📋 Public Policy: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Public policy is an essential area of study, particularly for reading comprehension passages that focus on societal frameworks, governance, and decision-making processes. Understanding public policy is critical for analyzing complex issues, recognizing stakeholder perspectives, and identifying cause-effect relationships in passages. This topic often involves debates on resource allocation, social welfare, and long-term societal goals, making it a vital area for critical thinking and comprehension.
📋 Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these key Public Policy-related concepts:
- Policy Analysis
- Welfare Policies
- Education Policy
- Health Policy
- Environmental Policy
- Public Administration
- Policy Implementation
- Policy Evaluation
- Social Policy
- Economic Policy
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. Policy Analysis
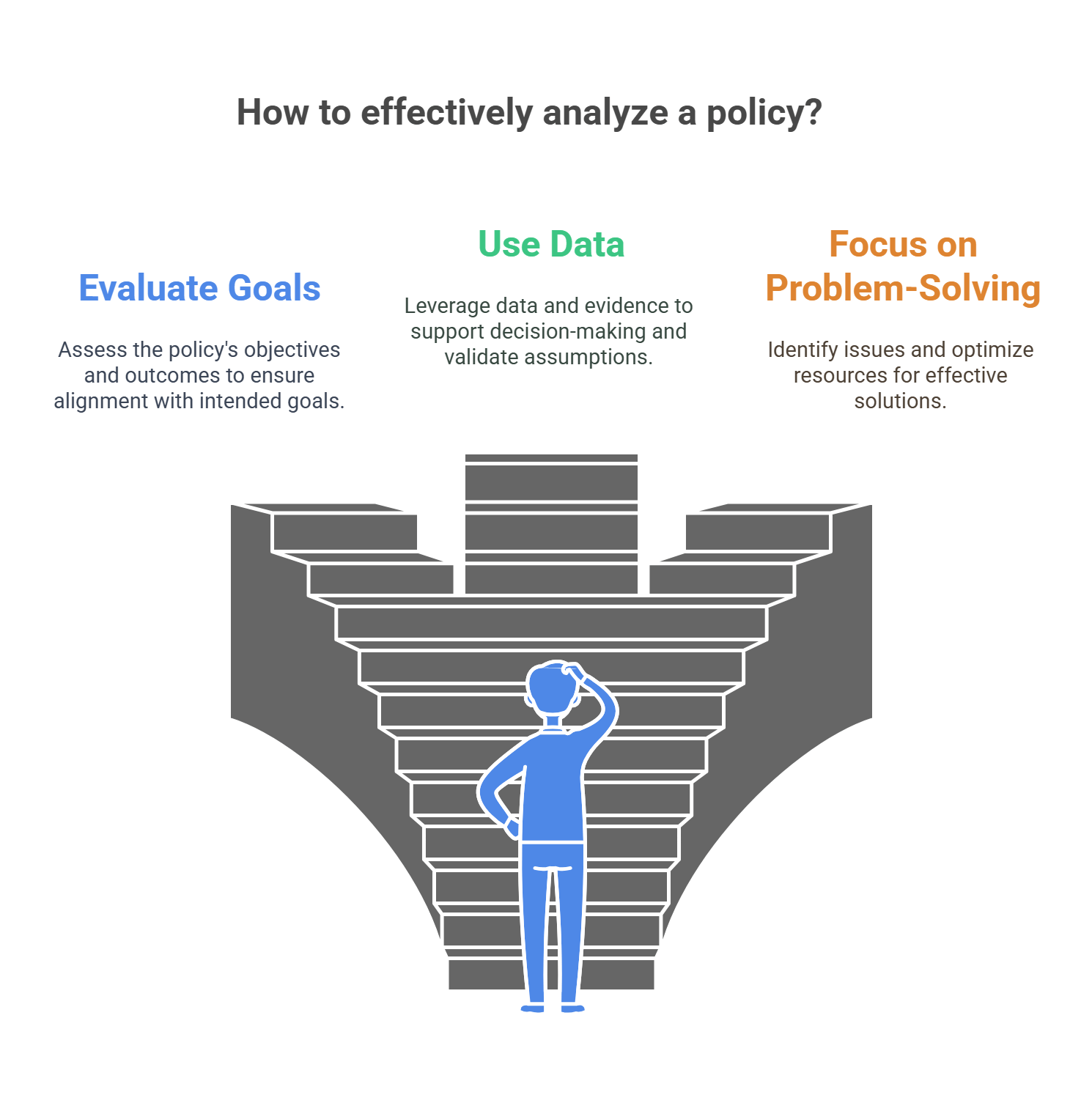
Policy analysis involves examining and evaluating policies to understand their impact, feasibility, and effectiveness. This process often includes identifying problems, proposing solutions, and assessing alternatives. Analysts weigh costs and benefits, forecast outcomes, and consider ethical implications.
- Evaluates the goals and outcomes of policies.
- Uses data and evidence to support decisions.
- Focuses on problem-solving and optimizing resources.
- Considers social, economic, and environmental factors.
- Involves multiple stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and citizens.
Explained Simply: Imagine you and your friends decide to build a treehouse. Before starting, you think about where to build it, how much wood you need, and how safe it will be. Policy analysis is like this planning step but for big decisions like building schools or roads for a country.
