🏙️ Urban Studies: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Urban Studies examines how cities evolve, function, and influence human life. Understanding this subject is essential for tackling reading comprehension (RC) passages, as it provides context for analyzing critical issues like urbanization, governance, and sustainable development. RC passages often explore debates on urbanization trends, policies, and challenges, making familiarity with these topics crucial for identifying arguments, conclusions, and underlying assumptions.
📋 Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these key Urban Studies-related concepts:
- Urbanization Trends
- Smart Cities
- Urban Sociology
- Urban Planning
- Urban Economics
- Gentrification
- Urban Sprawl
- Sustainable Urban Development
- Public Space
- Urban Governance
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. Urbanization Trends
Urbanization refers to the increasing population shift from rural to urban areas. It is driven by industrialization, job opportunities, and lifestyle changes. This trend influences housing, infrastructure, and public services. In RC passages, urbanization is often linked to societal changes, environmental impacts, and economic development.
- Rapid growth in urban populations worldwide.
- Challenges: overcrowding, pollution, and resource strain.
- Benefits: economic growth, innovation, and diversity.
- Role of urbanization in shaping culture and politics.
- Impacts of rural-to-urban migration on rural communities.
Explained Simply: Imagine a small village where a few people live. Suddenly, everyone starts moving to a big city nearby because it has more jobs, schools, and fun things to do. But when too many people move in, the city can get crowded, and there might not be enough houses or clean water for everyone. That’s what urbanization is like.
2. Smart Cities
Smart Cities use technology and data to improve the quality of life for residents. They emphasize efficient transportation, energy usage, and public services. In RC passages, Smart Cities are discussed as solutions to urban challenges.
- Use of AI, IoT, and data for urban management.
- Examples: smart traffic lights, energy-efficient buildings.
- Focus on sustainability and convenience.
- Criticism: concerns over privacy and accessibility.
- Role in modern urban development strategies.
