⚖️ Law: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Legal topics in reading passages often examine frameworks that govern society, ethics, and power structures. Understanding essential legal concepts enhances comprehension of arguments related to justice, governance, and societal norms. Familiarity with legal terminology and principles helps interpret passages discussing regulations, case laws, or international treaties.
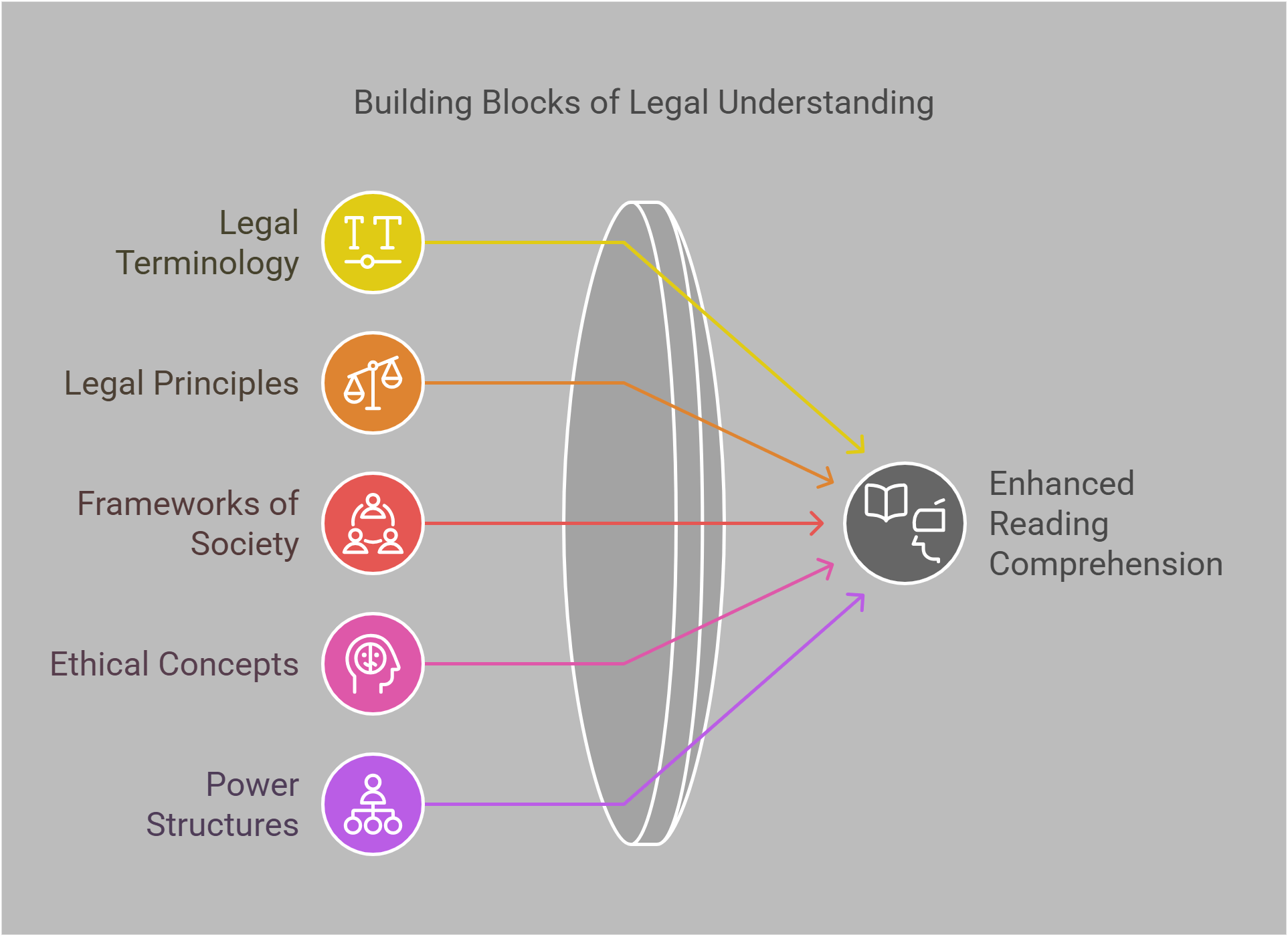
📋 Overview
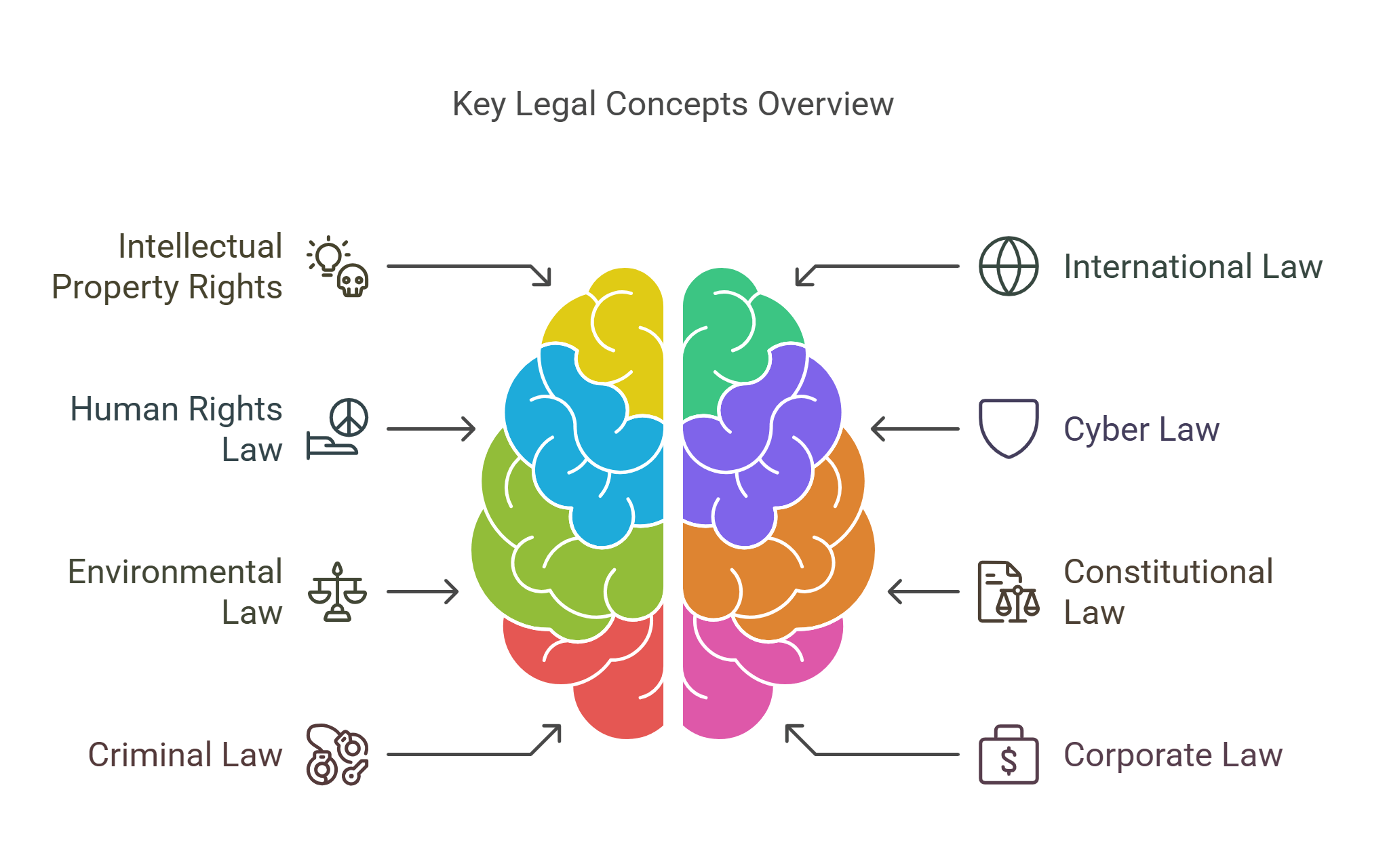