2. Welfare Policies
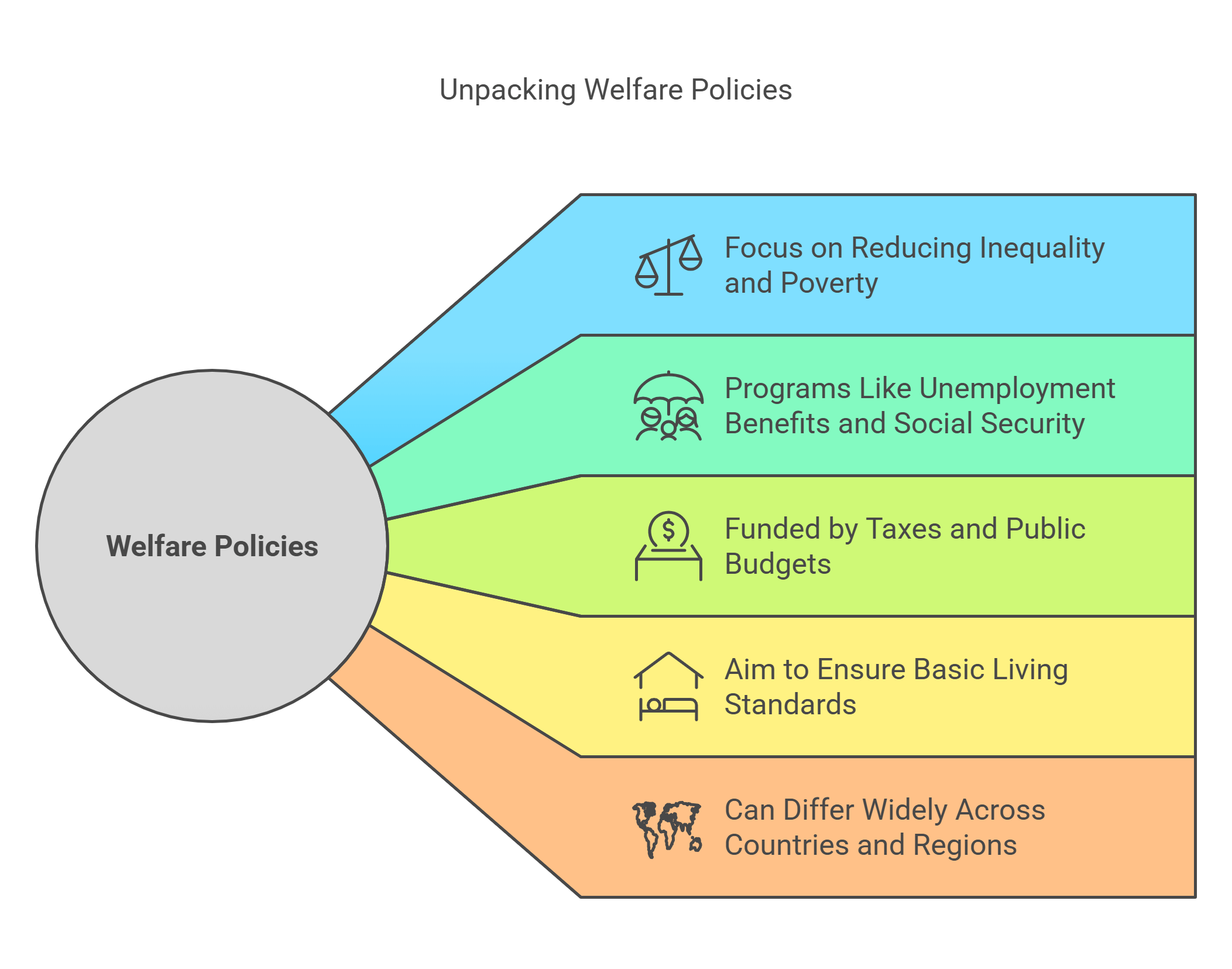
Welfare policies are designed to support individuals and communities by providing essential resources like food, housing, and healthcare. These policies aim to reduce poverty and promote equality. Governments use taxes and funds to implement these programs, often sparking debates about their efficiency and fairness.
- Focus on reducing inequality and poverty.
- Include programs like unemployment benefits, social security, and healthcare.
- Often funded by taxes and public budgets.
- Aim to ensure basic living standards for all.
- Can differ widely across countries and regions.
Explained Simply: Think about a teacher who notices some kids don’t have lunch. The teacher decides to bring extra sandwiches every day so everyone can eat. Welfare policies are like those sandwiches—they help people who need extra support to live a better life.
