🌍 International Relations: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
International Relations (IR) is a multidisciplinary field that examines how countries interact, the principles guiding these interactions, and their impact on global affairs. For Reading Comprehension (RC) passages, understanding IR is crucial for analyzing arguments about diplomacy, trade, security, and global governance. Familiarity with IR concepts can help in identifying the main ideas, dissecting arguments, and evaluating the implications of global challenges often discussed in RC passages.
📋 Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these key International Relations-related concepts:
- Diplomacy
- International Organizations
- Global Security
- International Trade
- Humanitarian Interventions
- Foreign Policy
- International Law
- Conflict Resolution
- Global Governance
- International Political Economy
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. Diplomacy
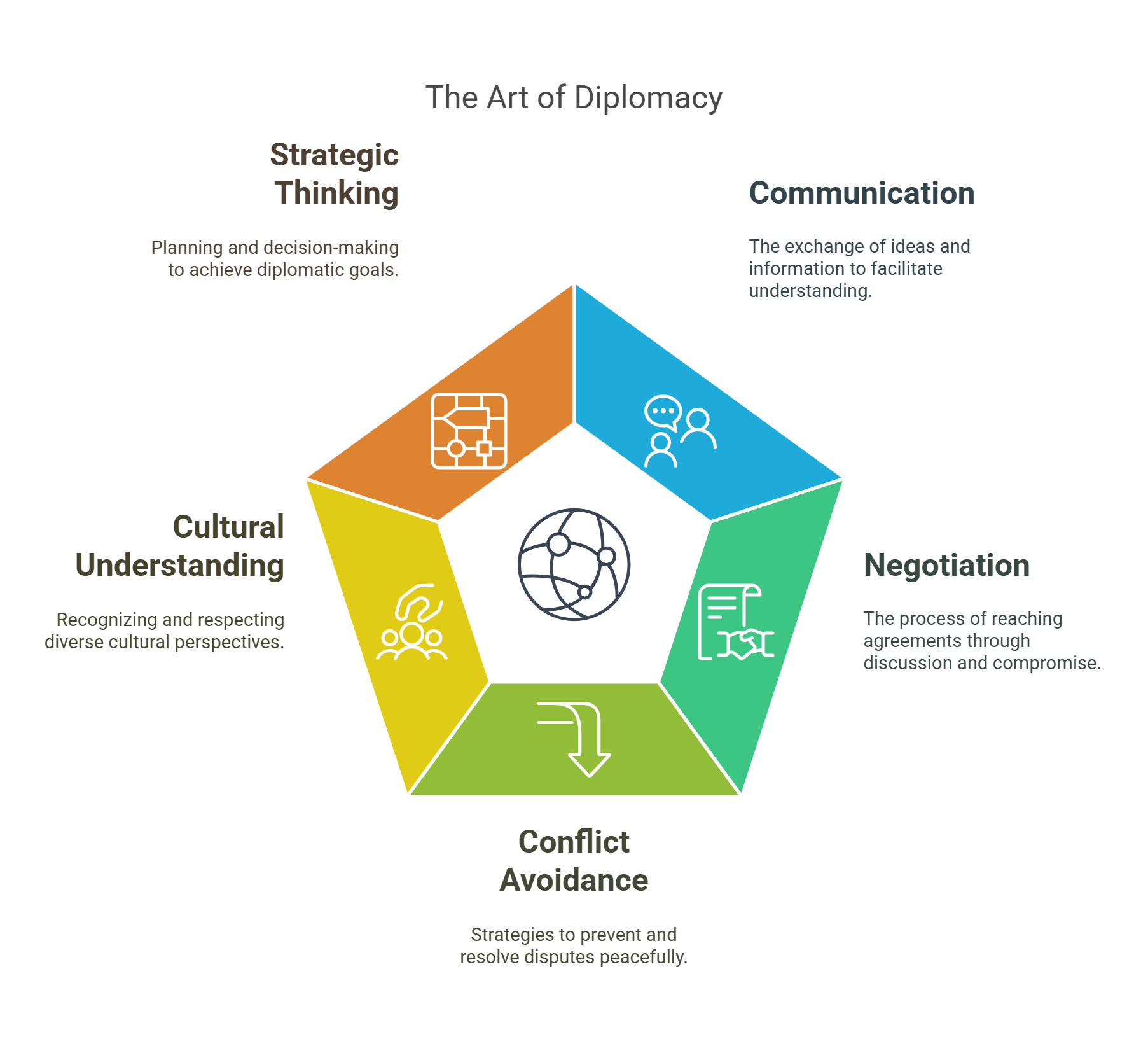
Diplomacy refers to the practice of managing relations between countries through dialogue and negotiation rather than conflict. It serves as the cornerstone of peaceful international interactions, enabling nations to resolve disputes, form alliances, and cooperate on global issues.
- Relies on communication and negotiation.
- Avoids war and conflict by finding common ground.
- Examples include United Nations peacekeeping missions or climate summits.
- Often involves both public and behind-the-scenes discussions.
- Requires cultural understanding and strategic thinking.
Explained Simply: Diplomacy is like when two kids on a playground want to share a swing but don’t want to fight. Instead, they talk it out and decide to take turns, making sure everyone is happy and safe.