Explained Simply: Think of a city where everything works with cool gadgets. Traffic lights know when to change to avoid jams, and garbage bins tell workers when they’re full. It’s like giving the city a brain to make things work better!
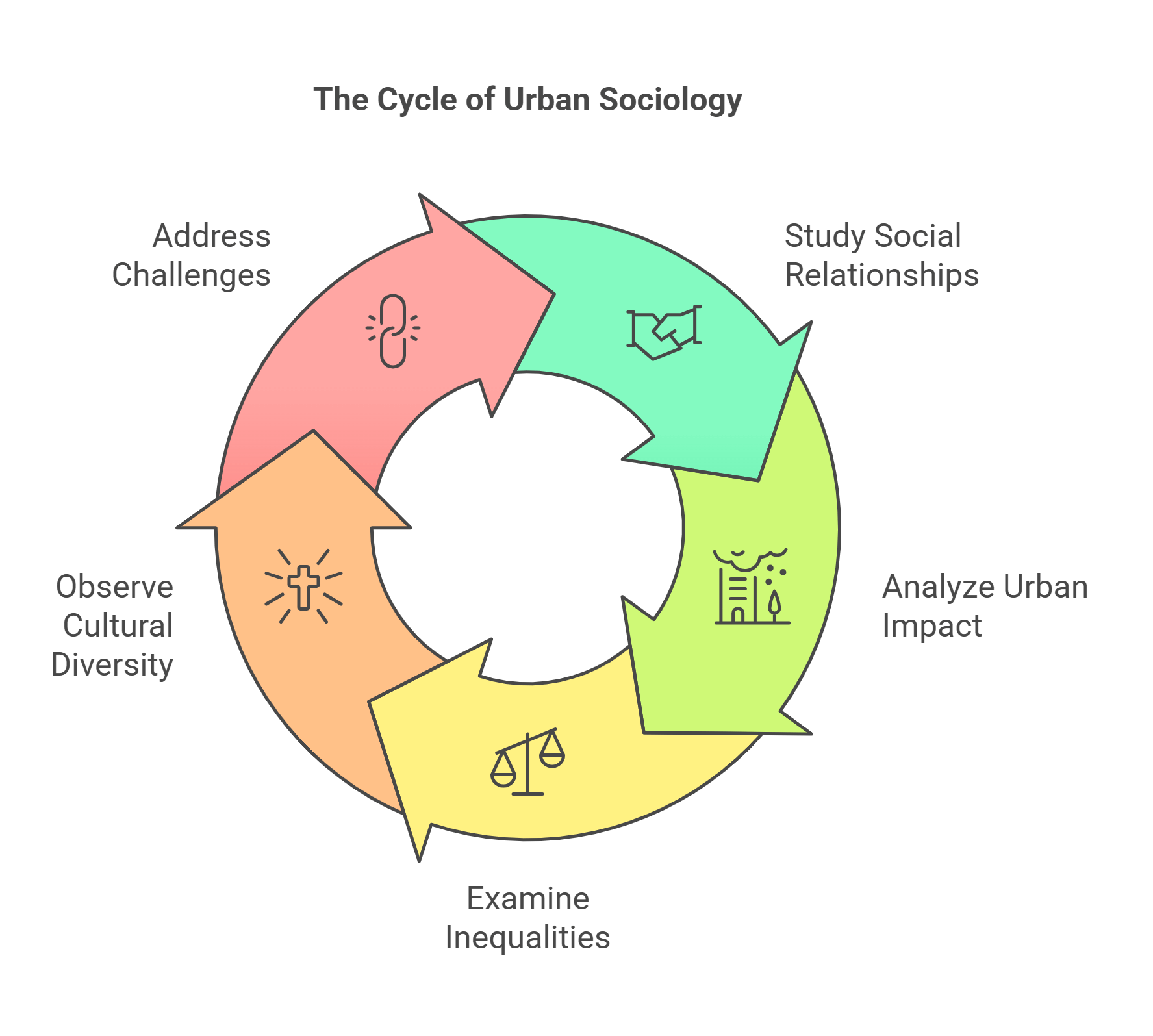
3. Urban Sociology
Urban Sociology studies how individuals and groups interact within urban environments. It examines how city life influences social behaviors, relationships, and community structures. RC passages often explore how urban settings shape culture, identity, and social inequality.
- Focus on social relationships in cities.
- Impact of urban life on community ties and personal identity.
- Examination of class, race, and gender in urban settings.
- How urbanization fosters cultural diversity and innovation.
- Challenges: social alienation and inequality.
Explained Simply: Imagine you live in a huge city with many different kinds of people. Some people are very rich, some are not, and everyone has different jobs and cultures. Urban Sociology studies how all these people live together, make friends, and solve problems—or sometimes don’t.
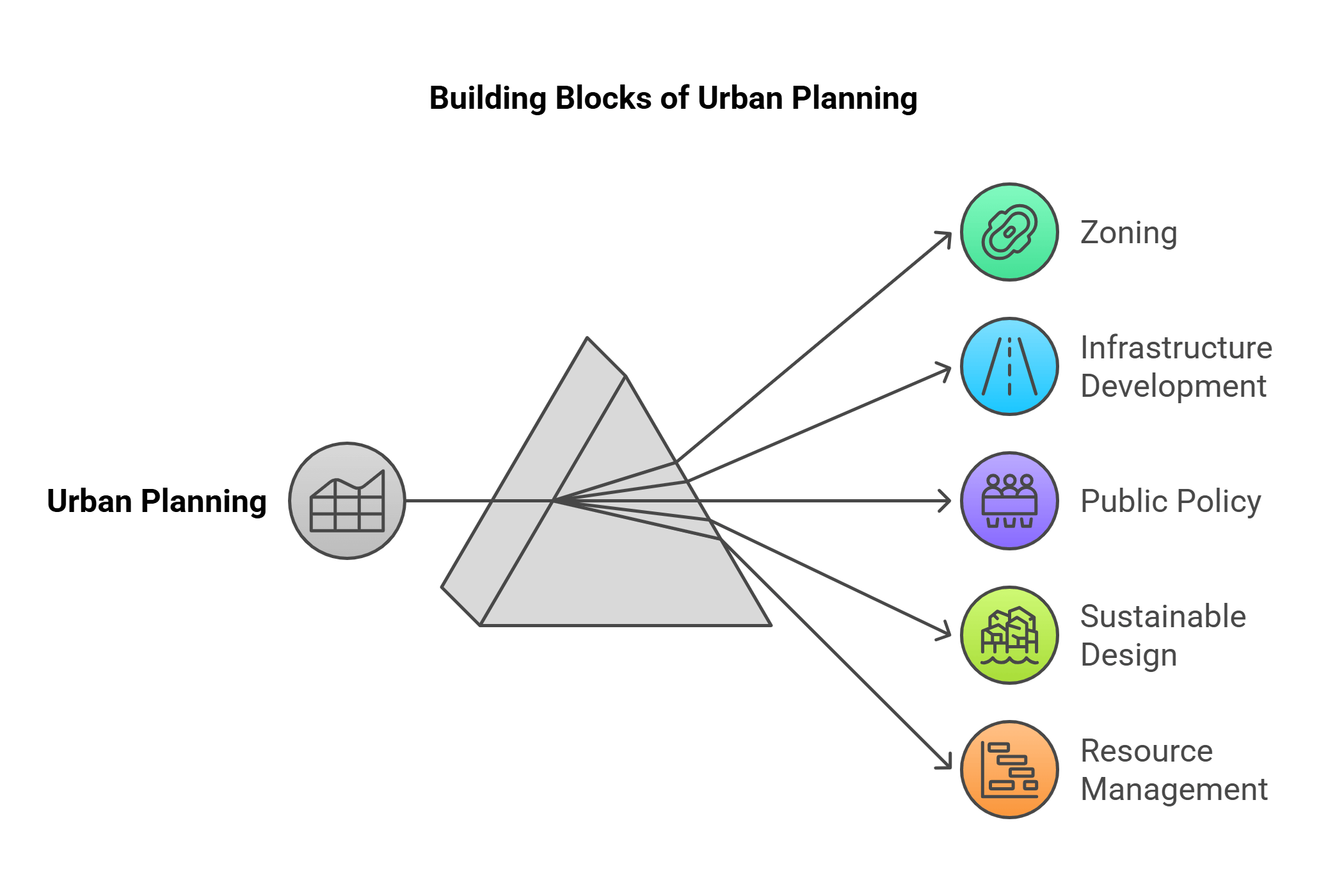
4. Urban Planning