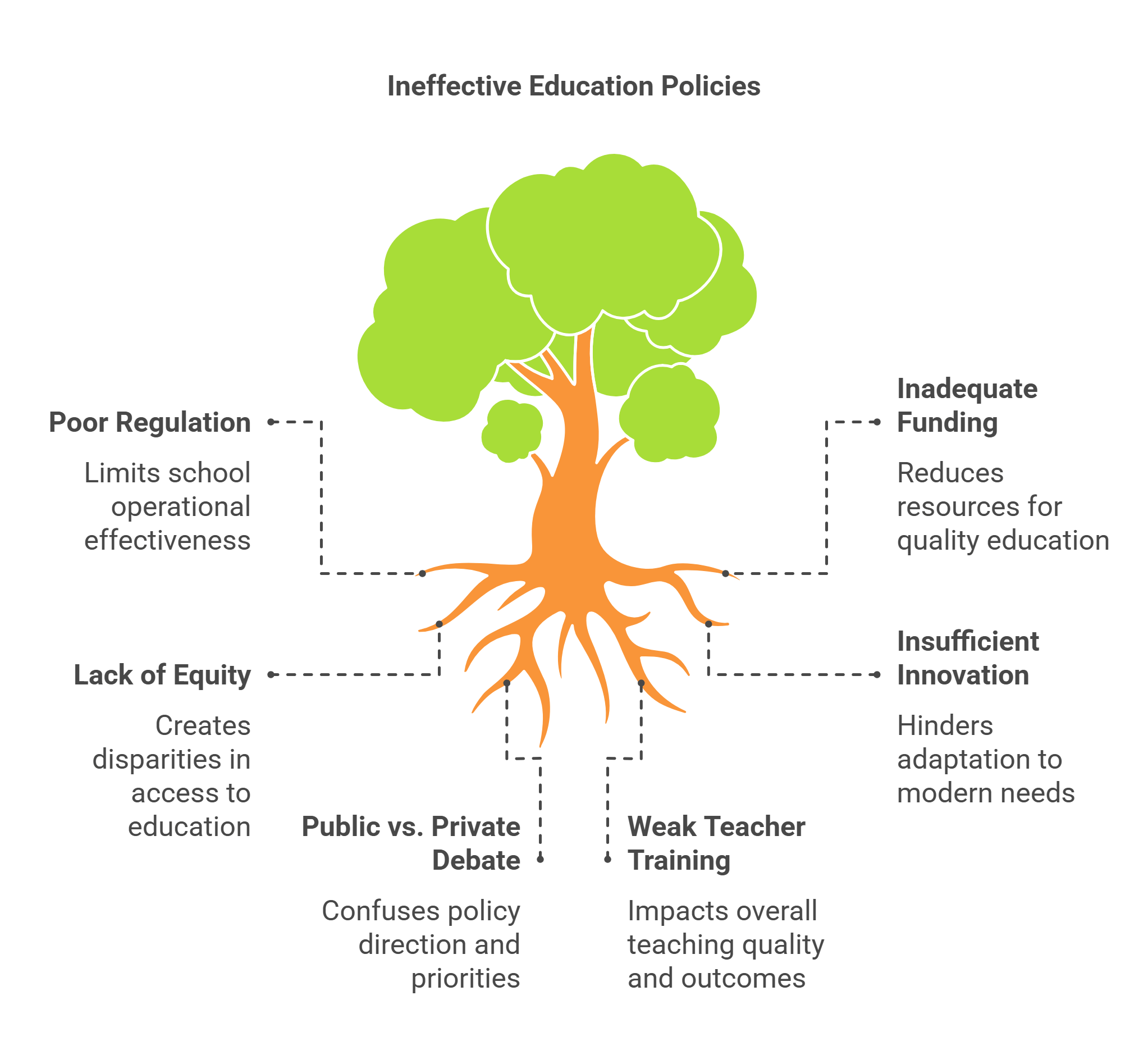
3. Education Policy
Education policies set the rules for how schools and colleges operate, including funding, curriculum, and teacher training. These policies shape how societies educate their citizens, making them vital for economic growth and social progress.
- Regulate how education systems function.
- Impact teacher quality, student outcomes, and resource allocation.
- Include issues like access, equity, and innovation.
- Often linked to economic and social development.
- Can spark debates about public vs. private education.
Explained Simply: Imagine your school decides to add more art classes because kids love drawing. Education policy is about making these kinds of decisions but for every school in a city or country.
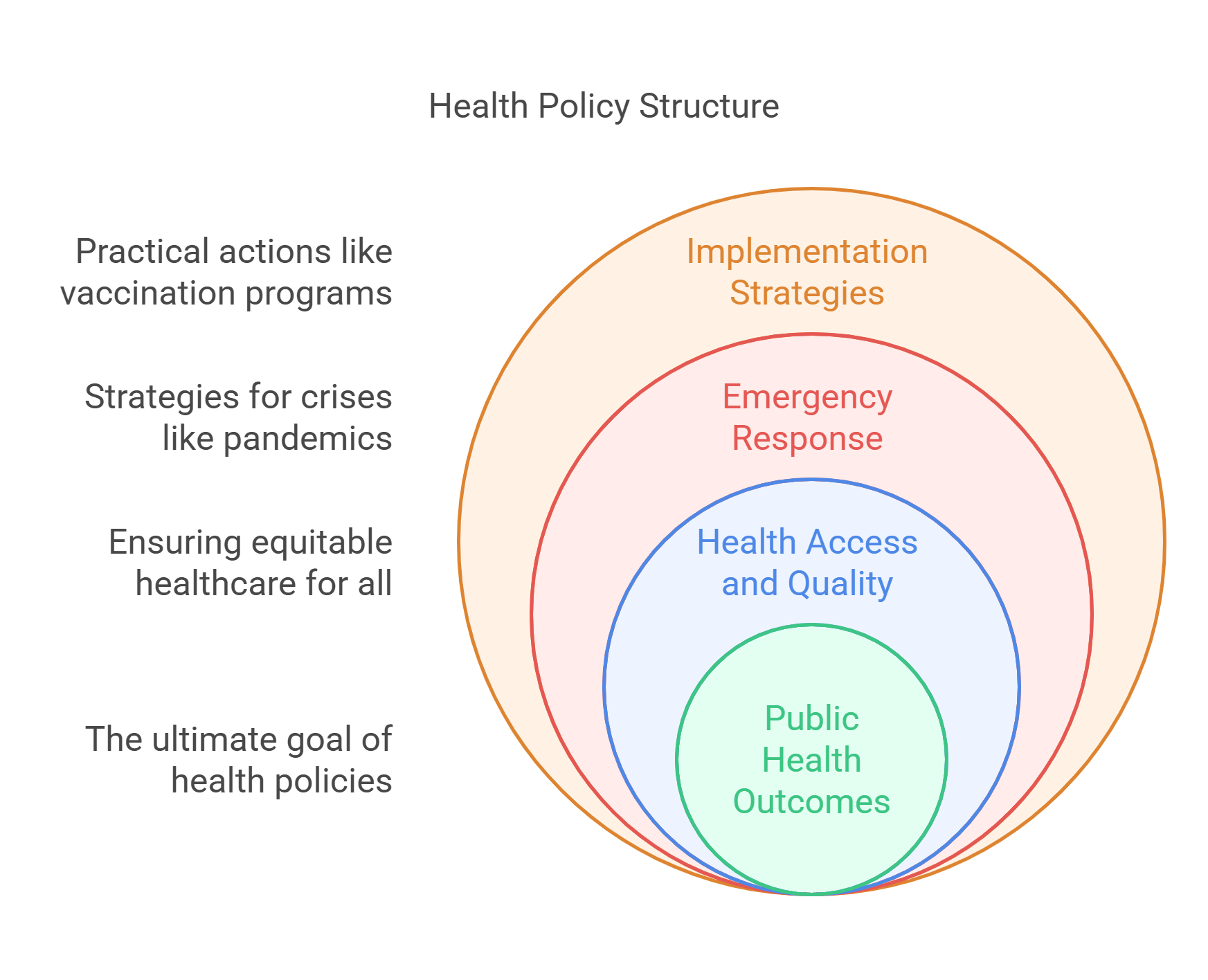
4. Health Policy
Health policy refers to decisions, plans, and actions aimed at achieving specific healthcare goals within a society. It encompasses issues like access to healthcare, funding for medical services, and strategies to combat public health crises like pandemics.