In this guide, we’ll explore these key legal concepts:
- Intellectual Property Rights
- International Law
- Human Rights Law
- Cyber Law
- Environmental Law
- Constitutional Law
- Criminal Law
- Corporate Law
- Contract Law
- Legal Ethics
🔍 Detailed Explanations
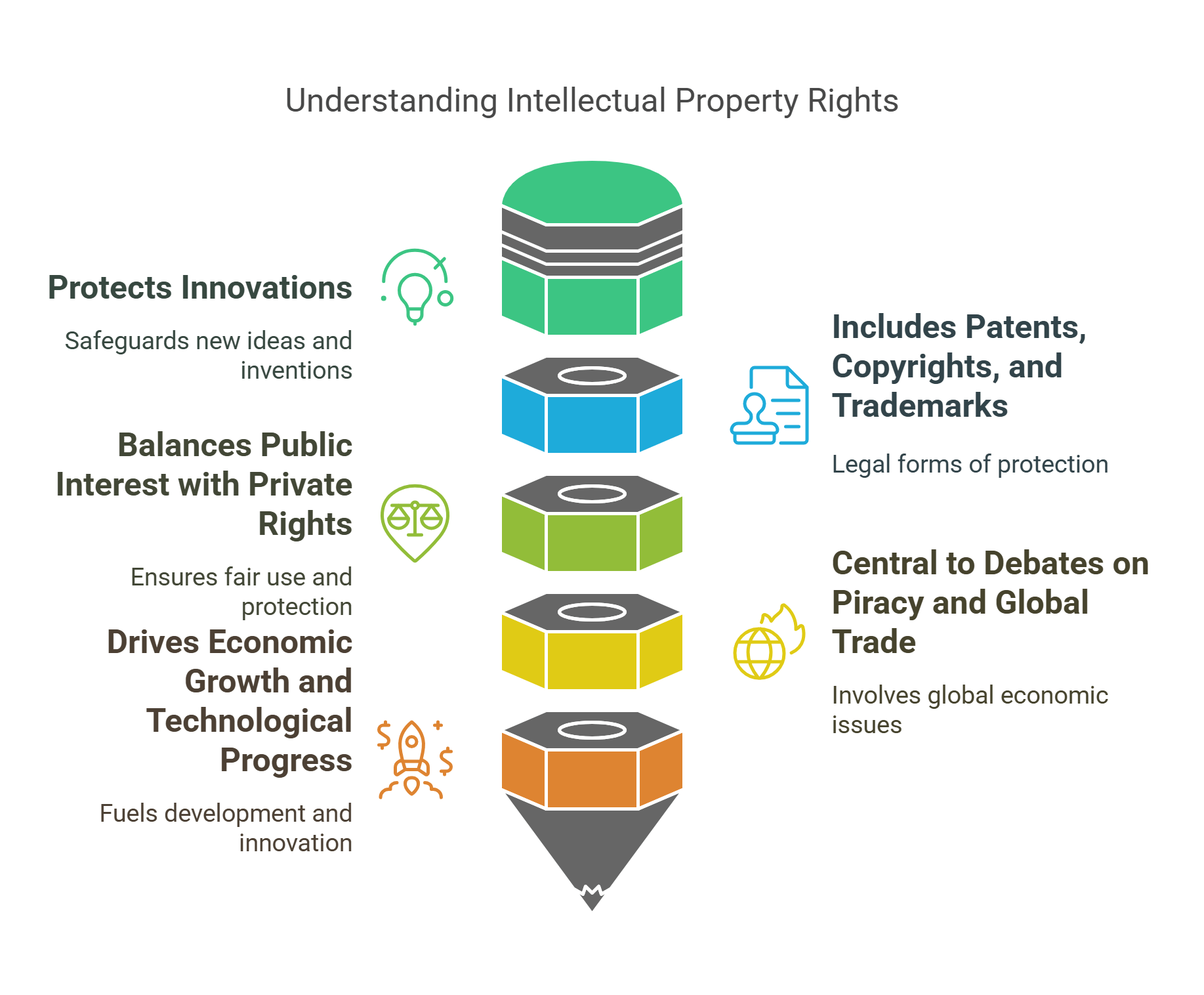
1. Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
IPR refers to the legal protections granted to creators for their inventions, designs, trademarks, or artistic works. These rights encourage innovation by ensuring that creators can benefit financially from their efforts. In RC passages, IPR may be linked to debates on creativity, technology, and global trade.
- Protects innovations and creations.
- Includes patents, copyrights, and trademarks.
- Balances public interest with private rights.
- Central to debates on piracy and global trade.
- Drives economic growth and technological progress.
Explained Simply: Imagine you draw a comic book hero. IPR is like a magic shield that stops others from copying your hero and selling it without your permission.
