Geo: The Root of Earth's Wonders
Discover the fascinating world of "Geo," the Greek root meaning "Earth." From geography and geology to geophysics and geothermal energy, this root connects us to Earth's physical and cultural landscapes, emphasizing our planet's central role in science, history, and daily life.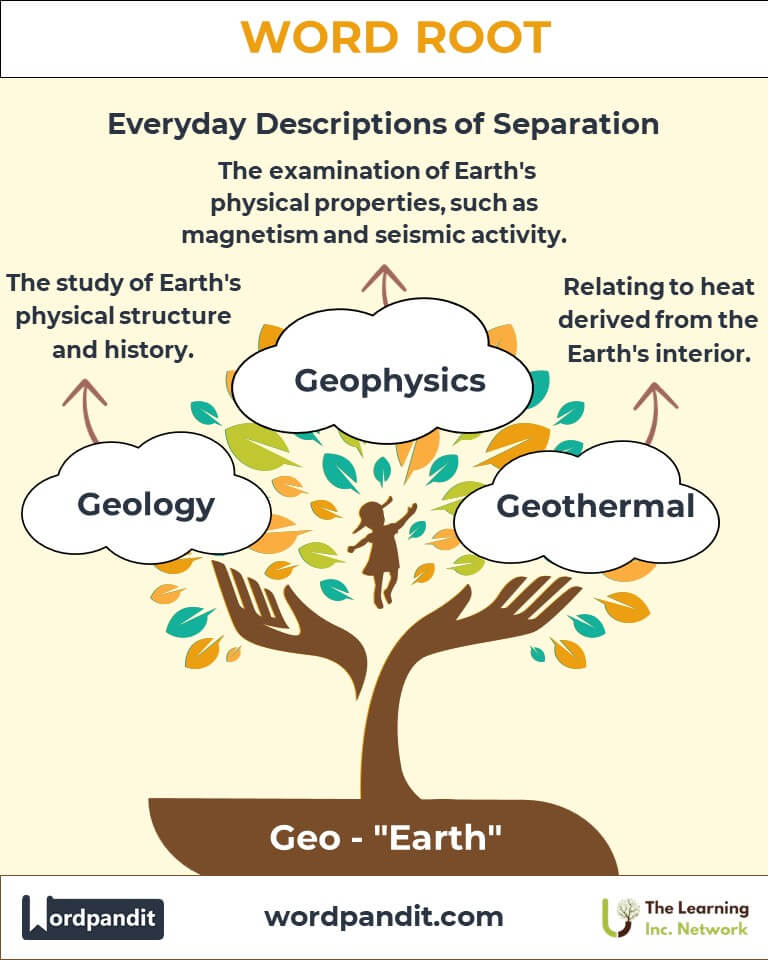
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Geo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Geo
- Common Geo-Related Words
- Geo Through Time
- Geo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Geo in Action
- Cultural Significance of Geo
- The Geo Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Foundation of Geo
Introduction: The Significance of Geo
The root "Geo," derived from the Greek word "ge," meaning "Earth," serves as the foundation for words and fields of study that explore our planet. From the detailed analysis of physical landscapes in geology to the spatial patterns of life and cultures in geography, "Geo" reminds us of the dynamic and interconnected nature of our world.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The term "Geo" has its origins in ancient Greece, where "ge" signified Earth or land. Greek philosophers like Aristotle and Ptolemy used this root to develop concepts about Earth's shape, composition, and position in the cosmos. As language evolved, "Geo" merged with Latin and English, forming key scientific terms such as geology (study of Earth’s structure) and geocentric (Earth-centered astronomy).
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Geo
Imagine a globe spinning on your desk, its vast landscapes representing the essence of "Geo."
Mnemonic Device: “Geo grounds us in Earth's story, from its geology to its geography.”