2. International Organizations
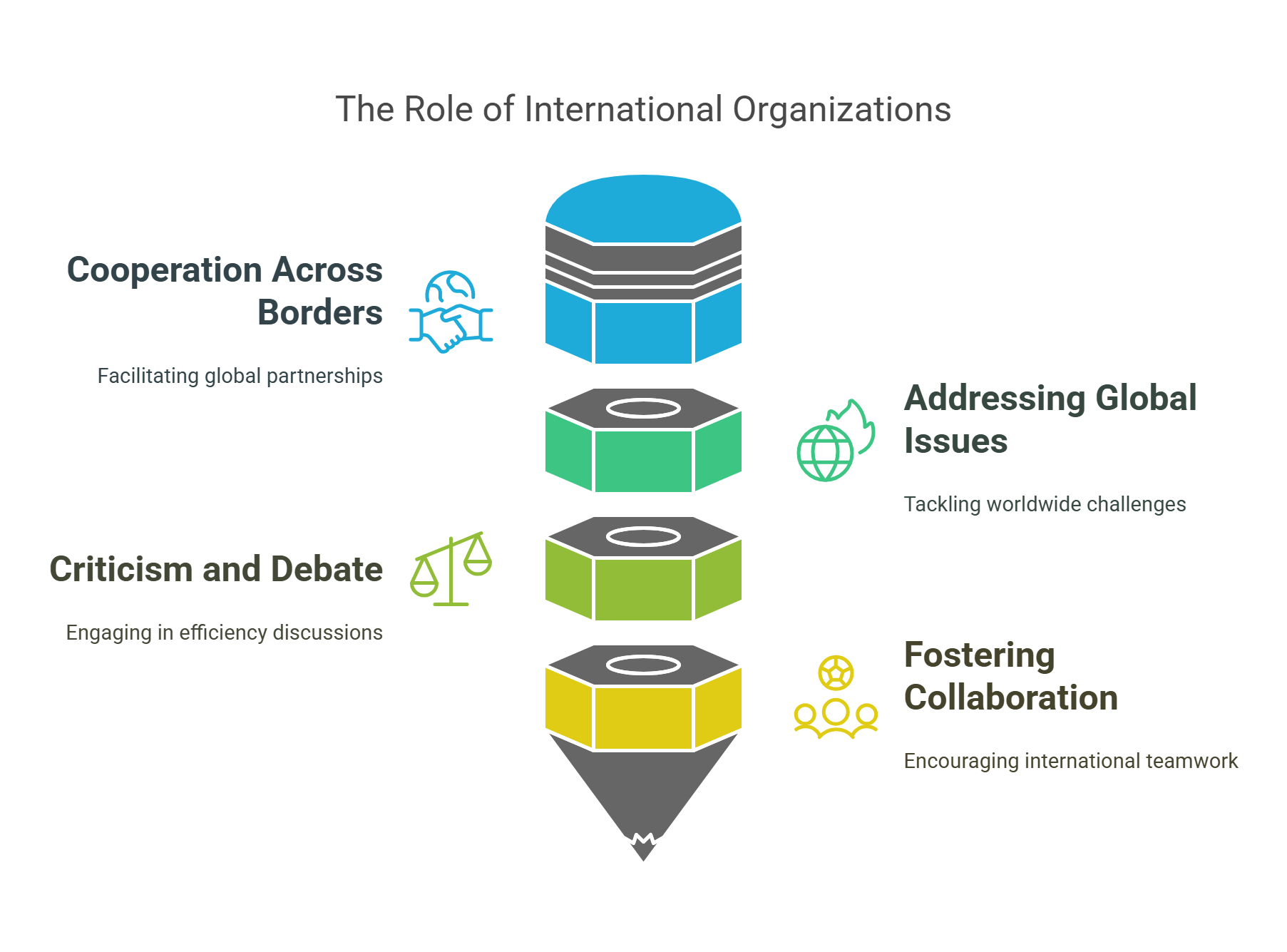
International organizations, such as the United Nations, World Health Organization, and NATO, are groups formed by countries to address global issues collectively. They promote cooperation in areas like health, security, and human rights.
- Work across borders for common goals.
- Examples include the United Nations and World Trade Organization.
- Tackle problems like pandemics, poverty, and climate change.
- Critics often debate their efficiency or biases.
- Vital for fostering collaboration among nations.
Explained Simply: Think of international organizations as a team of superheroes from different countries working together to solve big problems like sickness or pollution. Each hero brings their special powers to help.