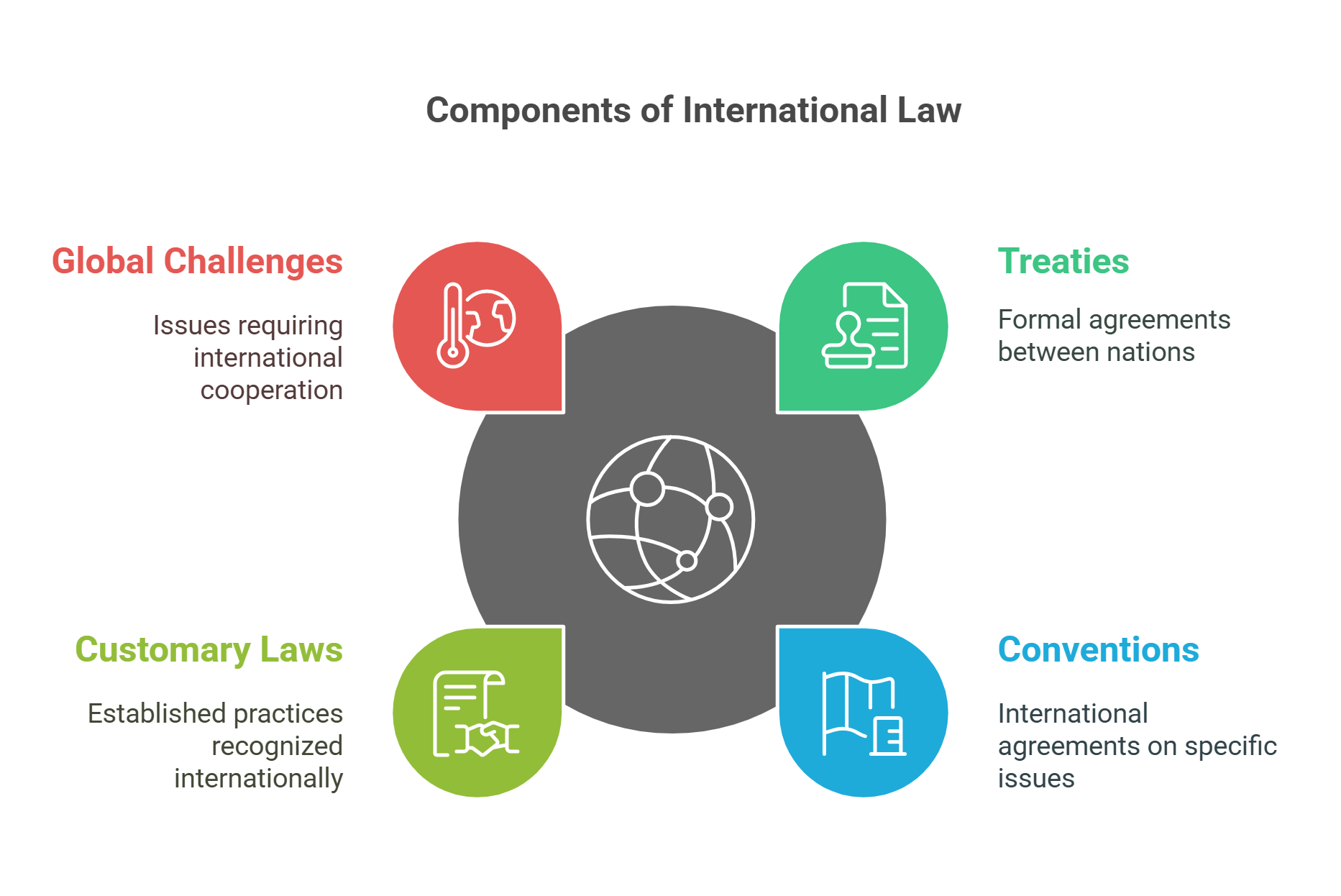
2. International Law
International law governs relationships between nations, including treaties, trade, and conflict resolution. It establishes rules for global cooperation and ensures accountability on issues like environmental protection and human rights.
- Governs interactions between countries.
- Includes treaties, conventions, and customary laws.
- Addresses global challenges like climate change and war crimes.
- Central to debates on sovereignty and globalization.
- Promotes cooperation and conflict resolution.
Explained Simply: Think of international law as a set of playground rules all countries agree to follow so everyone can play fairly and solve fights without punching.
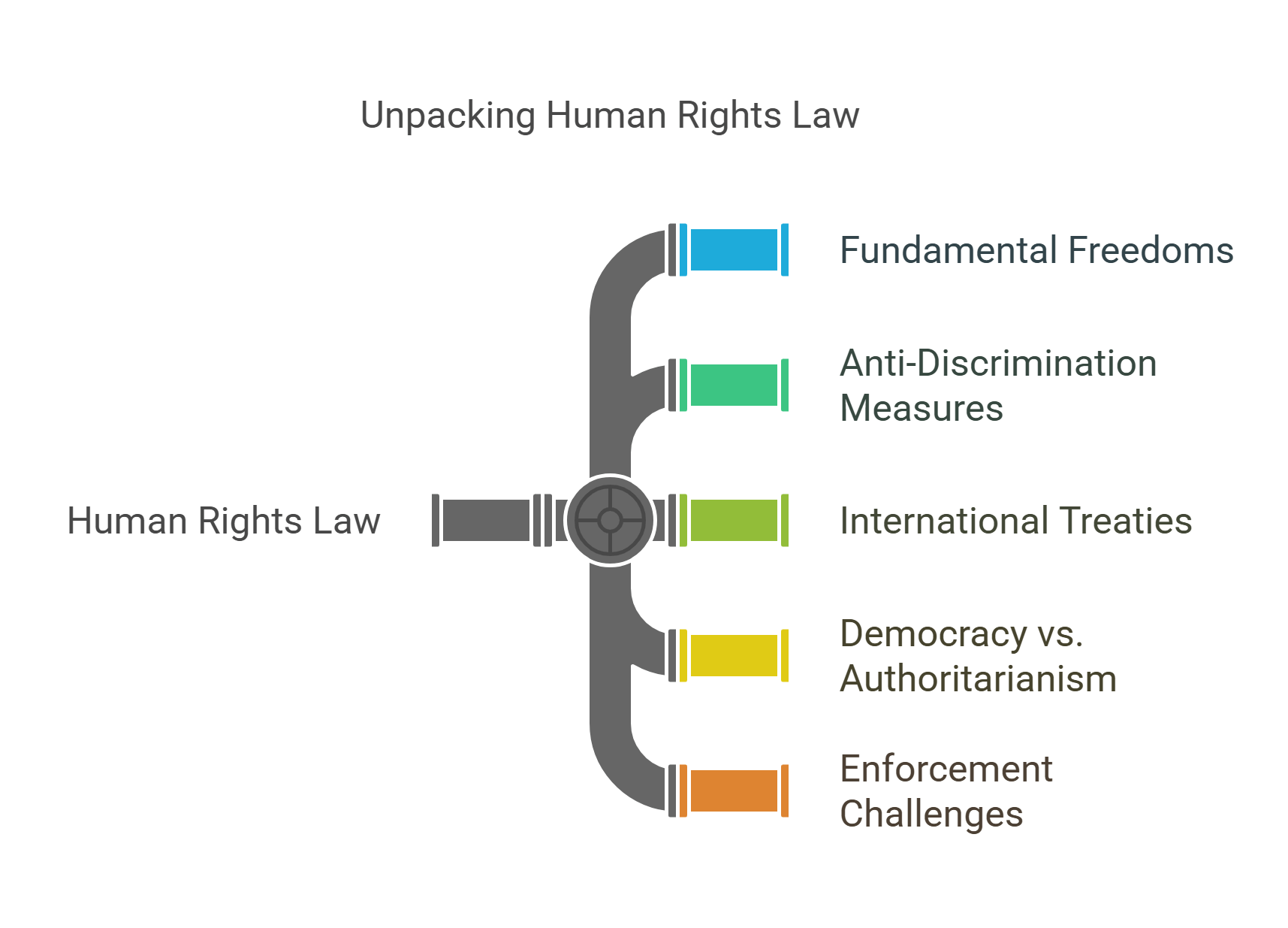
3. Human Rights Law
Human rights law protects individuals’ fundamental freedoms and dignity, such as the right to life, freedom of speech, and equality. This body of law often forms the backbone of RC passages analyzing issues of justice, oppression, or ethical governance.
- Ensures dignity and freedom for all individuals.
- Includes laws against discrimination and abuse.
- Often linked to UN declarations and treaties.
- Central to debates on democracy and authoritarianism.
