🔬 Science and Technology: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Science and technology have become integral parts of modern life, and their relevance in reading comprehension (RC) passages cannot be overstated. These topics often serve as the backbone of RC passages, testing the reader’s ability to analyze complex issues, synthesize critical arguments, and engage with futuristic or ethical implications. From breakthroughs in quantum mechanics to ethical dilemmas in biotechnology, understanding key concepts equips test-takers with the tools to navigate challenging RC passages effectively.
📋 Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore ten critical science and technology-related concepts often featured in RC passages:
- Nanotechnology
- Genetic Engineering
- Renewable Energy Technologies
- Space Exploration
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Biotechnology
- Robotics
- Artificial Intelligence
- Quantum Mechanics
- Materials Science
🔍 Detailed Explanations
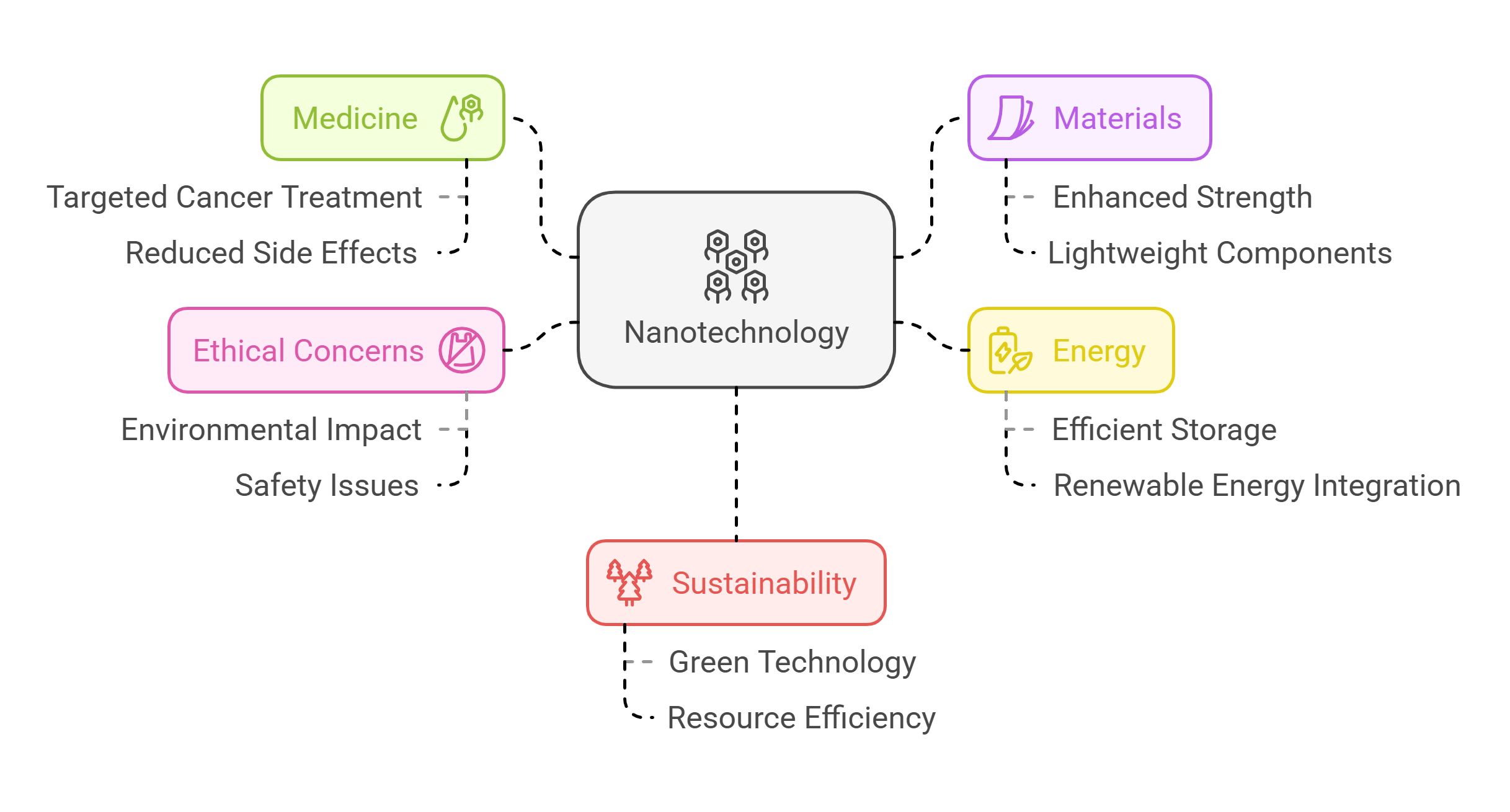
1. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology manipulates matter at the atomic or molecular level, enabling revolutionary advancements in medicine, materials, and energy. For instance, nanoscale drug delivery systems target cancer cells directly, reducing side effects. Its potential also extends to creating stronger, lighter materials and improving energy storage systems. However, ethical and environmental concerns about its misuse and long-term impact are critical topics in RC passages.