- Focuses on improving public health outcomes.
- Includes vaccination programs, hospital funding, and disease prevention.
- Addresses healthcare access, affordability, and quality.
- Responds to emergencies like pandemics or natural disasters.
- Often involves collaboration between governments and private sectors.
Explained Simply: Imagine a team of doctors and teachers decide that everyone in your town should wash their hands more to avoid getting sick. They give out soap and teach people how to use it. Health policy is like this but on a much larger scale to keep everyone healthy.
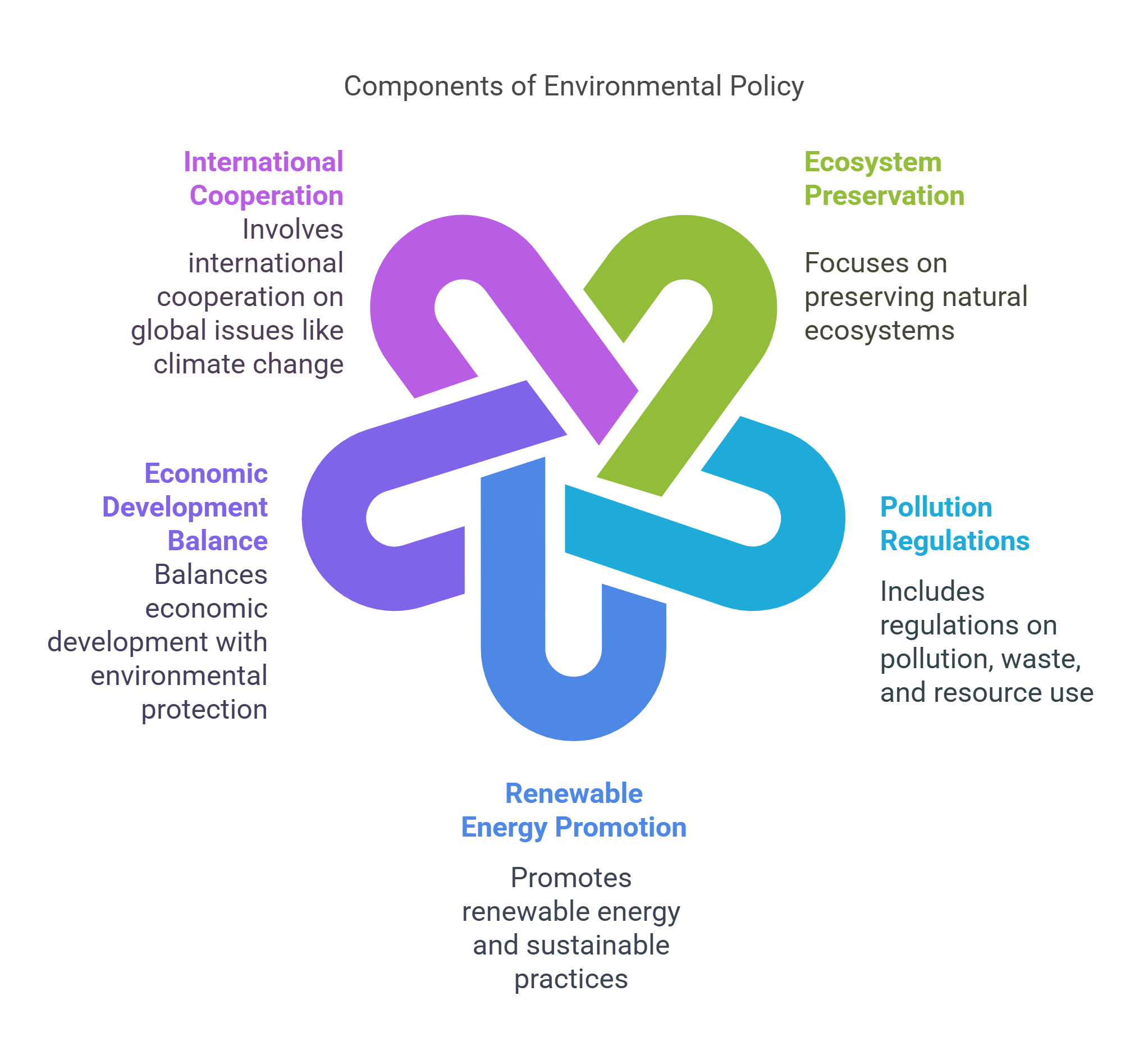
5. Environmental Policy
Environmental policy deals with regulations and laws aimed at protecting natural resources and reducing the impact of human activities on the environment. It addresses issues like climate change, pollution, and conservation, balancing economic growth with sustainability.