Common Geo-Related Words
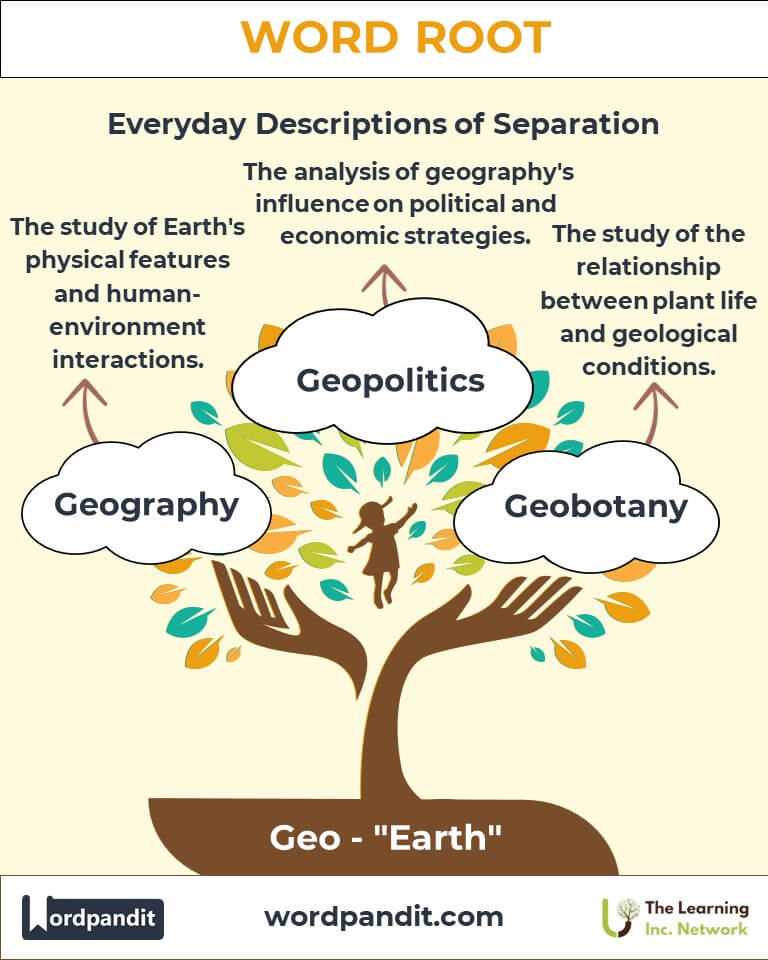
- Geography (jee-og-ruh-fee): The study of Earth’s physical features and human-environment interactions.
Example: "Geography helps us understand how natural features influence human settlement."
- Geology (jee-ol-uh-jee): The science of Earth's physical structure, history, and processes.
Example: "The geologist examined the rock layers to determine their age."
- Geometry (jee-om-i-tree): A branch of mathematics dealing with shapes, sizes, and spatial properties.
Example: "Geometry has its roots in measuring land for farming and construction."
- Geothermal (jee-oh-thur-muhl): Relating to heat derived from the Earth's interior.
Example: "Geothermal energy provides a sustainable power source."
Geo Through Time
- Geocentric Theory (Ancient): The belief that Earth is the center of the universe, prevalent in ancient Greek and medieval astronomy.
Shift: Replaced by the heliocentric model during the Renaissance.
- Geodesy (Historical): The study of Earth’s shape, size, and gravitational field, crucial for map-making and navigation.
Geo in Specialized Fields
- Geophysics:
Examines Earth's physical properties, such as magnetic fields and seismic activity, aiding in earthquake prediction and resource exploration.
- Geobotany:
Studies the relationship between geological conditions and plant life.
Example: "Geobotany explains why certain plants thrive in volcanic soils."
- Geopolitics:
Analyzes the influence of geography on political and economic strategies.
Example: "Geopolitics often dictates global trade routes and alliances."
Illustrative Story: Geo in Action
As a young geologist, Sarah traveled to Iceland to study its geothermal energy systems. Standing amidst geysers and bubbling hot springs, she marveled at Earth's power. Her work not only advanced renewable energy but also deepened her appreciation for Earth's dynamic processes, embodying the spirit of "Geo."