- Focuses on atomic or molecular manipulation.
- Enables targeted drug delivery in medicine.
- Improves material strength and efficiency.
- Raises ethical and safety concerns.
- Drives innovation in sustainability.
Explained Simply: It’s like building with invisible Legos so small you can’t see them. These Legos can make super materials that don’t break easily or medicine that only fixes the sick parts of your body.
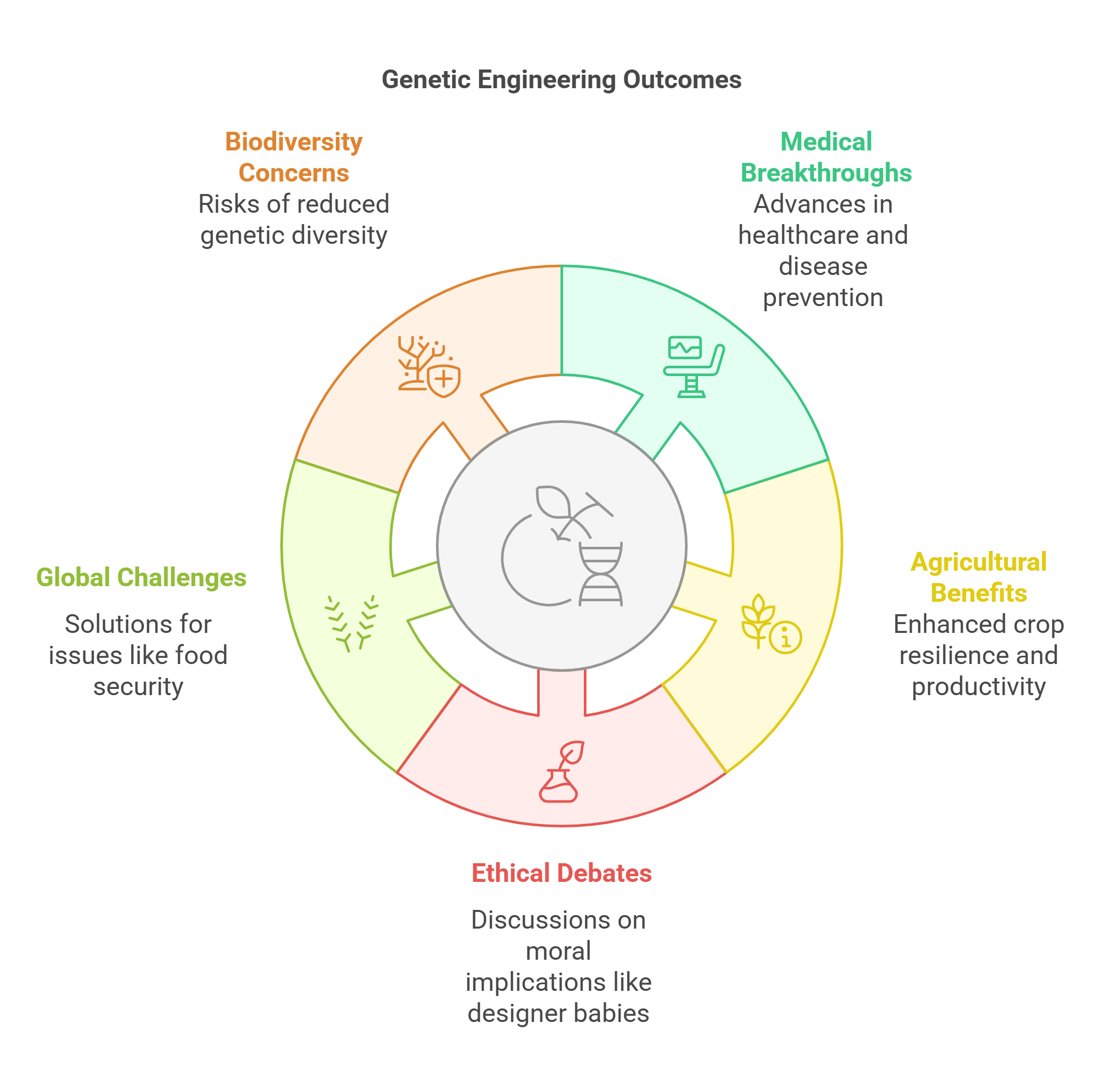
2. Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering involves modifying an organism’s DNA to achieve desired traits, such as disease resistance in crops or hereditary disease prevention in humans. It plays a key role in medical breakthroughs, agriculture, and ethical debates. Passages may explore its promises and pitfalls, including its societal and philosophical implications.
- Alters DNA to enhance or suppress traits.
- Used in agriculture, medicine, and disease prevention.