- Focuses on preserving natural ecosystems.
- Includes regulations on pollution, waste, and resource use.
- Promotes renewable energy and sustainable practices.
- Balances economic development with environmental protection.
- Involves international cooperation on global issues like climate change.
Explained Simply: Imagine your neighborhood decides to plant more trees and pick up litter to make the park cleaner and greener. Environmental policy is like this effort, but it helps protect forests, rivers, and even the air we breathe.
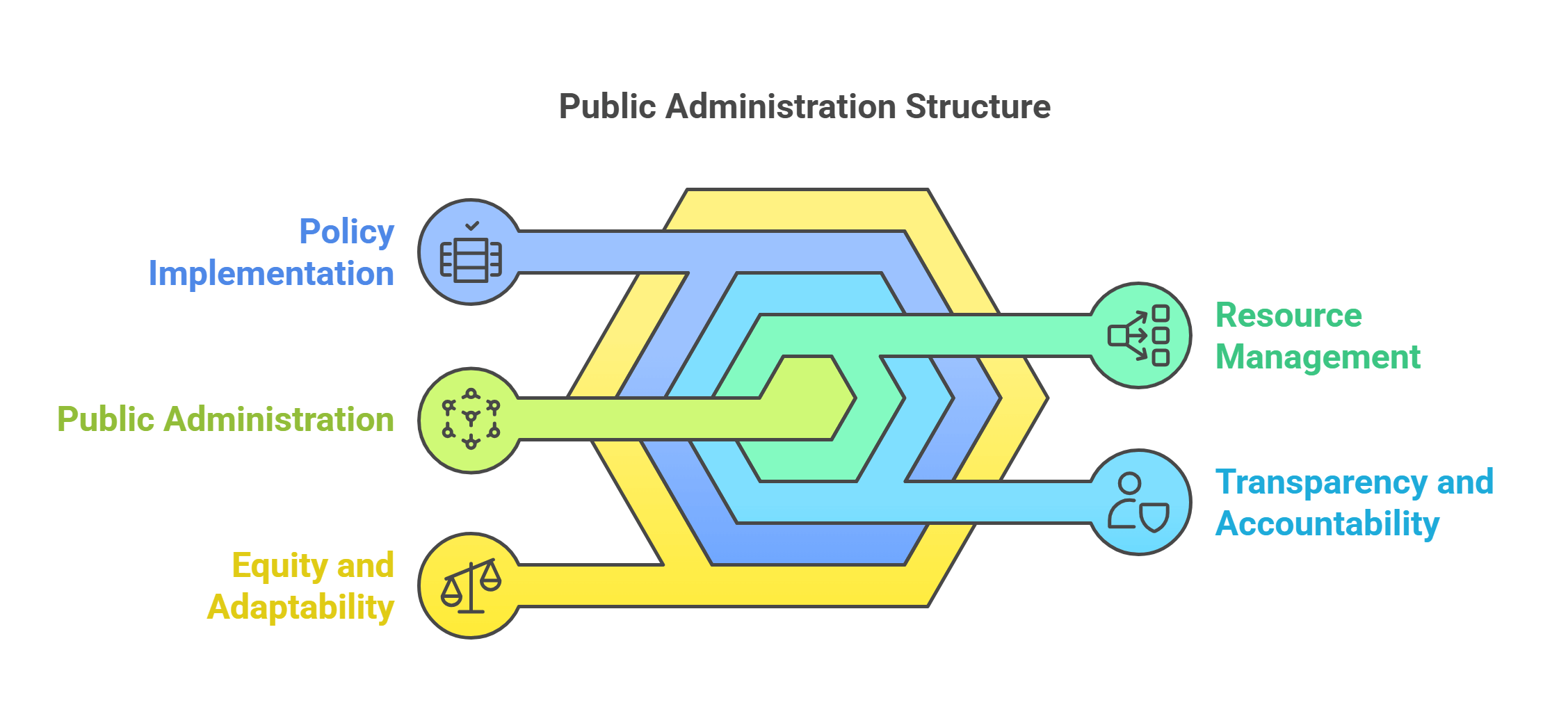
6. Public Administration
Public Administration is the implementation and management of public policies. It focuses on ensuring that governmental functions and services run efficiently and meet the needs of citizens.
- Manages public resources and services.
- Focuses on transparency and accountability.
- Implements policies through administrative systems.
- Balances efficiency with equity in service delivery.
- Adapts to changing societal demands.
Explained Simply: Public Administration is like organizing a town fair where everyone gets the rides, snacks, and games they expect without chaos. It ensures the fair runs smoothly for all!
