Environment: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Introduction
Environmental topics in Reading Comprehension passages frequently delve into how humanity interacts with the natural world, addressing critical issues like sustainability, conservation, and climate change. These passages often weave together scientific principles, ethical debates, and socio-economic implications, requiring a nuanced understanding of key environmental concepts. Mastering these ideas helps test-takers engage with complex arguments and evaluate proposed solutions effectively.
Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these essential environmental concepts:
- Climate Change Policies
- Renewable Energy
- Circular Economy
- Urban Biodiversity
- Sustainable Development
- Carbon Footprint
- Conservation Biology
- Environmental Ethics
- Greenhouse Gases
- Ecosystem Services

Detailed Explanations
1. Climate Change Policies
Climate change policies include actions and strategies implemented by governments, organizations, and international bodies to combat the effects of climate change. These policies aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy, and enhance climate resilience.
- Focus on reducing global warming impacts.
- Includes international agreements and national regulations.
- Promotes renewable energy and sustainable practices.
- Involves economic incentives like carbon credits.
- Balances environmental goals with economic growth.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine the Earth is a big home we all share, but it’s getting too hot because of how we use things like cars and factories. Climate change policies are like house rules to make sure everyone helps cool it down, like planting trees or using fans instead of making more heat.
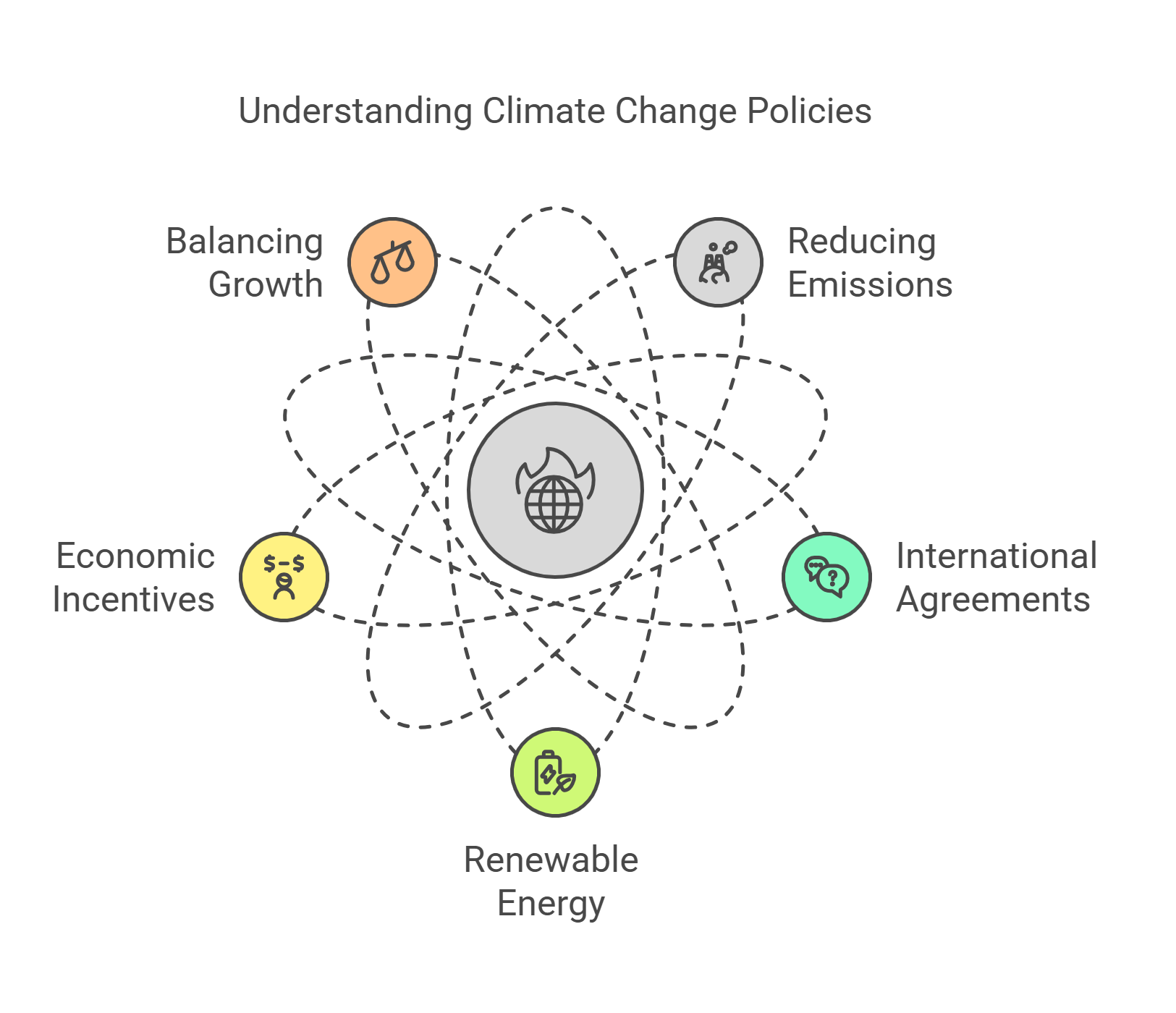
2. Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished, such as sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat. Unlike fossil fuels that release harmful emissions, renewable energy is cleaner and sustainable.