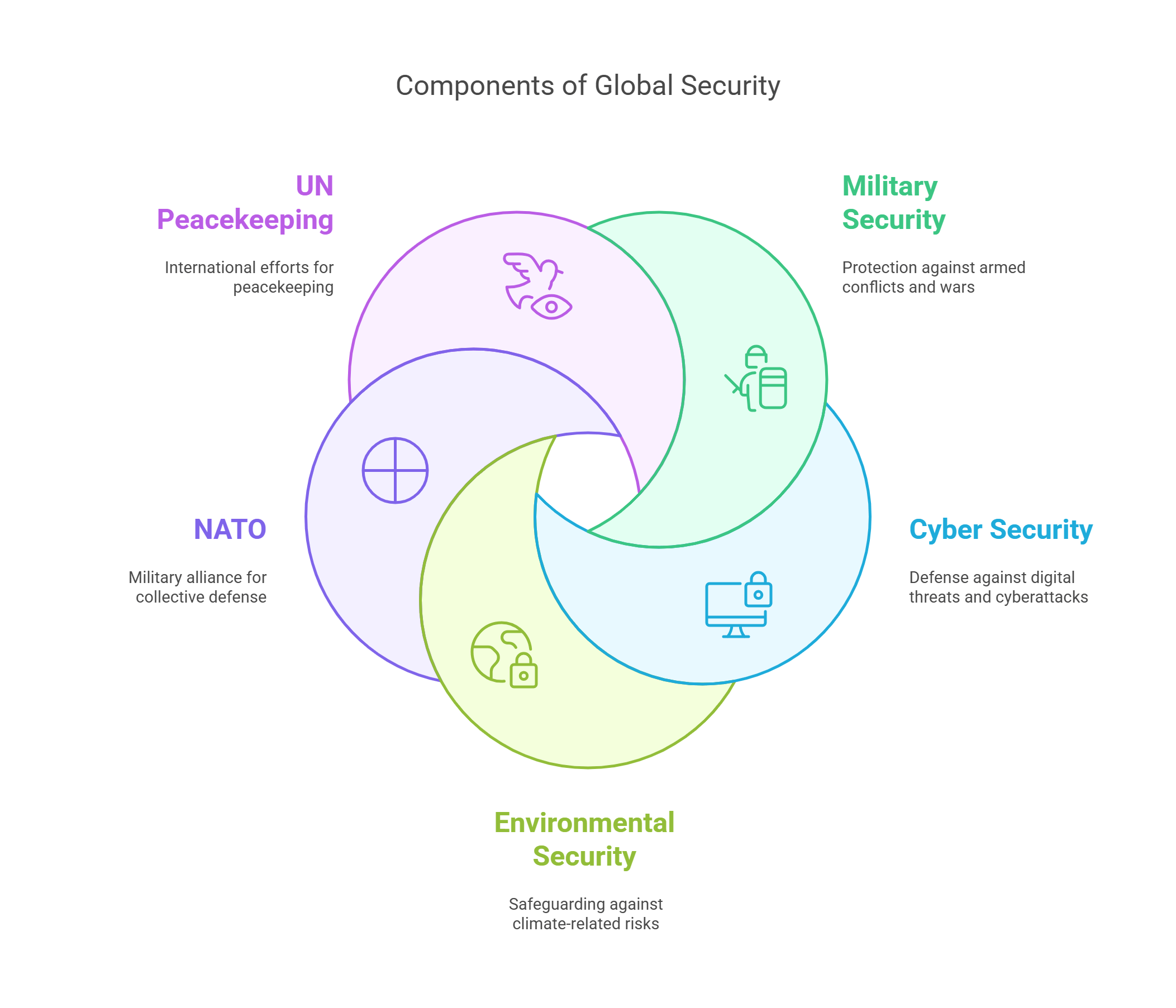
3. Global Security
Global security refers to efforts by countries and international organizations to maintain peace and protect against threats like terrorism, war, or cyberattacks. It emphasizes collective action to address challenges that no single nation can handle alone.
- Focuses on protecting countries from global threats.
- Includes military, cyber, and environmental security.
- NATO and UN peacekeeping forces are key players.
- Terrorism, nuclear proliferation, and climate change are common concerns.
- Requires global cooperation and shared responsibilities.
Explained Simply: Global security is like a neighborhood watch where everyone looks out for each other to keep their homes safe from burglars, storms, or other dangers.
4. International Trade
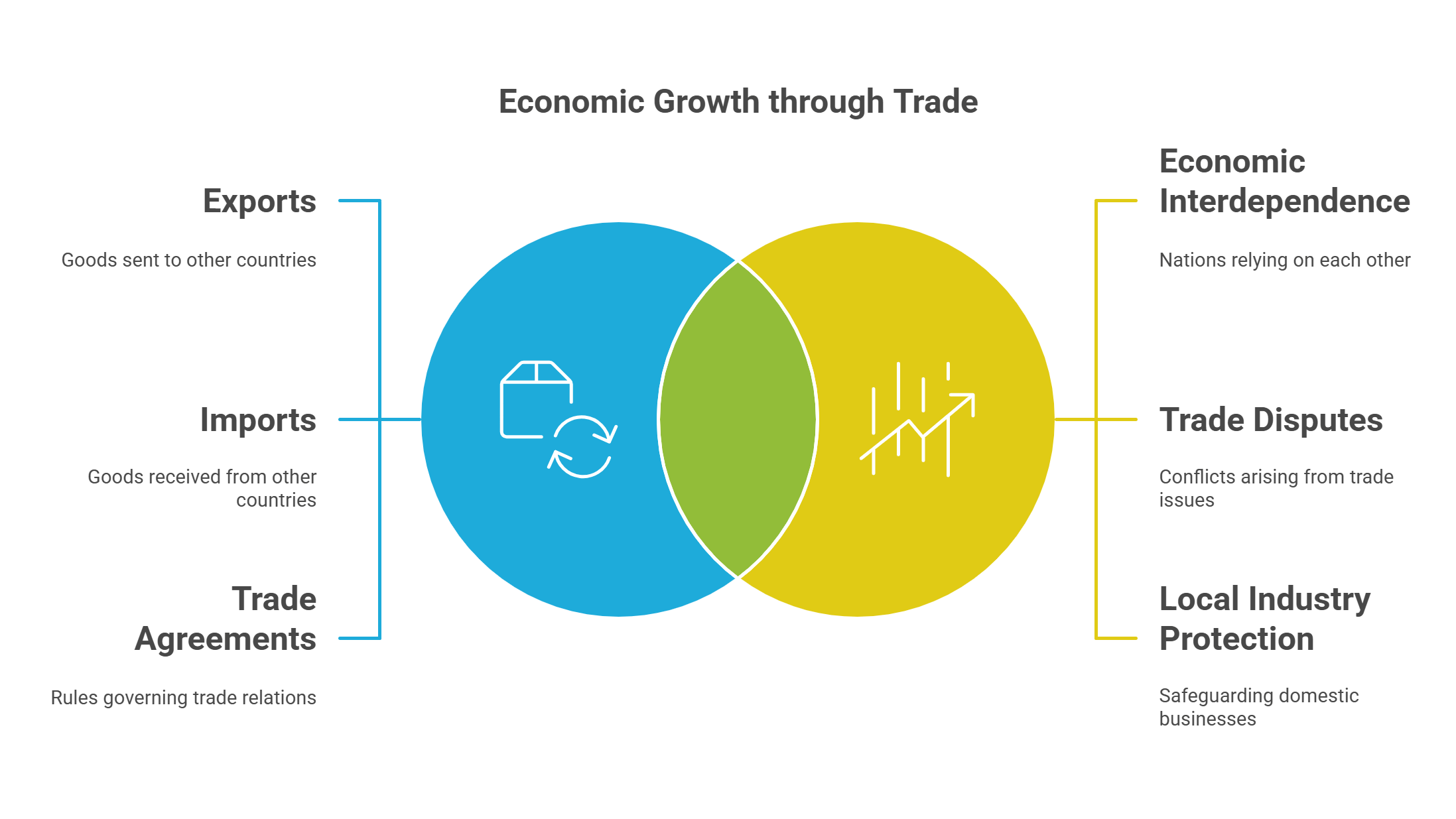
International trade involves the exchange of goods, services, and capital between countries. It drives economic growth and fosters relationships between nations.