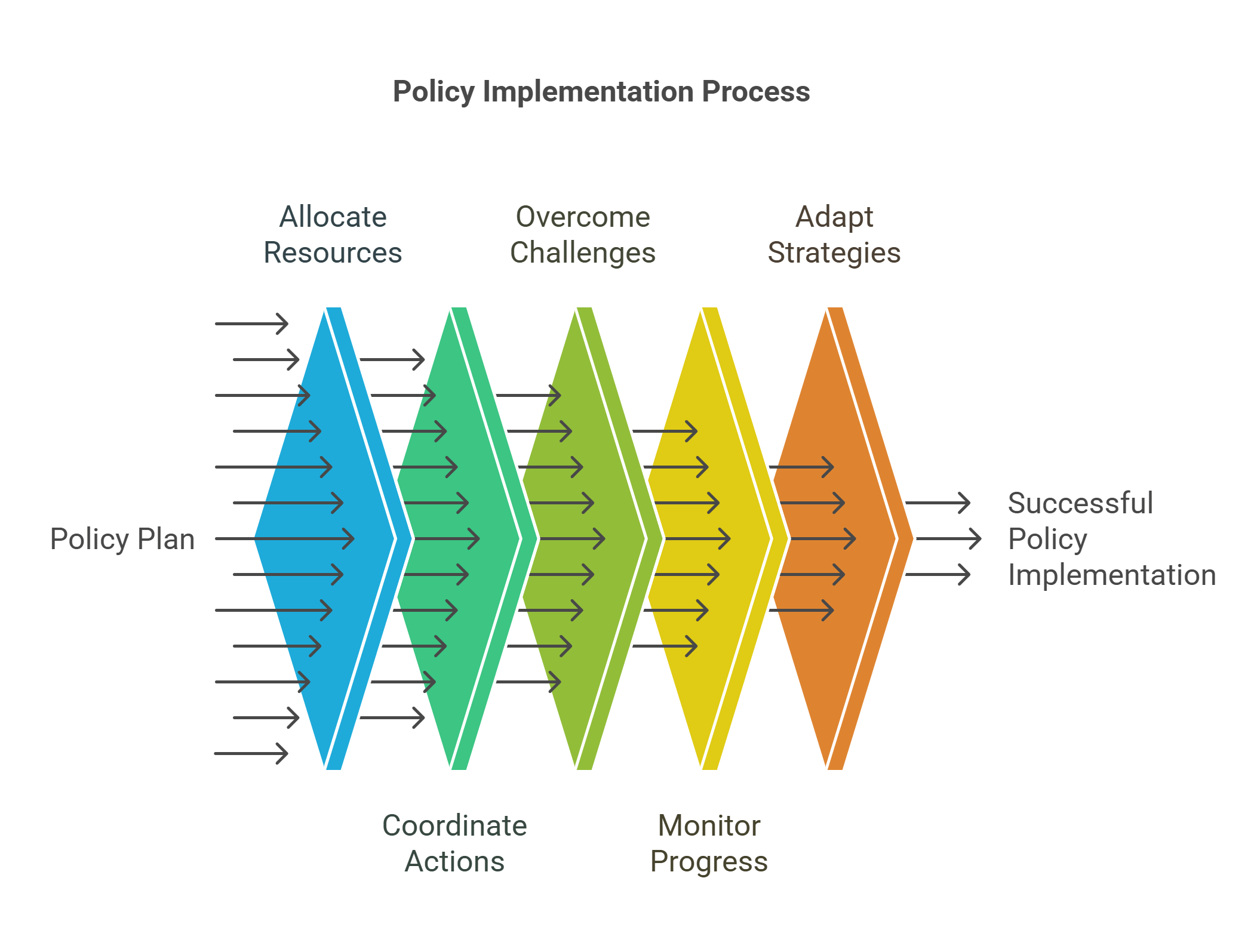
7. Policy Implementation
Policy implementation involves putting policies into action. It focuses on translating plans into tangible outcomes, requiring coordination across various stakeholders and government agencies.
- Turns plans into practical actions.
- Involves funding, staffing, and coordination.
- Faces challenges like political resistance or resource limitations.
- Requires monitoring to ensure success.
- Often adapts based on real-world feedback.
Explained Simply: Imagine drawing a treasure map (policy) and then following it step by step to reach the treasure. Policy implementation is about taking those steps to make the plan work.
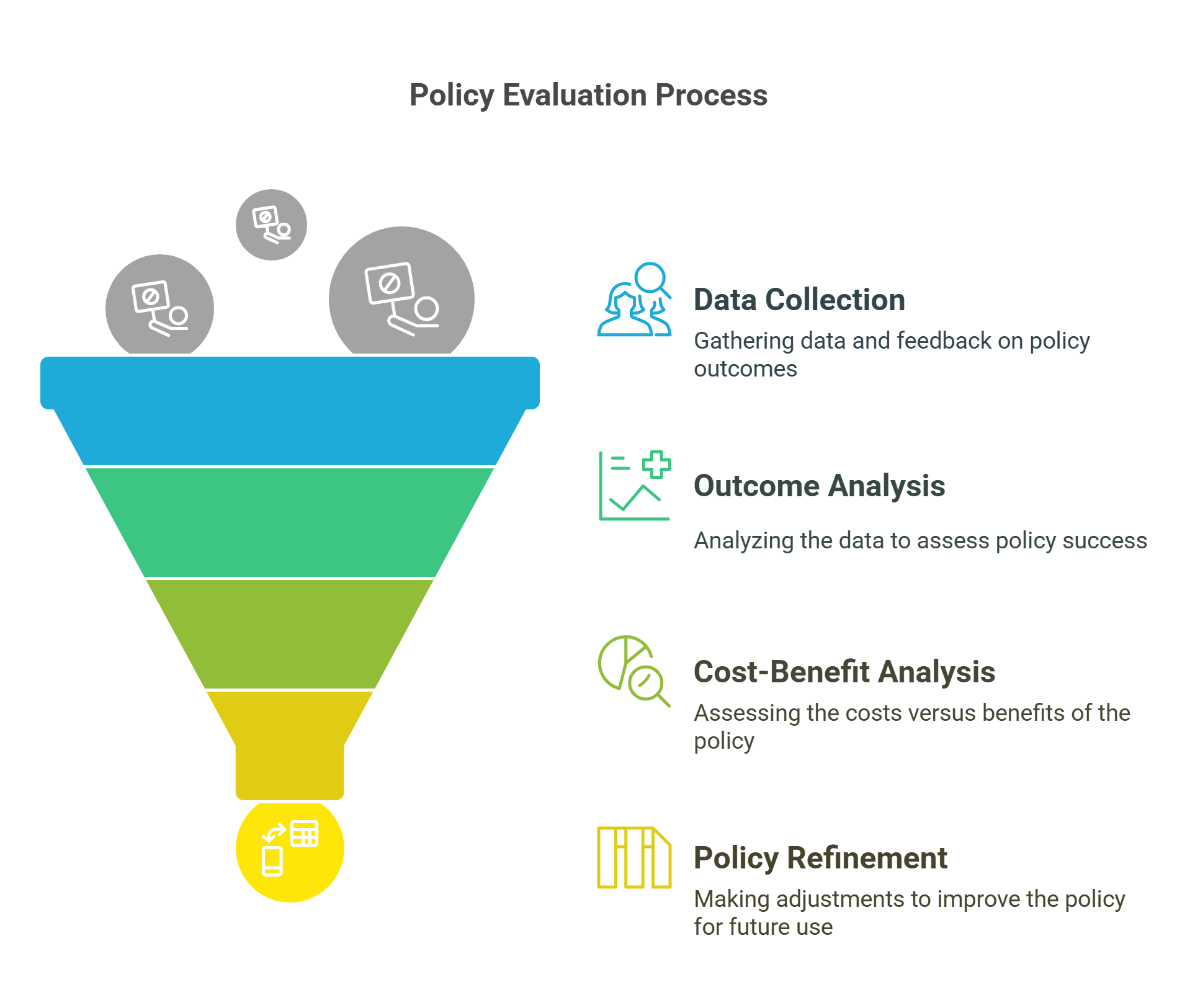
8. Policy Evaluation