- Derived from naturally replenishing resources.
- Includes solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy.
- Reduces dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Helps combat climate change and air pollution.
- Promotes energy independence and sustainability.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like using the sun and wind to power your video games instead of plugging into a wall that uses old, smoky fuel. The sun and wind never run out, so they’re like magic batteries!
3. Circular Economy
A circular economy is an innovative system aimed at eliminating waste by rethinking how we design, produce, and use products. It emphasizes repairing, reusing, and recycling items instead of discarding them.
- Focuses on sustainability and reducing waste.
- Promotes recycling, repairing, and reusing materials.
- Reduces environmental impacts of production and consumption.
- Encourages innovative product design and resource efficiency.
- Aims to decouple economic growth from resource depletion.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine if every broken toy you had could either be fixed or turned into something new instead of being thrown away. A circular economy is all about finding ways to reuse everything, like recycling your favorite crayons into new ones.
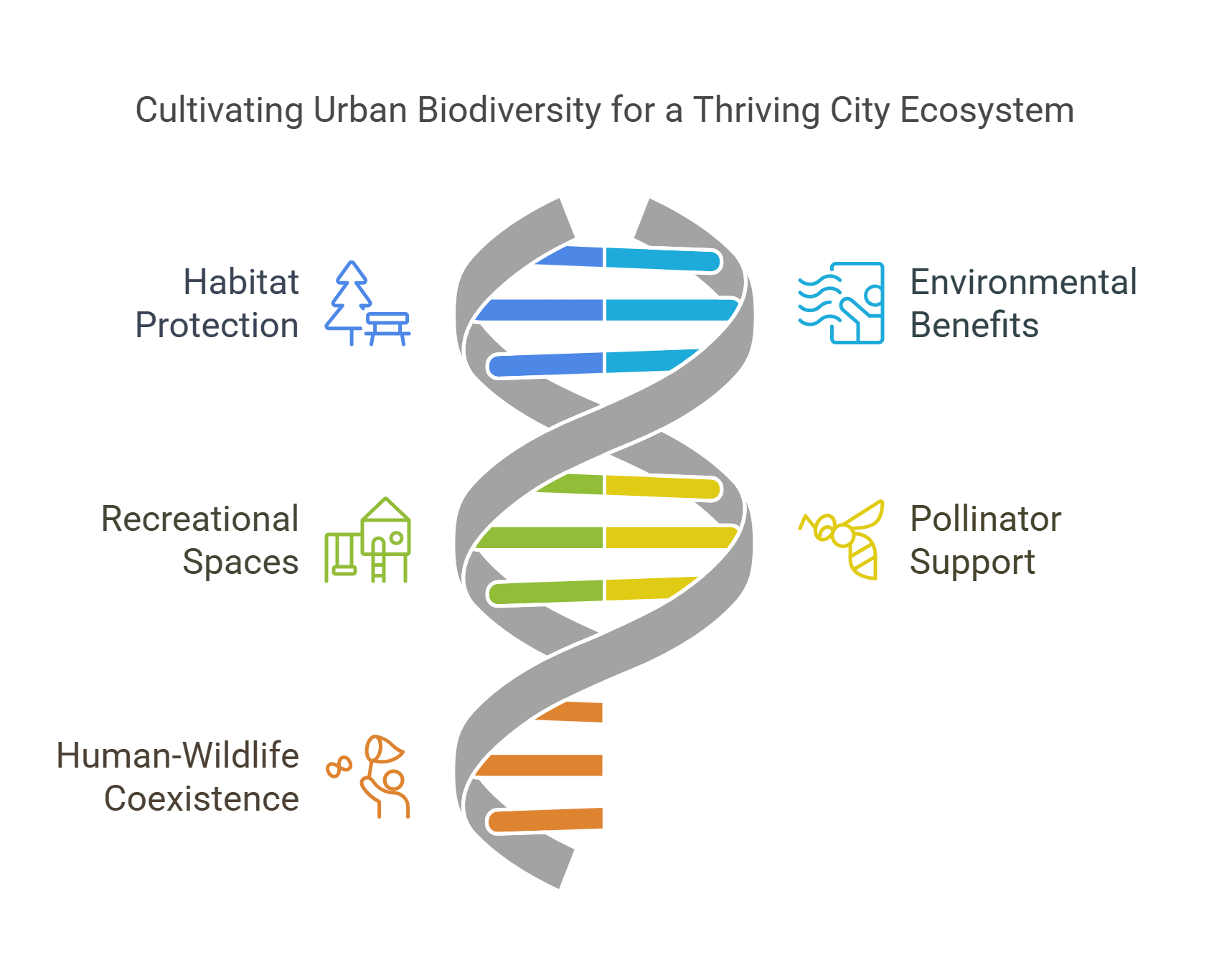