- Facilitates the exchange of resources between nations.
- Includes exports, imports, and trade agreements like NAFTA or WTO rules.
- Tariffs, sanctions, and subsidies are frequent discussion points.
- Promotes economic interdependence but may cause trade disputes.
- Balances free trade with the protection of local industries.
Explained Simply: International trade is like kids swapping snacks at lunch – one has chips, another has cookies, and they trade to share and enjoy more variety.
5. Humanitarian Interventions
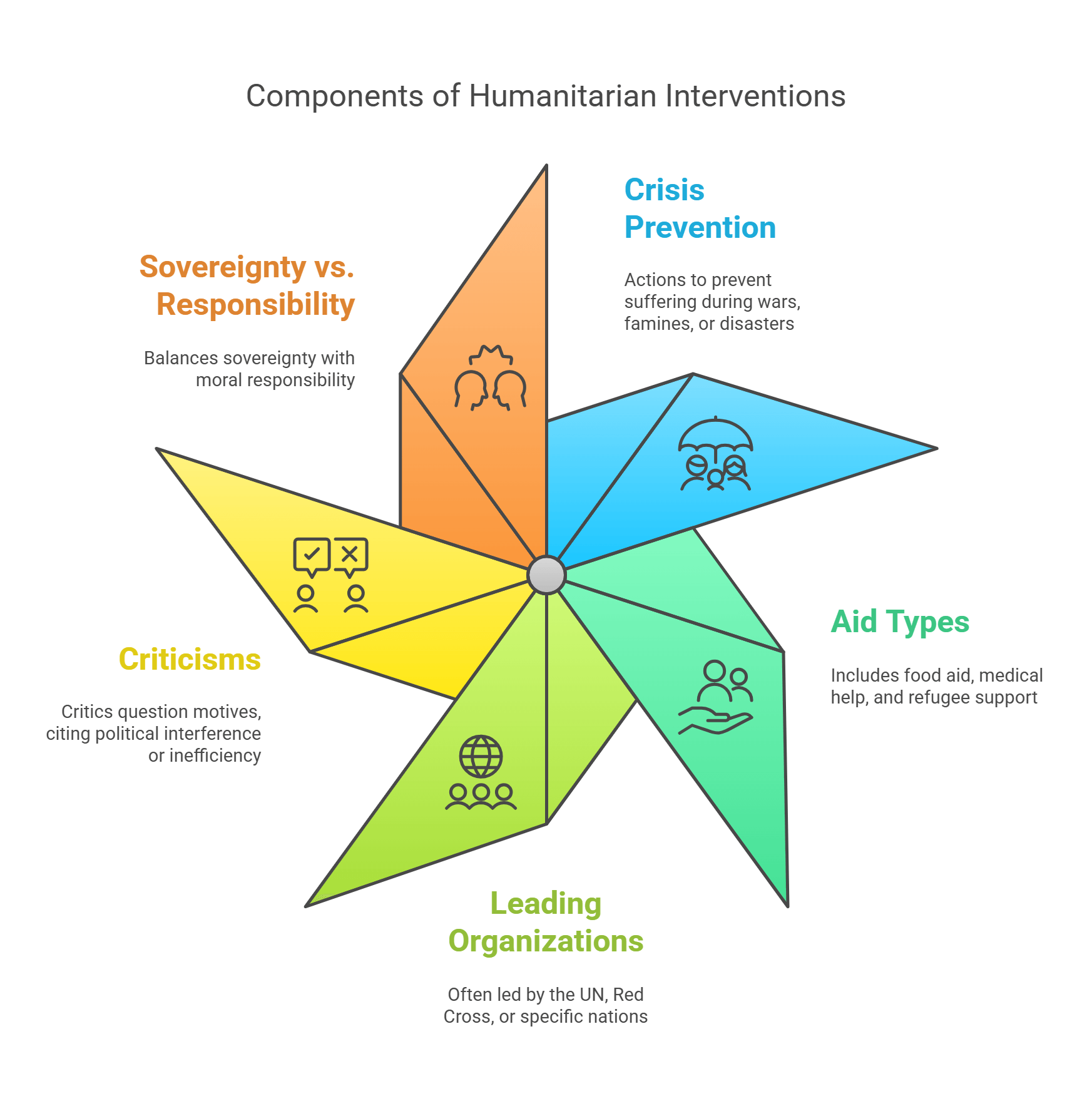
Humanitarian interventions are actions taken by countries or organizations to prevent human suffering during crises like wars, famines, or natural disasters. These can include providing aid, deploying peacekeepers, or imposing sanctions.