- Challenges: enforcement and cultural relativism.
Explained Simply: Human rights law is like a superhero rulebook that says everyone should be treated kindly and fairly, no matter where they’re from or who they are.
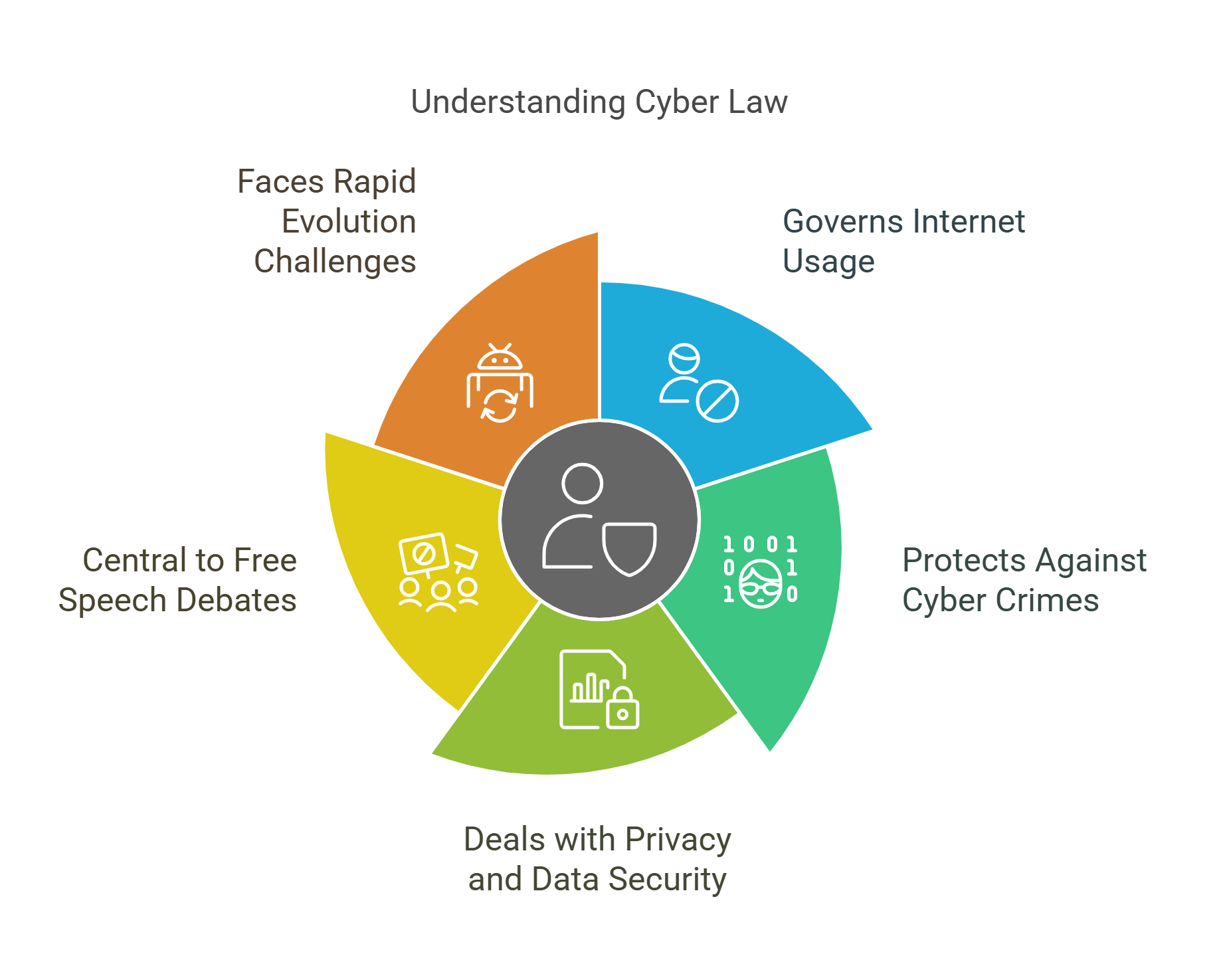
4. Cyber Law
Cyber law regulates online activities, including data privacy, cybercrimes, and intellectual property in digital spaces. With the internet’s growing influence, RC passages often discuss the balance between innovation and privacy concerns.
- Governs internet and technology usage.
- Protects against online crimes like hacking and fraud.
- Deals with privacy, data security, and digital rights.
- Central to debates on free speech and online censorship.
- Challenges: rapid tech evolution and global enforcement.
Explained Simply: Cyber law is like the rules for using your phone or tablet safely. It stops online bullies, keeps your secrets safe, and makes sure no one cheats.
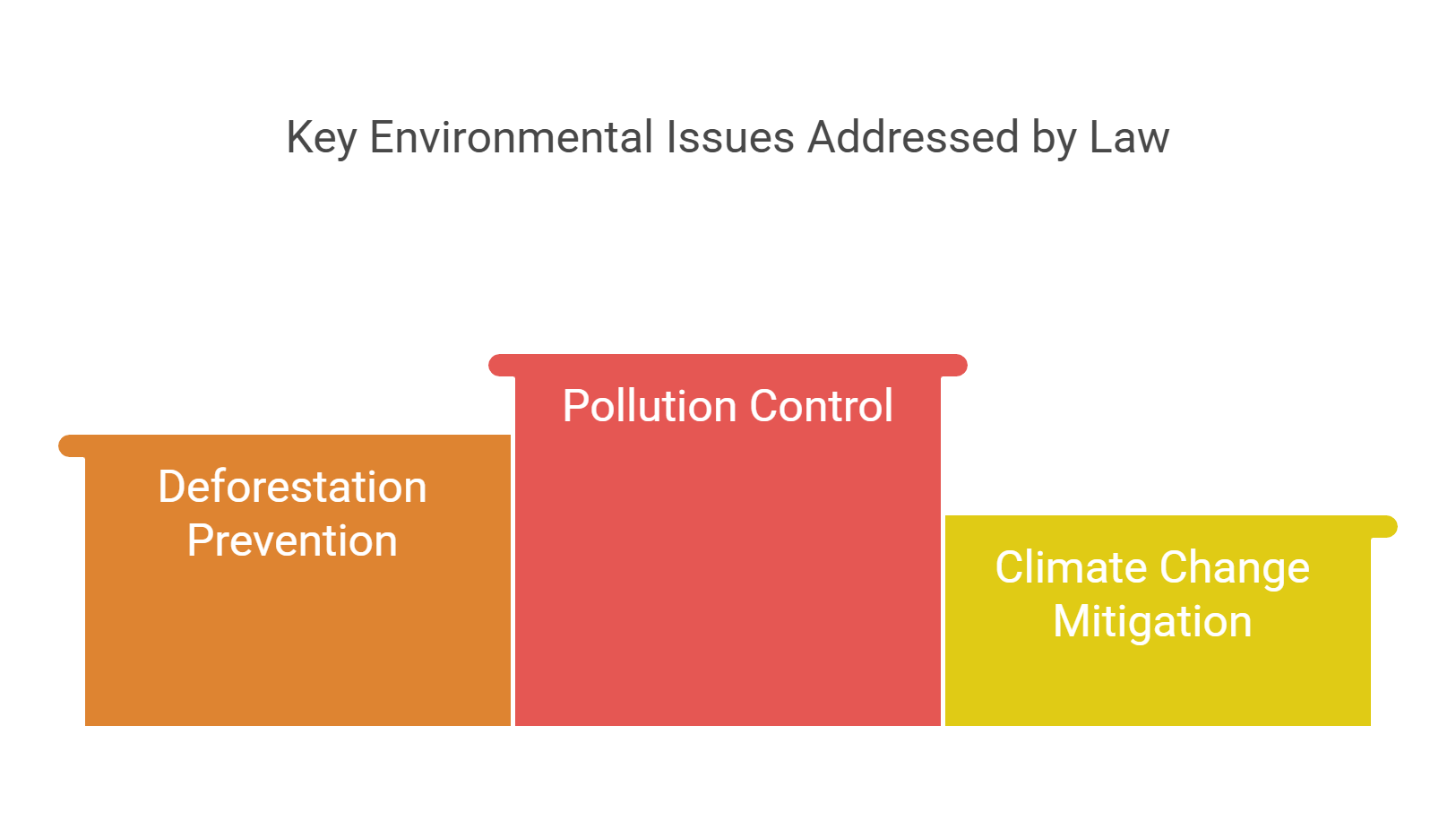
5. Environmental Law
Environmental law ensures the protection of natural resources, wildlife, and ecosystems. It often appears in RC passages focused on sustainability, climate change, and the balance between development and conservation.