4. Urban Biodiversity
Urban biodiversity is the variety of plant and animal life found in cities and towns. It involves integrating green spaces, like parks and gardens, to support wildlife and ecosystems even in built-up areas.
- Involves protecting and restoring natural habitats in cities.
- Enhances air quality, water management, and urban cooling.
- Provides spaces for recreation and mental well-being.
- Supports pollinators like bees and birds essential for ecosystems.
- Encourages coexistence of humans and wildlife.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine if your city had more trees and flowers where birds and butterflies could live. Urban biodiversity is like turning cities into fun playgrounds for nature and people to share.
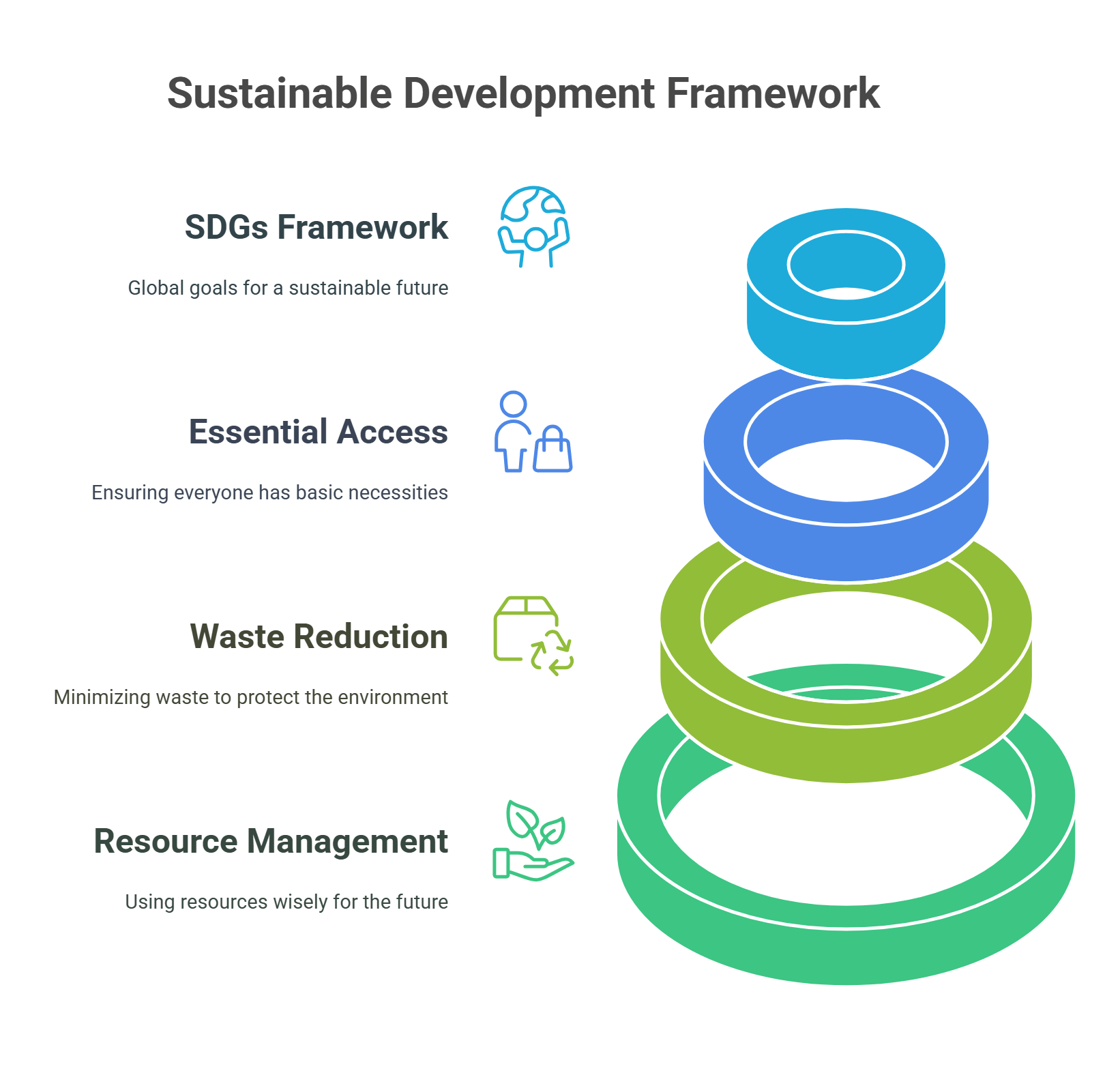
5. Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is about improving the quality of life for people today without harming resources for future generations. It includes finding ways to use natural resources responsibly, reducing waste, and ensuring fair access to necessities like clean water, education, and healthcare.
- Balances economic, environmental, and social goals.
- Focuses on long-term solutions for global challenges.
- Ensures resources remain available for future generations.
- Involves goals like clean water, education, and renewable energy.