Urban Planning is the process of designing and organizing city spaces to meet the needs of its residents. It involves zoning, infrastructure development, and public policy. In RC, this topic often touches on debates about effective city planning and its impact on quality of life.
- Aims to balance residential, commercial, and industrial spaces.
- Focus on public services like transportation, parks, and schools.
- Strategies to prevent overcrowding and manage resources.
- Emphasis on sustainable and inclusive city designs.
- Challenges: balancing development with environmental concerns.
Explained Simply: Think of a city like a giant Lego set. Urban planners decide where to put the houses, parks, roads, and schools so everyone has what they need and the city works smoothly.
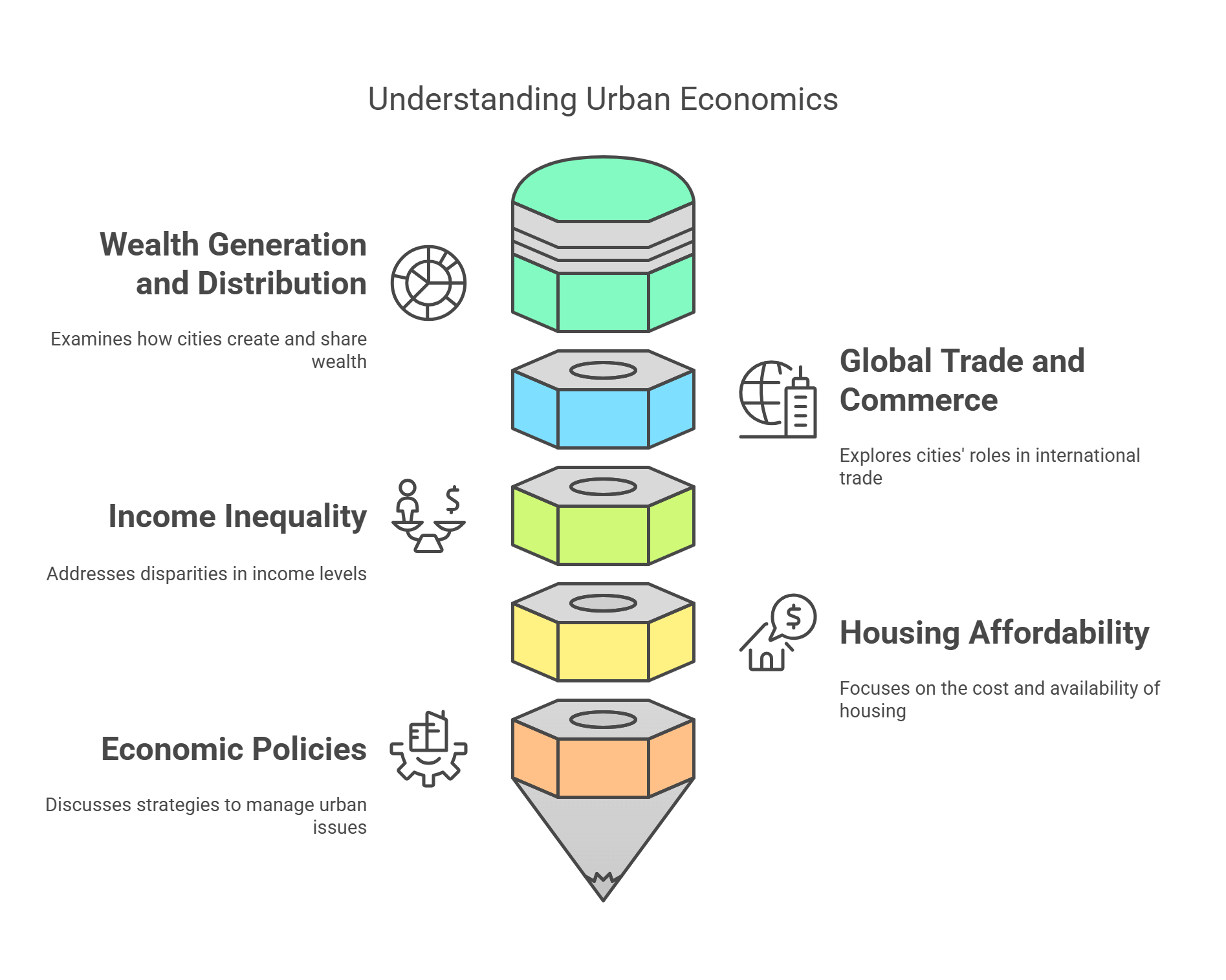
5. Urban Economics
Urban Economics focuses on the financial aspects of cities, including housing, labor markets, and resource distribution. It helps explain how economic activities are concentrated in urban areas. RC passages may explore the benefits and challenges of urban economic growth.
- Studies how cities generate and distribute wealth.