- Protects the environment and natural resources.
- Addresses pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
- Includes treaties like the Paris Agreement.
- Balances economic development with ecological preservation.
- Central to debates on global and local responsibilities.
Explained Simply: Think of environmental law as Mother Nature’s bodyguard, making sure we don’t hurt the planet while building our cities.
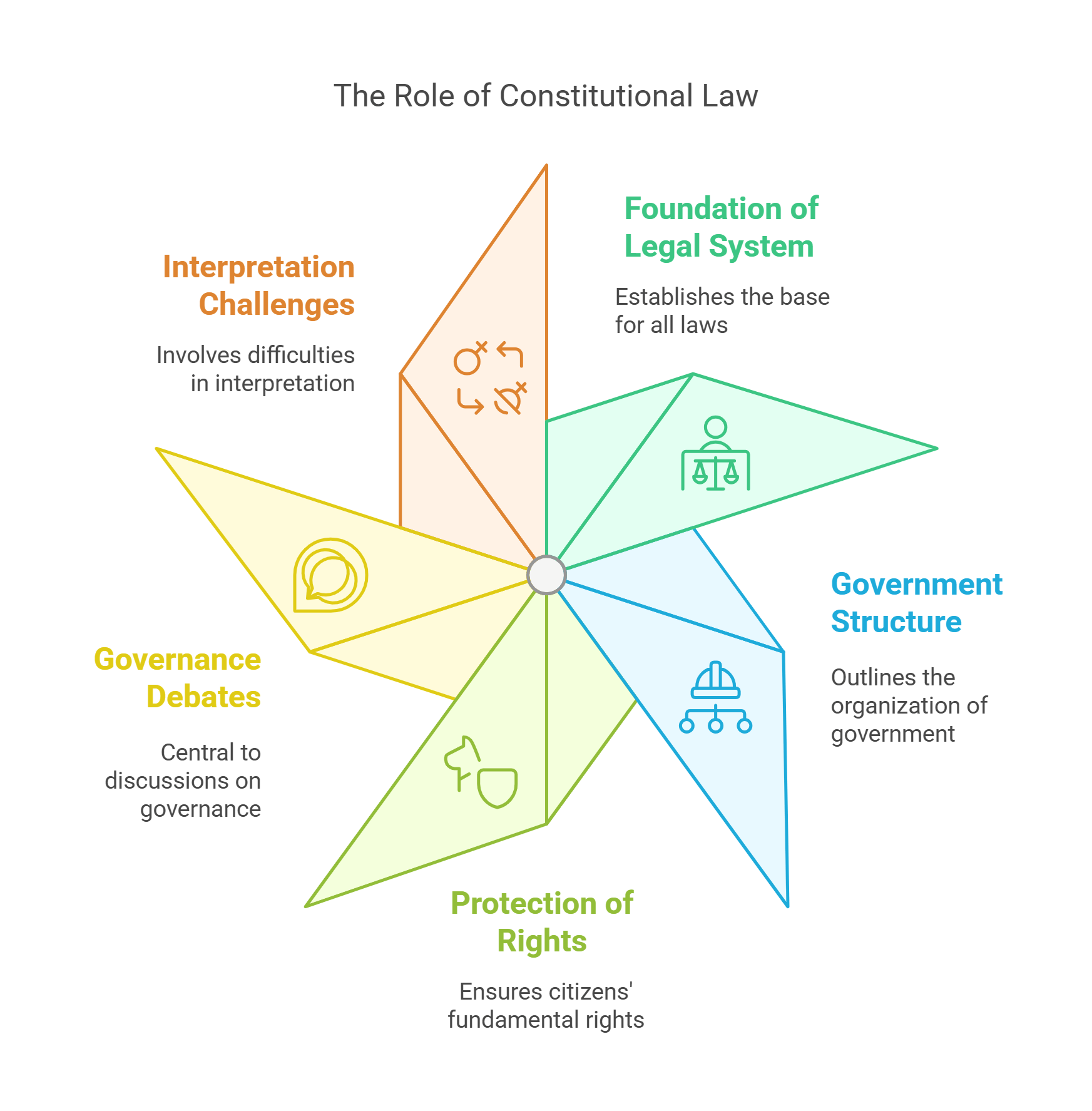
6. Constitutional Law
Constitutional law deals with the fundamental rules and principles of a nation, including citizens’ rights and government powers. RC passages often use it to explore themes of democracy, civil liberties, or judicial review.
- Forms the foundation of a country’s legal system.
- Defines government structure and powers.
- Protects fundamental rights of citizens.
- Central to debates on governance and rights.
- Challenges: interpretation and amendments.
Explained Simply: Constitutional law is like a giant rulebook for the country. It says what the government can do and makes sure everyone is treated fairly.
7. Criminal Law
Criminal law deals with actions considered harmful to society, such as theft, assault, or fraud. It appears in RC passages discussing justice systems, punishment, or societal norms.