- Central to international frameworks like the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like eating your favorite snacks carefully so there’s enough left for your friends and for tomorrow. Sustainable development is about sharing and saving for the future.
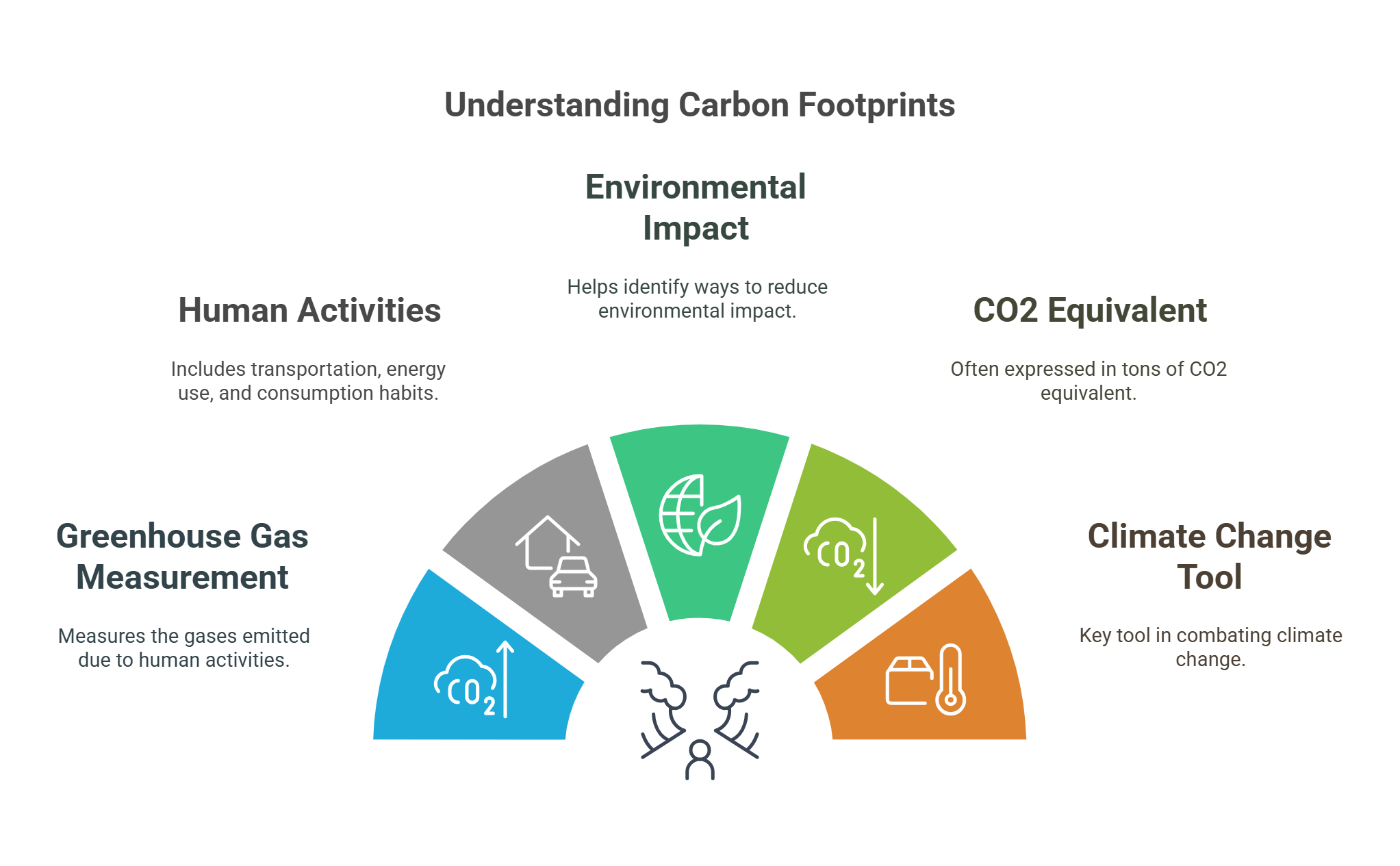
6. Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions produced directly or indirectly by an activity, person, or organization. Reducing a carbon footprint involves using energy-efficient appliances, recycling, and choosing renewable energy sources.
- Measures the greenhouse gases emitted due to human activities.
- Includes transportation, energy use, and consumption habits.
- Helps identify ways to reduce environmental impact.
- Often expressed in tons of CO2 equivalent.
- Key tool in combating climate change.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine every time you use something like a car or turn on a light, you leave invisible footprints in the air. A carbon footprint is how big those footprints are, and we try to make them as small as possible.
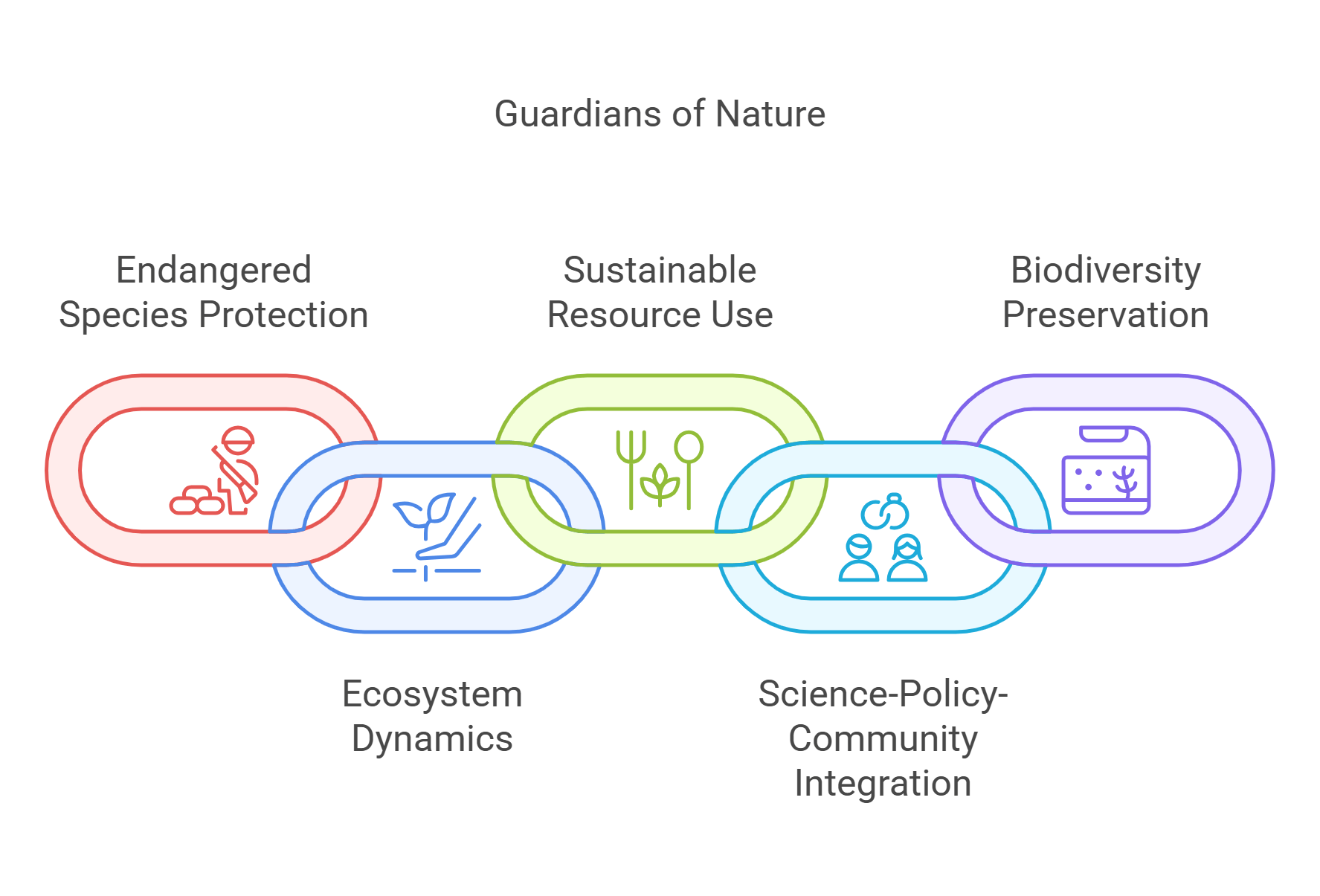
7. Conservation Biology
Conservation biology is the study of protecting and restoring the diversity of life on Earth. It focuses on saving endangered species, restoring damaged ecosystems, and finding ways to balance human activity with nature.