- Role of cities in global trade and commerce.
- Challenges like income inequality and housing affordability.
- Impact of industries and businesses in shaping cities.
- Economic policies to address urban poverty and unemployment.
Explained Simply: Imagine a city as a giant store where people work, buy, and sell things. Urban Economics is about understanding how this big store makes money and ensures everyone has enough to live happily.
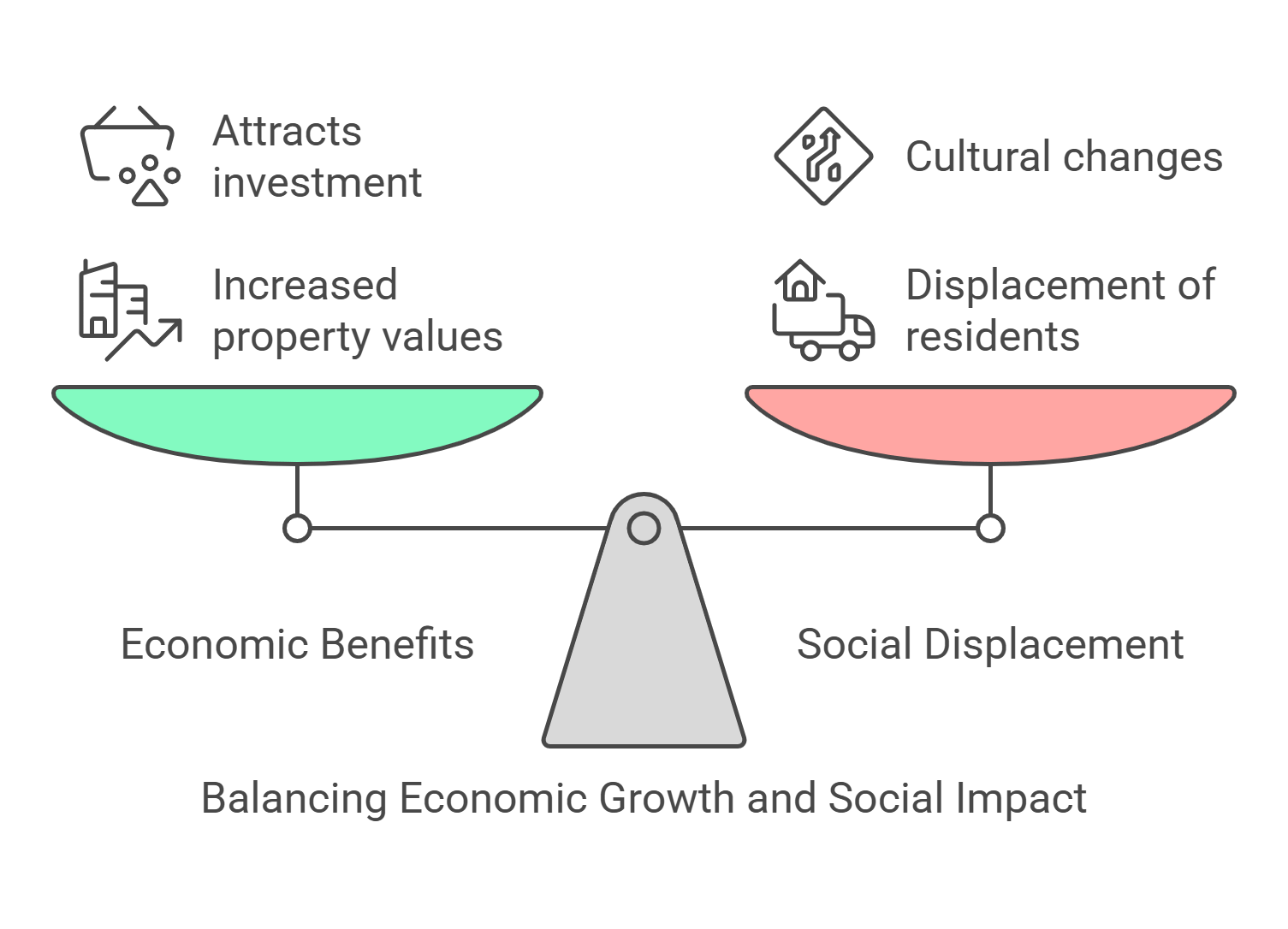
6. Gentrification
Gentrification refers to the transformation of urban neighborhoods as wealthier residents move in, often displacing lower-income residents. RC passages often discuss its impact on culture, economy, and community dynamics.
- Increases property values and attracts investment.
- Displaces longtime, low-income residents.
- Changes the cultural character of neighborhoods.
- Debated for its benefits and ethical concerns.
- Relevant to social and economic discussions.
Explained Simply: Imagine your favorite ice cream shop in the neighborhood gets replaced by a fancy café. It might look nice, but some people can’t afford the new place, and it changes the feel of the neighborhood. That’s gentrification!
