital age are like navigators, helping students steer through the vast sea of knowledge.
10. Future Trends in Educational Technology
The future of EdTech is shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, connectivity, and innovative teaching methods.
- Trends:
- Adaptive Learning: Systems that adjust content based on real-time performance.
- Blockchain for Credentials: Secure storage of academic records.
- Global Collaboration: Platforms that connect classrooms across the world.
- Examples:
- 5G technology enhances real-time virtual learning experiences.
- AI-driven platforms like Squirrel AI tailor content to individual learning speeds.
- Challenges: Ethical concerns around data privacy and equitable access.
Explained Simply: The future of EdTech is like a rapidly expanding toolkit, offering new ways to learn and connect every day.
✨ Conclusion
Educational technology revolutionizes learning by making it more accessible, engaging, and personalized. By mastering concepts like digital learning platforms, AI, and inclusion, readers can better analyze RC passages on this transformative topic. Understanding EdTech equips us to harness its potential to address educational challenges and shape the future of learning. 💻