Policy evaluation assesses the effectiveness, efficiency, and equity of policies after implementation. It determines whether goals were achieved and identifies areas for improvement.
- Measures the success of policies.
- Uses data and feedback to evaluate outcomes.
- Focuses on cost-benefit analysis and impact studies.
- Helps refine policies for future use.
- Ensures accountability and transparency.
Explained Simply: Think of baking a cake and then tasting it to see if it’s good. If it’s too salty, you adjust the recipe next time. Policy evaluation is like tasting the cake to see how well it turned out.
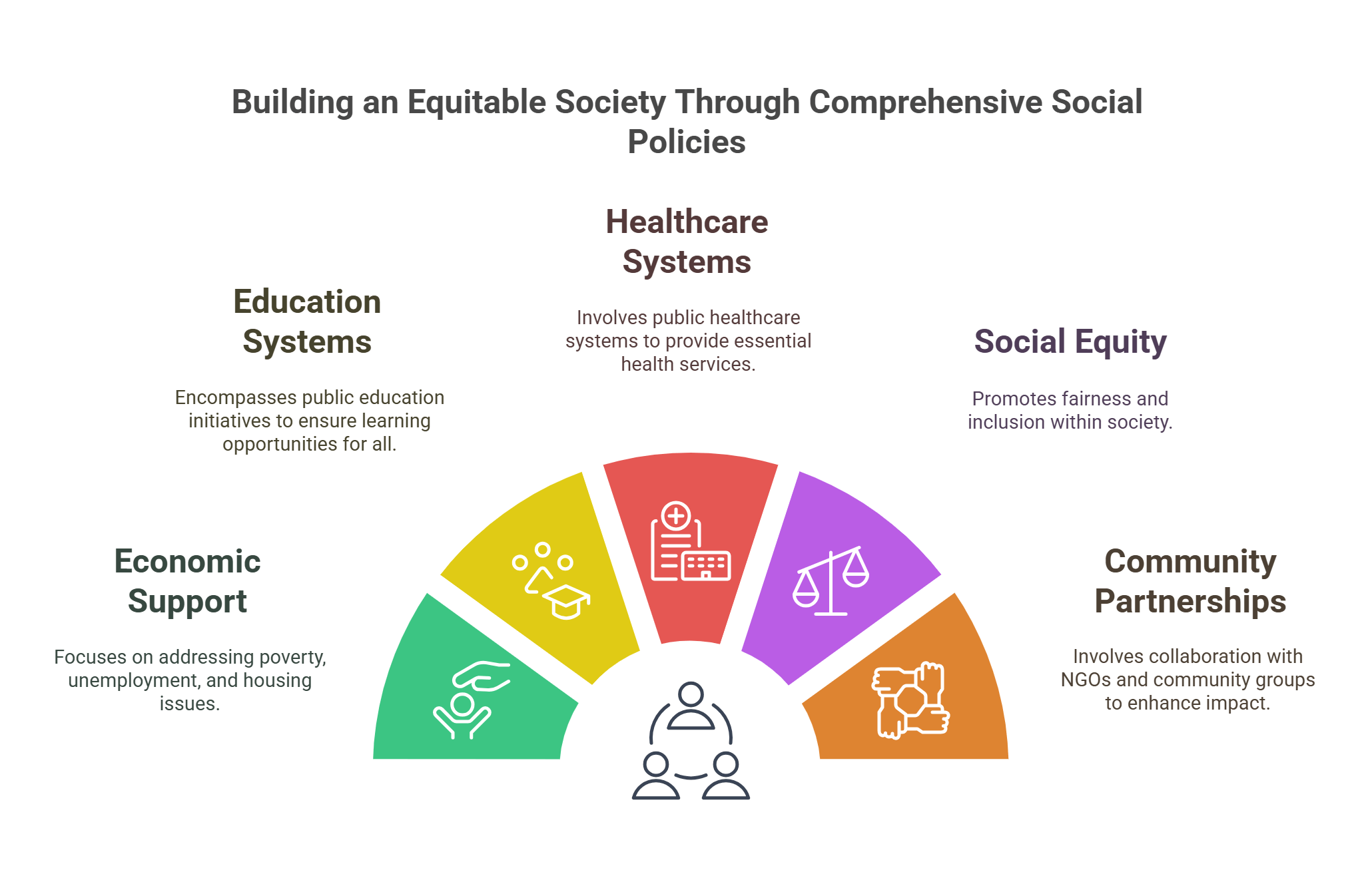
9. Social Policy
Social policies focus on improving societal welfare by addressing issues like inequality, education, and healthcare. They aim to create a just and equitable society.