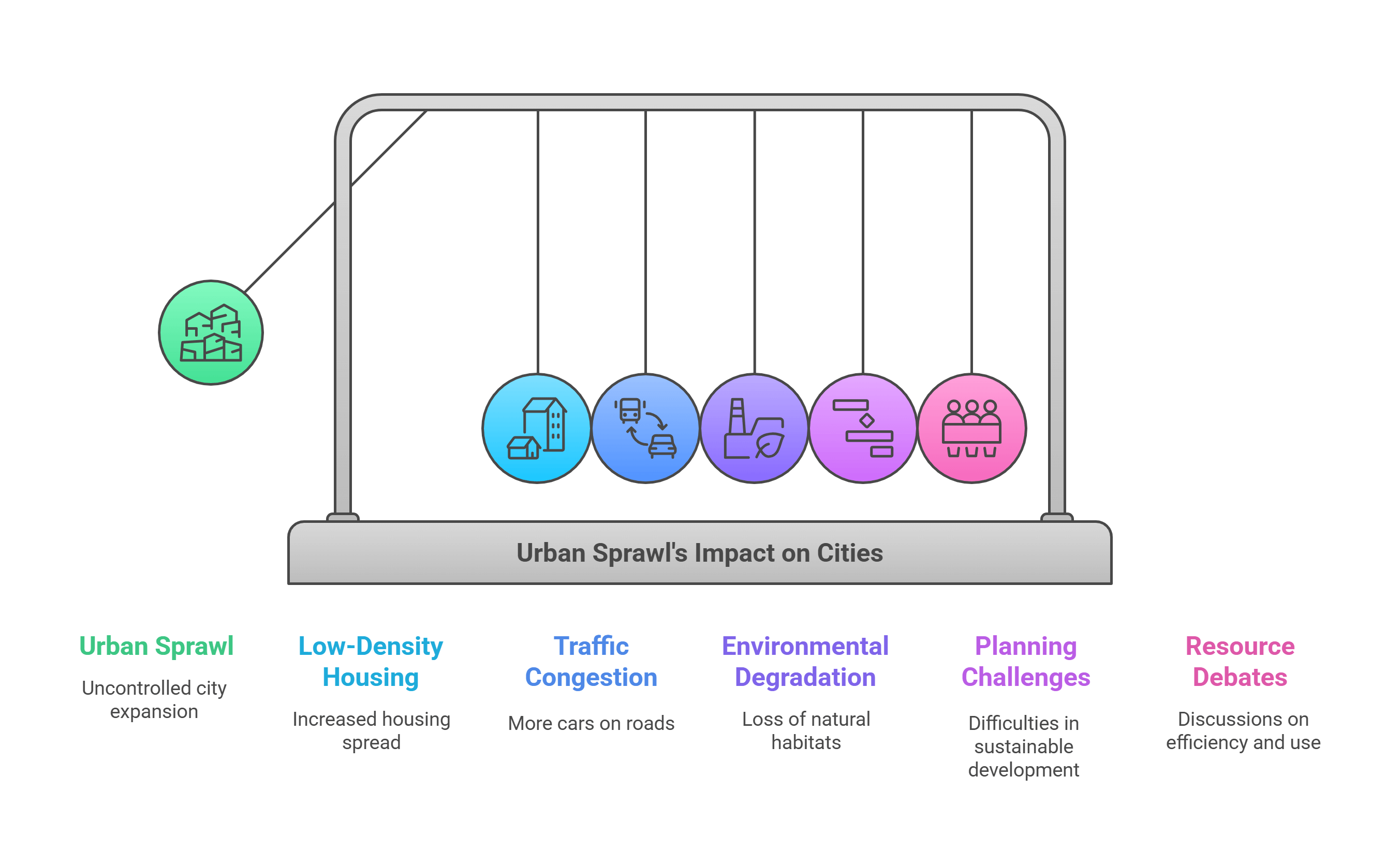
7. Urban Sprawl
Urban Sprawl describes the uncontrolled expansion of cities into surrounding rural areas. It often leads to increased car dependency and environmental degradation.
- Leads to low-density housing and infrastructure.
- Increases traffic congestion and pollution.
- Encroaches on farmland and natural habitats.
- Challenges sustainable city planning efforts.
- Promotes debates on urban efficiency and resource use.
Explained Simply: Imagine a city growing so big that it stretches into forests and farms, leaving fewer places for animals and plants. Urban Sprawl is about this kind of unchecked growth.