- Aimed at protecting people during crises.
- Includes food aid, medical help, and refugee support.
- Often led by the UN, Red Cross, or specific nations.
- Critics question motives, citing political interference or inefficiency.
- Balances sovereignty with moral responsibility.
Explained Simply: It’s like when someone sees their neighbor’s house on fire and rushes to help them, even though they don’t live there.
6. Foreign Policy
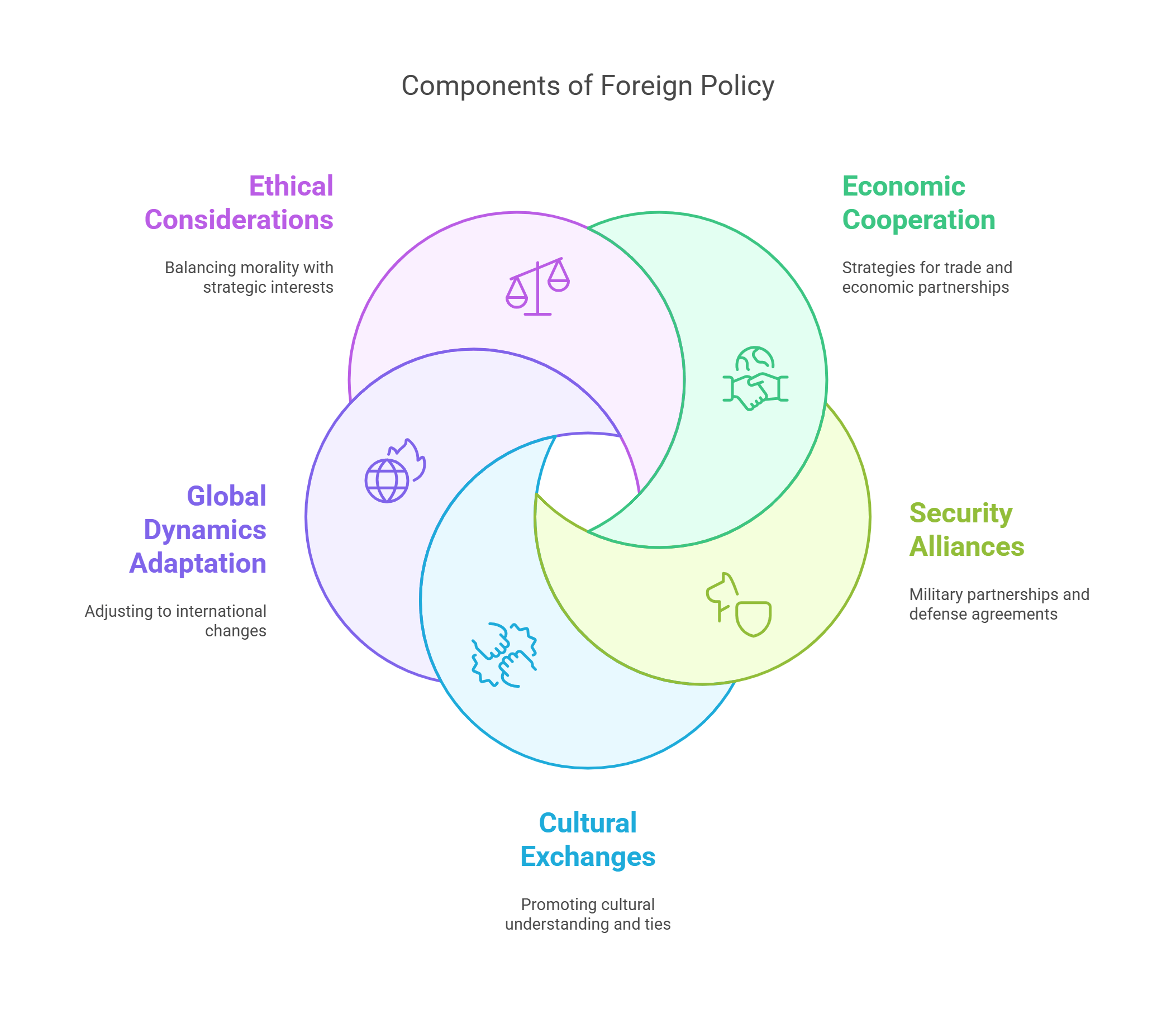
Foreign policy refers to a country’s strategy for managing relationships with other nations. It addresses goals like economic cooperation, security alliances, and cultural exchanges.
- Guides a nation’s actions on the global stage.
- Includes trade policies, military alliances, and diplomacy.
- Reflects national interests and values.
- Adapts to changes in global dynamics.
- Critiqued for balancing ethics with strategic interests.
Explained Simply: Foreign policy is like deciding which friends to play with and how to share toys while keeping your promises to everyone.