- Addresses poverty, unemployment, and housing.
- Includes public education and healthcare systems.
- Promotes social equity and inclusion.
- Involves partnerships with NGOs and community groups.
- Adapts to cultural and demographic changes.
Explained Simply: Social policy is like making sure everyone in a group has shoes that fit. If someone doesn’t, the group finds ways to provide them, so everyone can walk comfortably together.
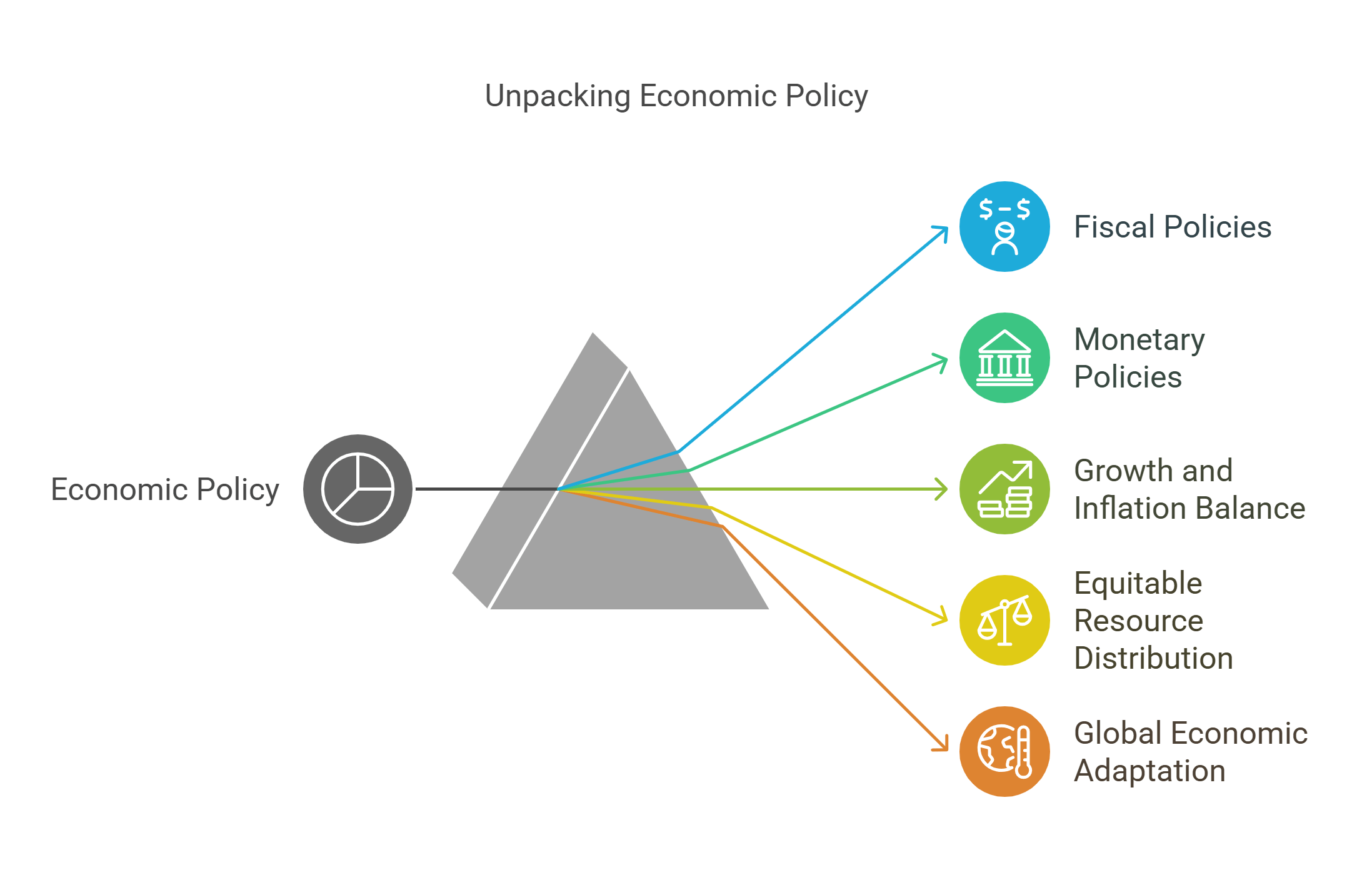
10. Economic Policy
Economic policy focuses on managing a country’s economy through decisions about taxation, government spending, and trade. It aims to promote growth, reduce unemployment, and control inflation.
- Includes fiscal policies like taxation and spending.
- Manages monetary policies like interest rates.
- Aims to balance growth and inflation.
- Promotes equitable distribution of resources.
- Adapts to global economic trends.
Explained Simply: Economic policy is like deciding how to split a big pie among everyone at a party, making sure no one gets too much or too little.
✨ Conclusion
Understanding public policy concepts equips you to analyze and engage with reading comprehension passages more effectively. These topics often involve debates, cause-effect relationships, and complex decision-making processes. By mastering these ideas, you enhance your ability to comprehend arguments, evaluate evidence, and draw connections, boosting both test performance and real-world knowledge.