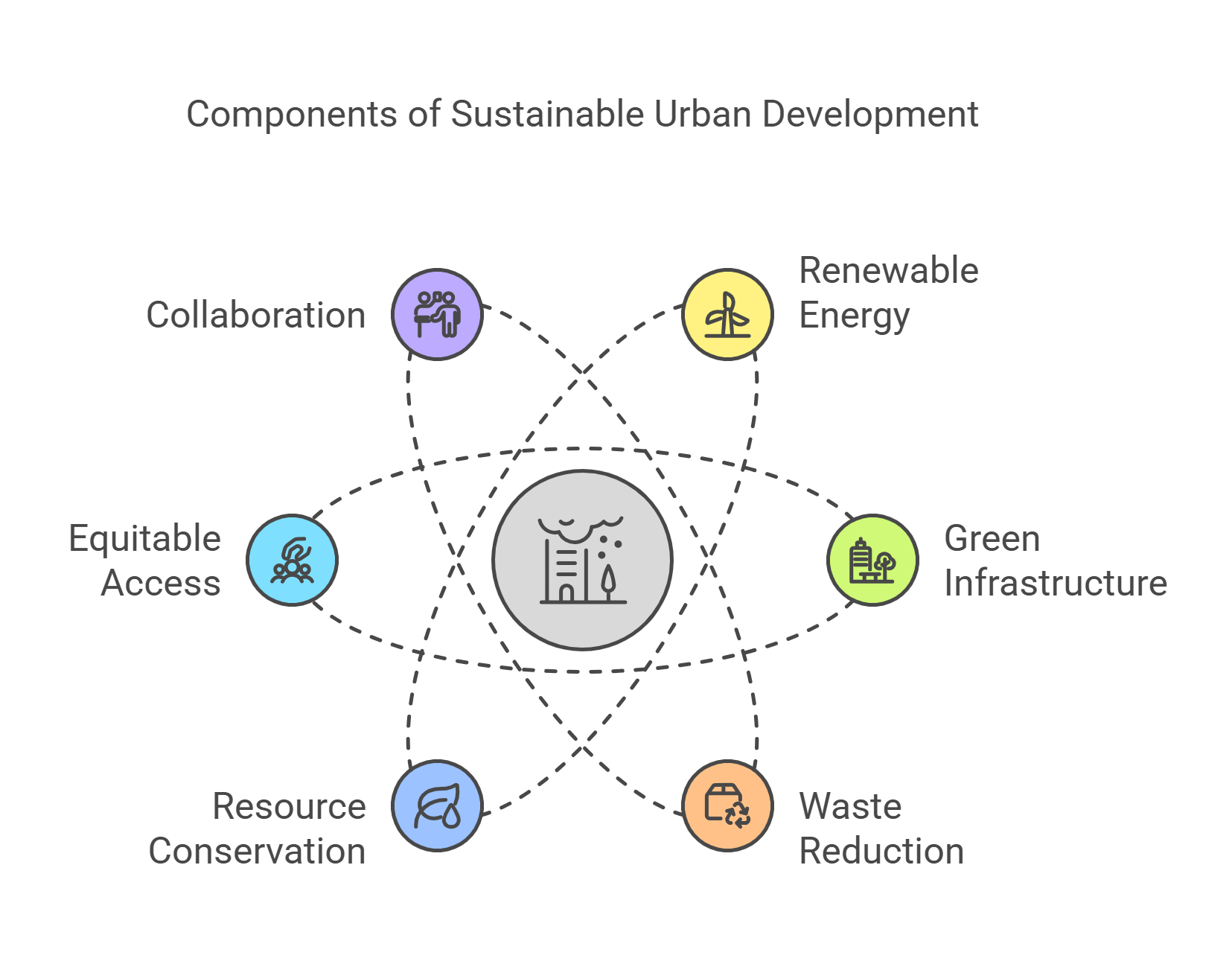
8. Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainable Urban Development focuses on creating cities that meet current needs without compromising future generations. It emphasizes eco-friendly designs, renewable energy, and inclusive policies.
- Uses renewable energy and green infrastructure.
- Reduces waste and conserves natural resources.
- Promotes equitable access to urban amenities.
- Focuses on long-term environmental and social benefits.
- Involves collaboration among governments, businesses, and communities.
Explained Simply: It’s like building a treehouse that uses recycled wood and solar lights so it’s good for you and the environment!