- Defines crimes and punishments.
- Aims to protect society and maintain order.
- Includes processes like trials and evidence collection.
- Central to debates on justice and rehabilitation.
- Challenges: fairness and systemic biases.
Explained Simply: Criminal law is like the rules in your classroom—if someone breaks them, they face consequences to keep everyone safe and happy.
8. Corporate Law
Corporate law governs businesses, addressing issues like ownership, mergers, and liability. RC passages may use it to discuss ethics, globalization, or economic growth.
- Regulates company formation and operations.
- Includes shareholder rights and corporate responsibilities.
- Addresses mergers, acquisitions, and bankruptcies.
- Central to debates on capitalism and ethics.
- Challenges: balancing profit and public interest.
Explained Simply: Corporate law is like the rules for running a lemonade stand, making sure you treat customers fairly and share profits with your friends.
9. Contract Law
Contract law ensures agreements between parties are legally binding and enforceable. RC passages might explore disputes or implications of contracts in various industries.
- Governs agreements between individuals or entities.
- Ensures promises are honored.
- Includes principles of offer, acceptance, and consideration.
- Central to debates on fairness and enforcement.
- Challenges: ambiguous terms and unequal bargaining power.
Explained Simply: Imagine you promise your friend cookies if they clean your room. Contract law makes sure both of you keep your promises.
10. Legal Ethics
Legal ethics focuses on the moral responsibilities of lawyers and judges. RC passages often discuss the role of ethics in ensuring justice and accountability in the legal profession.
- Governs professional behavior in the legal field.
- Ensures fairness, confidentiality, and honesty.
- Central to debates on corruption and judicial independence.
- Challenges: conflicts of interest and enforcement.
- Balances duty to clients with public good.
Explained Simply: Legal ethics are like the golden rules for lawyers, making sure they play fair and tell the truth while helping people.
✨ Conclusion
Mastering legal concepts enriches your understanding of reading comprehension passages on governance, ethics, and justice. This knowledge sharpens your ability to evaluate arguments, identify biases, and engage critically with texts, giving you an edge in exams like the CAT and GMAT.