- Sparks ethical debates about “designer babies.”
- Can address global challenges like food security.
- Raises concerns about biodiversity and misuse.
Explained Simply: Imagine if you could change the recipe for a cake to make it healthier or tastier. Genetic engineering changes the “recipe” of plants, animals, or people to make them stronger or healthier.
3. Renewable Energy Technologies
Renewable energy harnesses resources like sunlight, wind, and water to produce clean power. These technologies reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. RC passages often focus on their global importance and challenges in implementation.
- Uses natural resources like sun, wind, and water.
- Helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Offers sustainable energy solutions.
- Requires substantial investment and innovation.
- Plays a key role in climate change mitigation.
Explained Simply: It’s like using a toy car that runs on the sun or the wind instead of batteries. These energy sources don’t run out and don’t hurt the Earth.
4. Space Exploration
Space exploration pushes the boundaries of human knowledge, uncovering secrets about our universe. From moon landings to Mars rovers, it inspires innovation and raises questions about human survival beyond Earth. Passages may delve into its scientific, political, and philosophical implications.
- Expands human knowledge of the universe.
- Drives innovation in science and technology.
- Explores the potential for human life on other planets.
- Requires substantial global cooperation and funding.
- Raises ethical questions about resource allocation.
Explained Simply: Exploring space is like looking for treasure in the sky. We send robots and spaceships to find out more about planets and stars.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT connects devices to the internet, allowing them to communicate with each other. Smart homes, wearable fitness trackers, and automated systems are some examples. RC passages often focus on its transformative potential and concerns like cybersecurity.
- Connects devices to share information.
- Makes life more convenient through automation.
- Used in smart homes, health monitoring, and industries.
- Raises privacy and cybersecurity concerns.
- Represents a key trend in digital transformation.
Explained Simply: It’s like having all your toys talk to each other to help you—your clock wakes you up, your lights turn on, and your backpack tells you if you forgot your lunch.
6. Biotechnology
Biotechnology uses living organisms to create products and solve problems, from producing vaccines to developing biofuels. Passages often discuss its potential to tackle global challenges and the ethical concerns it raises.
- Combines biology and technology for innovation.
- Used in medicine, agriculture, and environmental solutions.
- Produces vaccines, genetically modified crops, and biofuels.
- Raises ethical issues in genetic manipulation.
- Offers solutions to pressing global challenges.
Explained Simply: Imagine using friendly germs to make yummy yogurt or plants that can grow anywhere to feed more people. That’s what biotechnology does!
7. Robotics
Robotics involves designing machines that can perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. RC passages often explore its applications, challenges, and implications for employment and ethics.
- Builds machines to perform specific tasks.
- Used in healthcare, manufacturing, and exploration.
- Reduces human effort in dangerous jobs.
- Raises questions about job displacement.
- Represents advances in artificial intelligence and mechanics.
Explained Simply: It’s like building a robot friend that can help clean your room or explore places humans can’t go, like underwater or in space.
8. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI enables machines to simulate human intelligence, learning and making decisions. It powers tools like chatbots, facial recognition, and autonomous vehicles. RC passages may explore its ethical, social, and economic implications.
- Teaches machines to think and learn like humans.
- Powers tools like virtual assistants and self-driving cars.
- Raises ethical questions about decision-making power.
- Impacts industries and job markets.
- Represents the future of technology and innovation.
Explained Simply: AI is like teaching a computer how to be super smart—like having a robot that can help with homework or tell you jokes.
9. Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics studies the behavior of particles at the smallest scales, like atoms and photons. It forms the basis of revolutionary technologies like quantum computing and advanced encryption. RC passages may explore its theoretical and practical dimensions.
- Studies the behavior of particles at microscopic levels.
- Drives technologies like quantum computers.
- Challenges classical physics theories.
- Offers solutions for advanced data encryption.
- Raises philosophical questions about reality and probability.
Explained Simply: It’s like learning about the tiniest building blocks of everything around us and how they sometimes behave like magic!
10. Materials Science
Materials science studies the properties and performance of materials, enabling innovations like lightweight alloys, super-strong composites, and smart materials. RC passages may focus on its role in technology and sustainability.
- Focuses on improving materials for specific uses.
- Drives advancements in construction, electronics, and healthcare.
- Addresses sustainability challenges.
- Integrates physics, chemistry, and engineering.
- Leads to revolutionary products like graphene batteries.
Explained Simply: Think of materials scientists as chefs who make better “ingredients” for everything—from buildings to gadgets—so they last longer and work better.
✨ Conclusion
Understanding these 10 concepts helps build a solid foundation for engaging with science and technology RC passages. These ideas sharpen your critical thinking, making it easier to analyze arguments, understand technical terms, and connect broader implications to the passage context. Preparing for RC with such knowledge ensures you’re equipped to tackle the complexities of modern reading comprehension challenges.