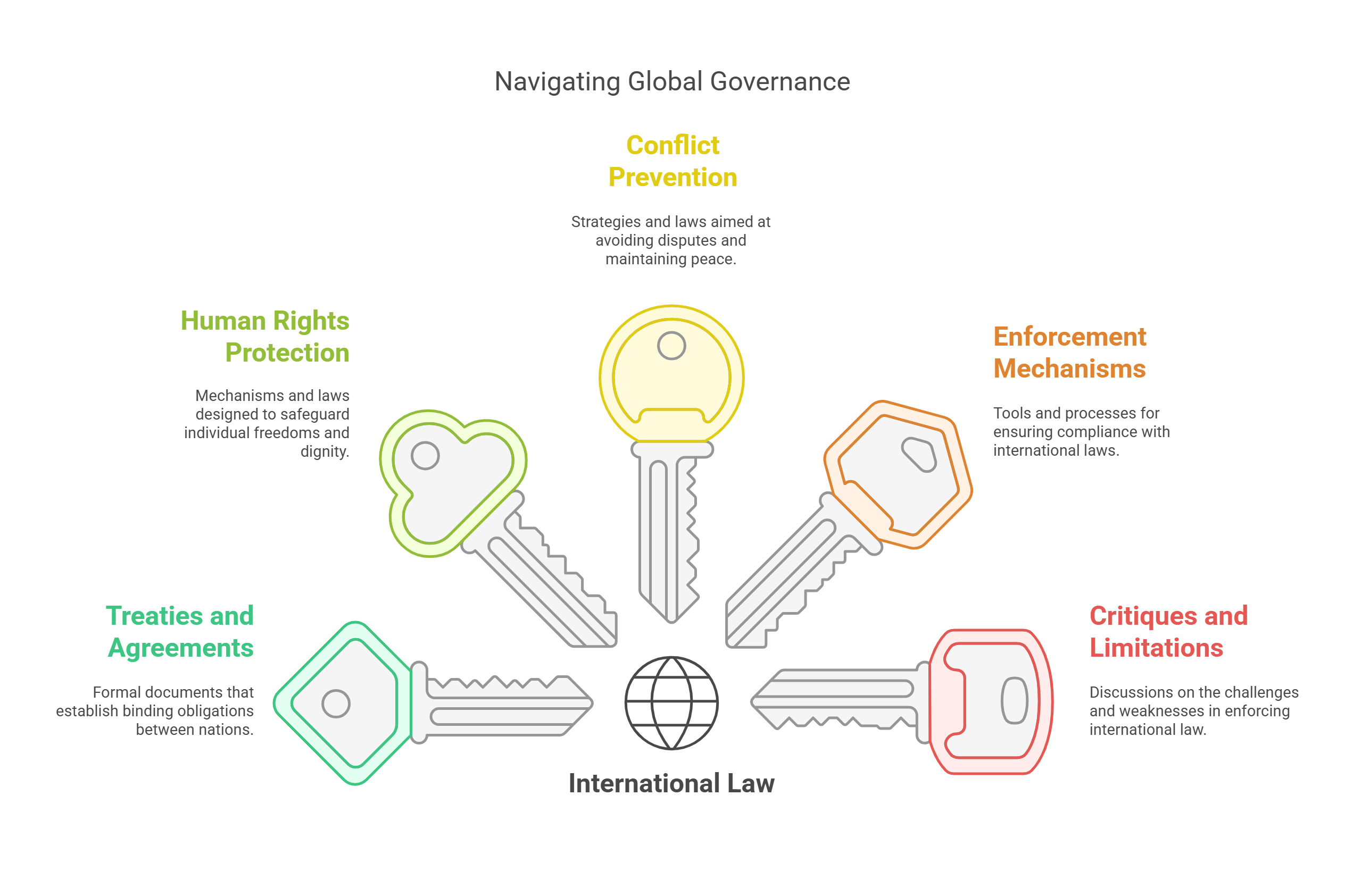
7. International Law
International law consists of rules and agreements that govern how nations interact. It addresses issues like trade, human rights, and territorial disputes, aiming to maintain order and justice globally.
- Includes treaties, conventions, and customary practices.
- Examples: Geneva Conventions, Paris Climate Agreement.
- Protects human rights and prevents conflicts.
- Relies on cooperation and enforcement mechanisms.
- Critiqued for limited enforcement power.
Explained Simply: International law is like rules for a big game where all countries are players, ensuring everyone plays fair and solves disputes peacefully.
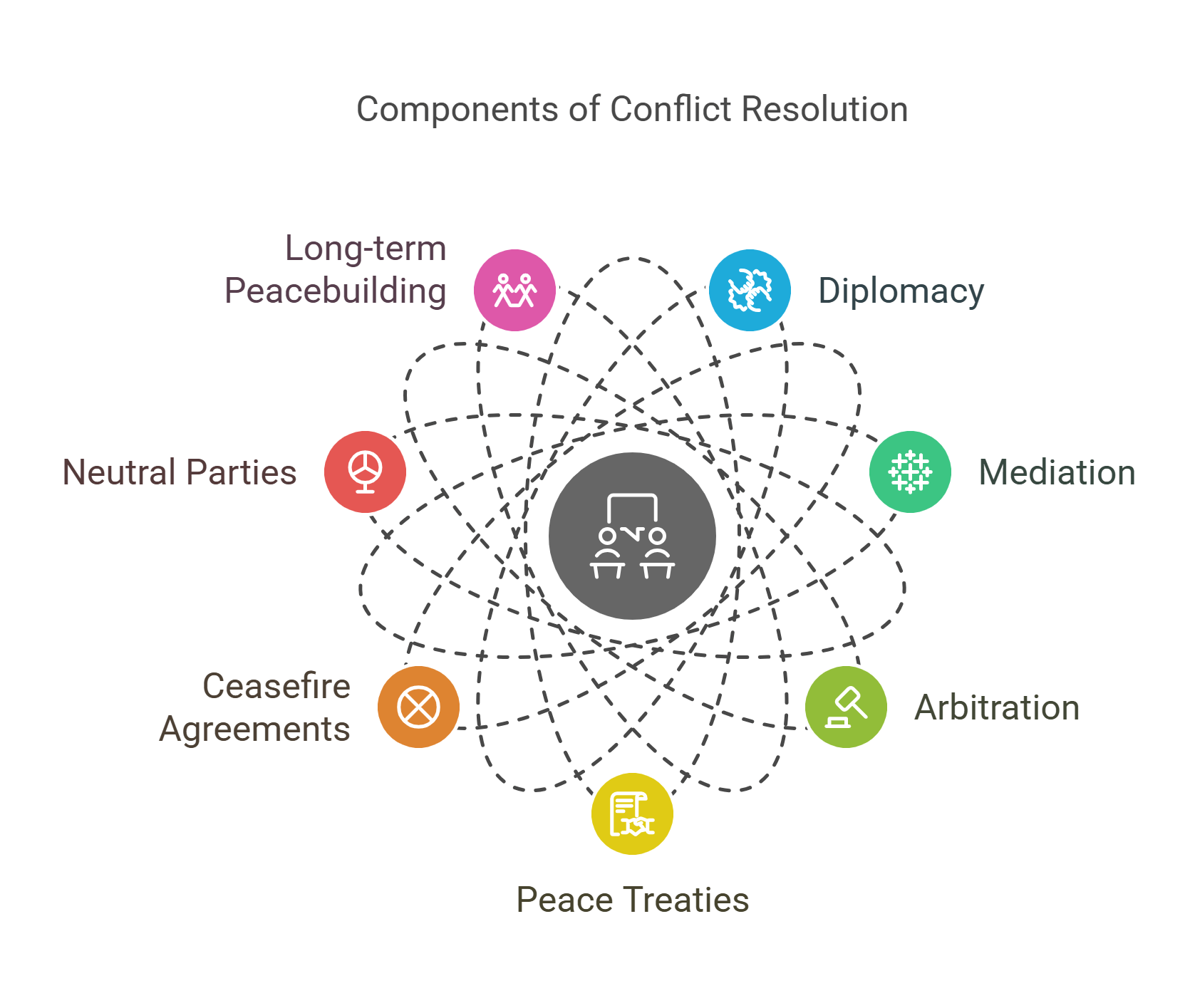
8. Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution focuses on settling disputes between nations through peaceful means like mediation, arbitration, or negotiation. It aims to prevent wars and foster lasting agreements.
- Uses diplomacy, mediation, and arbitration techniques.
- Examples: peace treaties, ceasefire agreements.
- Involves neutral parties like the UN or mediators.
- Balances conflicting interests to reach agreements.
- Emphasizes long-term peacebuilding strategies.
Explained Simply: Conflict resolution is like a referee helping two players who argue over a game, making sure they shake hands and play nicely again.
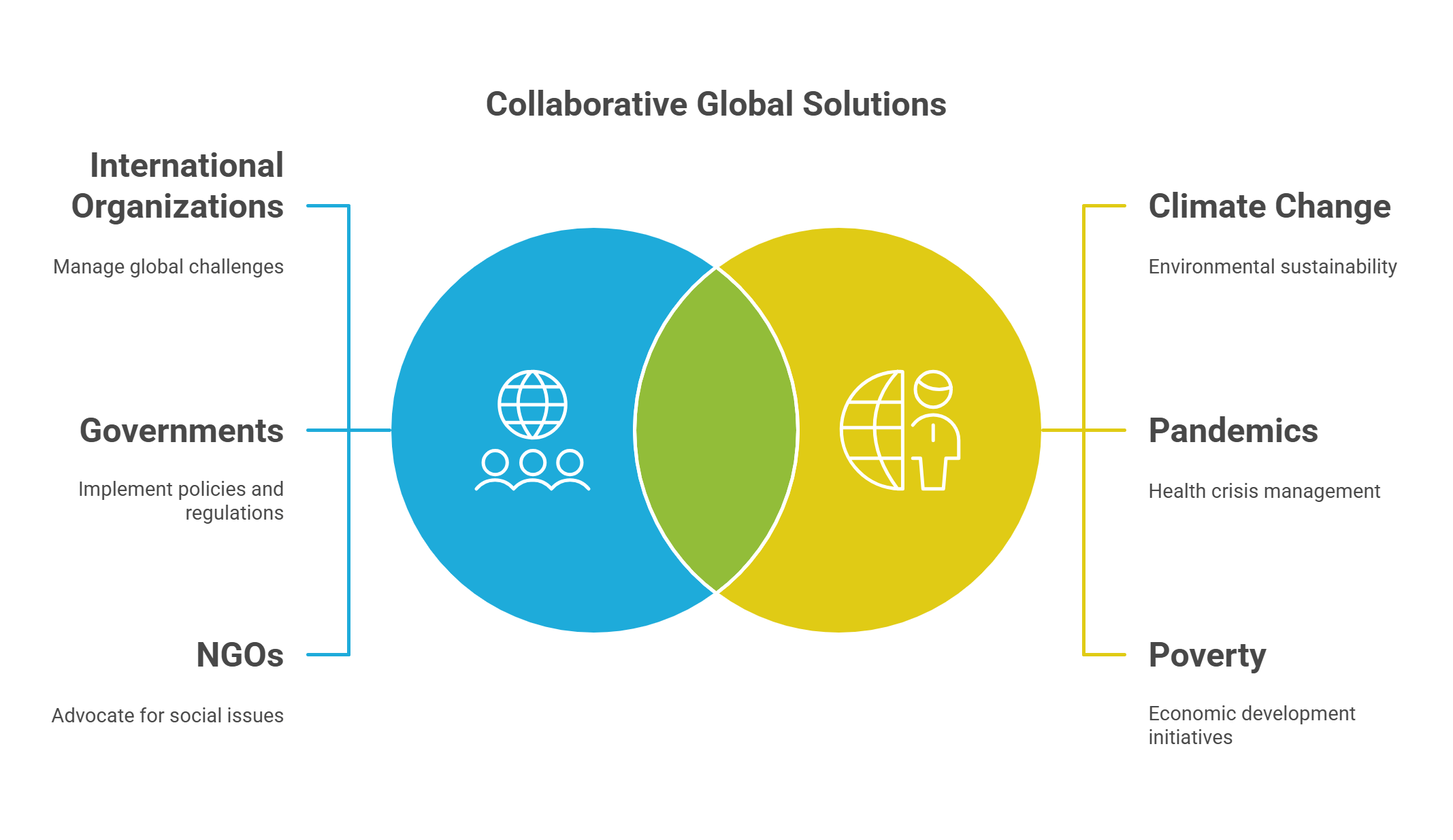
9. Global Governance
Global governance refers to collective efforts by international organizations, governments, and NGOs to manage global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and poverty.