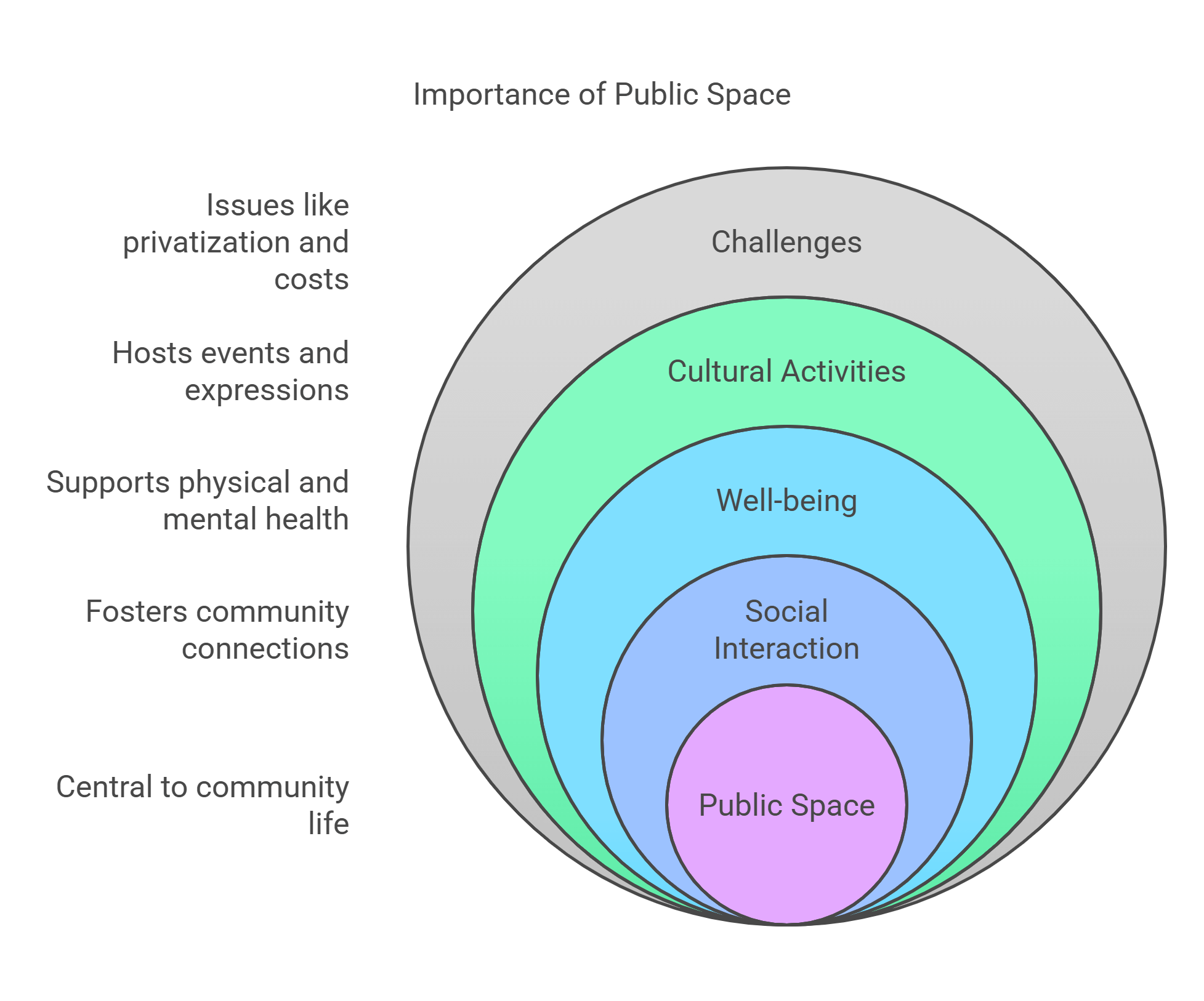
9. Public Space
Public Space includes parks, plazas, and streets open to everyone. These areas are essential for fostering community, recreation, and cultural expression.
- Encourages social interaction and inclusion.
- Supports physical and mental well-being.
- Hosts cultural and recreational activities.
- Reflects a city’s identity and values.
- Challenges include privatization and maintenance costs.
Explained Simply: Public Space is like the playground at school—everyone can use it to play, meet friends, or just relax.
10. Urban Governance
Urban Governance refers to how cities are managed, involving local governments, businesses, and citizens. Effective governance ensures equitable access to resources and addresses challenges like housing, transport, and public safety.
- Manages urban resources and infrastructure.
- Focuses on transparency and citizen participation.
- Addresses social inequality and resource distribution.
- Collaborates with private and public stakeholders.
- Adapts to global urban challenges like climate change.
Explained Simply: Urban Governance is like a group of leaders organizing a giant festival where everyone gets food, fun, and a safe place to enjoy!

✨ Conclusion
Urban Studies provides critical insights into the functioning and evolution of cities, making it a vital subject for RC preparation. Understanding concepts like urbanization, gentrification, and sustainable development enables you to better analyze complex passages. By mastering these ideas, you’ll enhance your ability to identify arguments, evaluate perspectives, and draw well-reasoned conclusions, ensuring success in the Reading Comprehension section.