Cultural Significance of Geo
From ancient myths where Earth was personified as Gaia, the mother goddess, to modern movements emphasizing environmental stewardship, "Geo" captures humanity's evolving relationship with the planet. It bridges science, culture, and philosophy, reminding us of our responsibility to cherish and protect our home.

The Geo Family Tree
- Terra- (Latin: "Earth/land"):
- Terrarium: A container replicating a terrestrial environment.
- Terrestrial: Pertaining to land or Earth.
- Gaia- (Greek: "Earth"):
- Gaian: Related to Earth-centric ecological perspectives.
- Humus- (Latin: "Soil/ground"):
- Humus: Organic material in soil essential for plant growth.
FAQs About the Geo Word Root
Q: What does "Geo" mean?
A: "Geo" is derived from the Greek word "ge," meaning "Earth." It is used as a root in many words related to the study, description, and exploration of Earth’s physical properties, processes, and interactions with human life. For example, "geology" focuses on Earth's structure and substances, while "geography" examines the spatial relationships on its surface.
Q: What is the difference between Geography and Geology?
A:
- Geography: Studies Earth's surface, focusing on physical features, human activity, and the interactions between them. For example, it explores climate patterns, population distribution, and land use.
- Geology: Delves deeper into Earth's physical composition and processes, including rock formations, tectonic activity, and the history of the planet. Geology investigates phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Q: What is Geothermal energy?
A: Geothermal energy refers to the heat stored within Earth’s interior. This renewable energy source is harnessed by tapping into underground reservoirs of steam or hot water, often near tectonic plate boundaries. It is used for electricity generation, heating buildings, and other applications. Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Q: What is Geodesy?
A: Geodesy is the scientific study of Earth’s shape, size, orientation in space, and gravitational field. This discipline provides essential data for mapping, navigation, and understanding sea-level changes. Modern geodesy relies on advanced tools like satellites and GPS systems to measure and monitor Earth's features.
Q: How is "Geo" used in culture and mythology?
A: In ancient Greek mythology, "Geo" (or Gaia) was personified as the Earth goddess, representing life and fertility. Gaia played a central role as the mother of all life and was revered in rituals and cosmological beliefs. Today, "Gaia" also symbolizes ecological awareness, as seen in terms like the Gaia hypothesis, which views Earth as a self-regulating system.
Q: What is the Geocentric model, and how did it change?
A: The geocentric model was an ancient belief that Earth was the center of the universe, with all celestial bodies revolving around it. Promoted by thinkers like Ptolemy, this view dominated astronomy until the 16th century, when Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the heliocentric model, which placed the Sun at the center. This paradigm shift revolutionized scientific understanding of the cosmos.
Q: Why is Geometry connected to "Geo"?
A: Geometry, meaning "Earth measurement," originated in ancient civilizations as a practical method to measure land for farming, construction, and boundaries. The study expanded into a mathematical field dealing with shapes, sizes, and spatial properties. Its name reflects its early application in understanding Earth’s landscapes.
Q: How does Geopolitics use the "Geo" root?
A: Geopolitics examines the influence of geography on political and economic strategies. For example, nations might prioritize control of natural resources or trade routes based on their geographic positions. Geopolitics highlights how physical terrain, climate, and access to oceans or rivers can shape global power dynamics.
Q: What does Geobotany study?
A: Geobotany explores the relationship between plants and their geological environment. This field investigates how soil composition, mineral availability, and climate influence plant growth and distribution. It is vital for understanding ecosystems, agriculture, and biodiversity.
Test Your Knowledge: Geo Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Geo" signify?
2. Which word describes Earth-centered astronomy?
3. What does Geothermal energy utilize?
4. Which term describes the study of Earth’s physical structure and materials?
5. What does Geobotany study?
Conclusion: The Foundation of Geo
The root "Geo" serves as a linguistic and conceptual bridge to understanding Earth's complexities. From studying its physical features to harnessing its resources, "Geo" emphasizes humanity’s connection to our planet. As we face challenges like climate change, the lessons of "Geo" remind us of the importance of preserving Earth’s balance for future generations.