- Involves collaboration between nations and organizations.
- Addresses transnational issues beyond borders.
- Examples: Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Critics question fairness and accountability.
- Key to managing global interdependence.
Explained Simply: Global governance is like a big team project where every country works together to solve problems that affect everyone, like cleaning a shared playground.
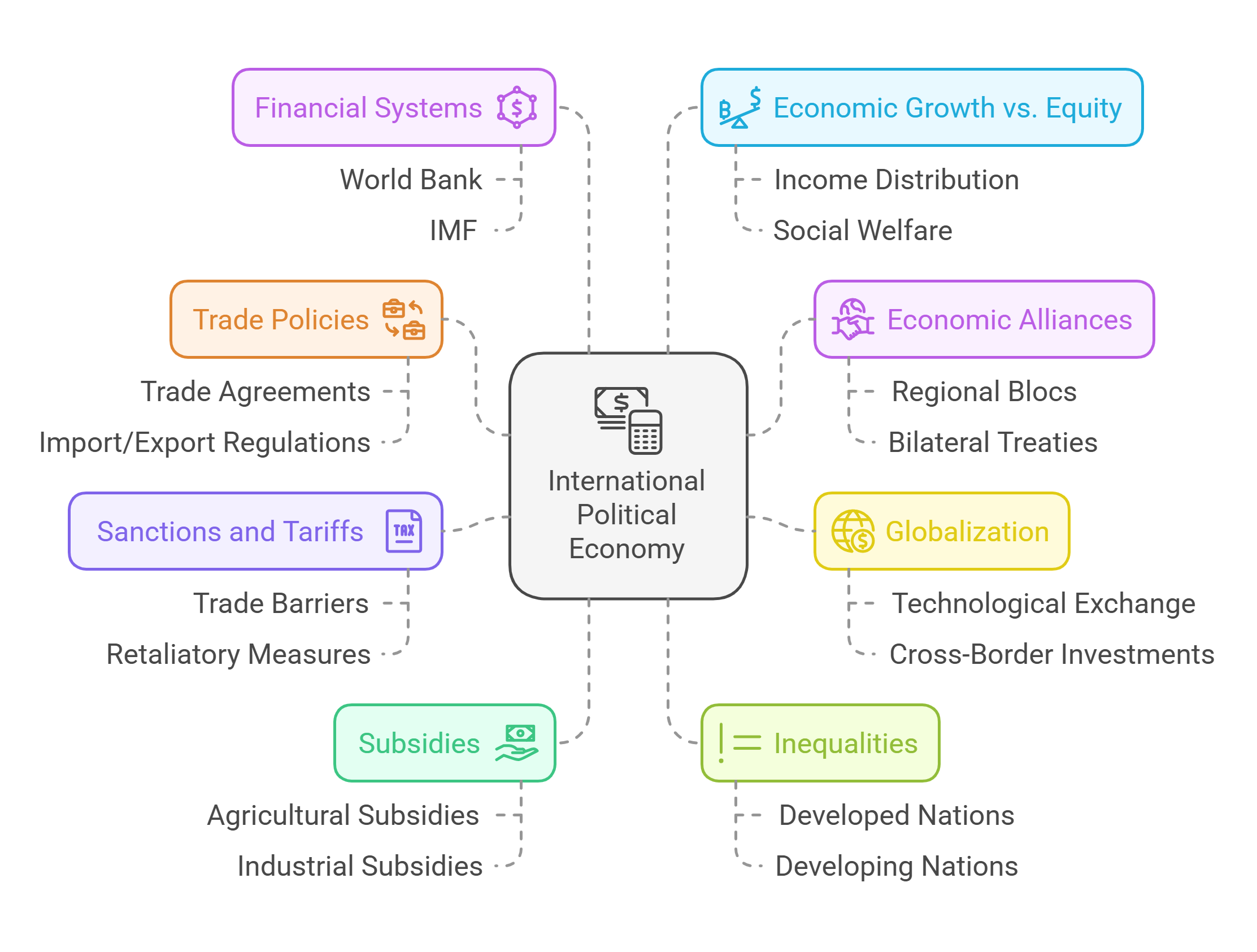
10. International Political Economy
International Political Economy examines how politics and economics intersect on a global scale. It explores trade, investment, and the role of institutions like the World Bank and IMF.
- Studies trade policies, economic alliances, and globalization.
- Analyzes the impact of sanctions, tariffs, and subsidies.
- Explores inequalities between developed and developing nations.
- Focuses on global financial systems and institutions.
- Addresses the balance between economic growth and equity.
Explained Simply: International Political Economy is like understanding who makes the most money in a marketplace and why some sellers are richer than others.
✨ Conclusion
Understanding International Relations concepts equips you with tools to analyze RC passages that tackle complex global issues. These topics appear frequently in exams, offering insights into debates on trade, security, and global governance. By mastering these ideas, you enhance your ability to engage with sophisticated arguments and critical issues, strengthening your overall test readiness.