- Protects endangered species and habitats.
- Studies ecosystem dynamics and human impact.
- Encourages sustainable use of natural resources.
- Integrates science, policy, and community action.
- Vital for preserving biodiversity and ecosystem services.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like being a superhero for animals and plants, saving their homes so they don’t disappear forever.
8. Environmental Ethics
Environmental ethics is a branch of philosophy that considers the moral relationship between humans and nature. It questions how we should treat the environment and whether non-human life and ecosystems have intrinsic value.
- Studies the moral value of nature and ecosystems.
- Explores human responsibilities toward the environment.
- Encourages practices like conservation and sustainability.
- Addresses issues like deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
- Balances human needs with nature’s rights.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Think of the Earth as a friend who needs our care and respect. Environmental ethics teaches us how to take care of that friend so they stay happy and healthy.
9. Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere, maintaining the planet’s temperature. However, excess GHGs, like carbon dioxide and methane, contribute to global warming.
- Includes gases like CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide.
- Traps heat and regulates Earth’s temperature.
- Excessive GHG emissions lead to global warming.
- Key focus in climate change mitigation.
- Reduced through renewable energy and conservation efforts.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Greenhouse gases are like a blanket keeping Earth warm. But if the blanket gets too thick, it gets uncomfortably hot, like wearing three blankets in summer!
10. Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits nature provides to humans, such as clean air, water, pollination, and climate regulation. These services are critical for survival and support economic and recreational activities.
- Provides essentials like air, water, and food.
- Includes pollination, soil fertility, and climate regulation.
- Supports economic and recreational activities.
- Essential for biodiversity and human health.
- Threatened by habitat destruction and pollution.
Conclusion
Environmental concepts provide critical insights for tackling RC passages, helping you evaluate complex issues like sustainability, conservation, and climate resilience. By understanding these ideas, you can better engage with diverse arguments and contribute meaningfully to discussions about our planet’s future.













