Actino: The Radiant Root Illuminating Science and Nature
Dive into the luminous world of the root "actino," derived from the Greek word aktinos, meaning "ray." From measuring solar intensity with actinometers to classifying unique bacteria as actinomycetes, this radiant root has shaped language and science across diverse fields.

Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Actino
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Actino
- Common Actino-Related Terms
- Actino Through Time
- Actino in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Actino in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Actino Root
- The Actino Family Tree
- FAQs about the Actino Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Actino Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Actino
1. Introduction: The Essence of Actino
Imagine the brilliance of a sunbeam piercing through clouds or the delicate rays of a starfish. These images capture the root "actino," from the Greek aktinos, meaning "ray." Pronounced "ak-tee-noh," this root weaves through scientific terminology, connecting light, radiation, and structure. Its influence spans from tools measuring solar radiation to organisms vital in ecosystems and medicine.
2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root aktinos originated in ancient Greek, where it described "rays" or "beams." It entered scientific nomenclature in the 18th and 19th centuries as discoveries in optics, biology, and physics flourished. Pioneers in science, inspired by this root, used it to name phenomena and organisms characterized by radiating forms or properties, including solar energy and microbial growth patterns.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Actino
Visualize a radiant sun spreading beams across the sky. Each ray symbolizes the root "actino" and its connection to light, energy, and radiating forms.
Mnemonic Device: “Actino shines like the sun’s ray—radiating knowledge in science every day!”
4. Common Actino-Related Terms
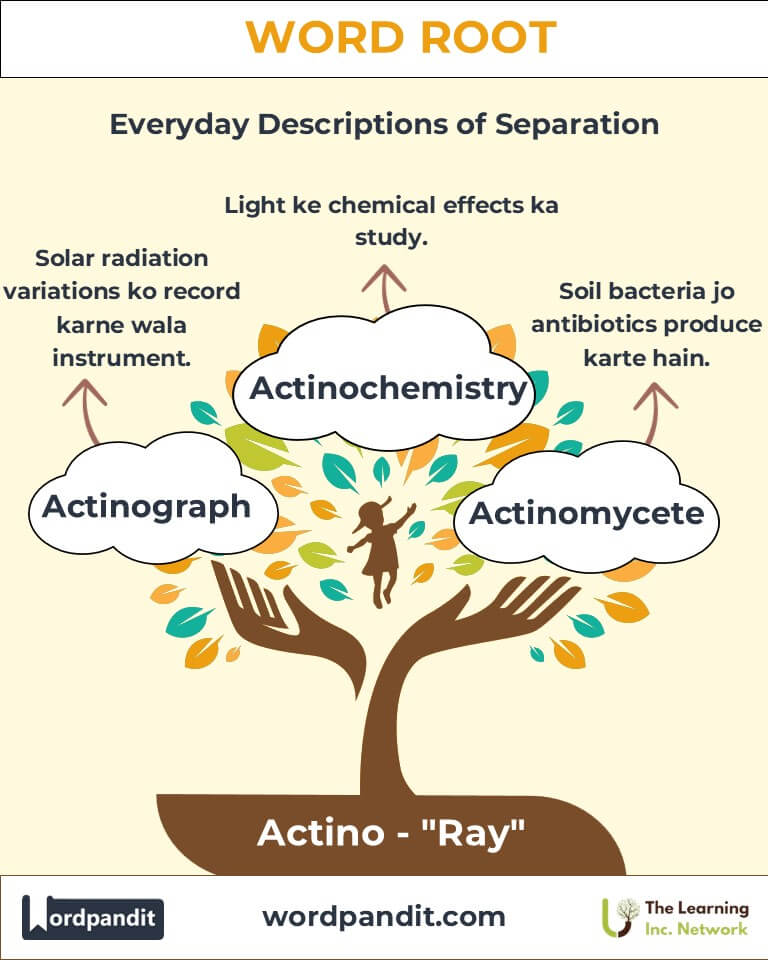
- Actinometer (ak-tih-nom-uh-ter):
- Definition: A device for measuring the intensity of solar radiation.
- Example: "Meteorologists use actinometers to track sunlight levels for climate studies."
- Actinomycete (ak-tih-noh-my-seet):
- Definition: A type of filamentous bacterium that resembles fungi, often found in soil.
- Example: "Actinomycetes are crucial in producing antibiotics like streptomycin."
- Actinotherapy (ak-tih-noh-ther-uh-pee):
- Definition: Treatment using light or radiation.
- Example: "Actinotherapy is used in skin conditions like psoriasis."
- Actinograph (ak-tih-noh-graf):
- Definition: An instrument that records variations in solar radiation over time.
- Example: "The actinograph documented changes in sunlight during the eclipse."
- Actinomorphic (ak-tih-noh-mor-fik):
- Definition: Describing organisms or structures with radial symmetry.
- Example: "Starfish and daisies are examples of actinomorphic forms."
5. Actino Through Time
- Early Applications: The root emerged in Greek descriptions of radiating natural phenomena, such as sunlight and star patterns.
- 19th Century Science: Actinometers advanced climate studies by quantifying sunlight.
- Modern Medicine: Actinotherapy highlights the root’s relevance in therapeutic applications.
6. Actino in Specialized Fields
- Meteorology:
- Actinometer measures solar radiation, crucial for weather forecasting and climate studies.
- Microbiology:
- Actinomycetes produce life-saving antibiotics like streptomycin and rifamycin.
- Botany and Zoology:
- Actinomorphic describes organisms with radial symmetry, such as flowers and echinoderms.
- Healthcare:
- Actinotherapy demonstrates the healing potential of light and radiation.
- Physics:
- Instruments like actinographs monitor solar energy for advancements in renewable energy.
7. Illustrative Story: Actino in Action
Dr. Mira Patel, a microbiologist, was fascinated by soil bacteria's ability to combat diseases. During her research on actinomycetes, she discovered a strain producing a powerful antibiotic against resistant infections. Meanwhile, meteorologists used an actinometer to monitor sunlight in the region, indirectly supporting her research by optimizing growth conditions for the bacteria. Together, their efforts highlighted the transformative potential of "actino"-based science.
8. Cultural Significance of the Actino Root
The concept of "rays" has deep cultural resonance, symbolizing enlightenment, energy, and connection. Ancient civilizations revered sunlight, associating it with divinity and life. Today, the root "actino" continues this legacy, underpinning innovations in science and medicine.
9. The Actino Family Tree
- Phot- (Light):
- Examples: Photosynthesis – Process by which plants convert sunlight into energy; Phototherapy – Treatment using light.
- Rad- (Ray):
- Examples: Radiology – Medical imaging using radiation; Radiance – Light emitted in rays.
- Helio- (Sun):
- Examples: Heliotherapy – Treatment using sunlight; Heliocentric – Sun-centered model of the solar system.
10. FAQs About " Actino "
Q: What does "actino" mean, and where does it come from?
A: The root "actino" means "ray," derived from the Greek word aktinos. It is used to describe phenomena, organisms, or instruments that involve radiating forms or properties, such as sunlight, energy, or symmetry.
Q: What is an actinometer, and how is it used?
A: An actinometer is an instrument used to measure the intensity of solar radiation. It is crucial in meteorology for studying sunlight's effects on climate, agriculture, and energy production, as well as in research on renewable energy sources.
Q: What are actinomycetes, and why are they important?
A: Actinomycetes are a type of filamentous bacteria found in soil. They are vital in microbiology and medicine because they produce antibiotics like streptomycin and rifamycin, which are used to treat various infections, including tuberculosis.
Q: What does actinomorphic mean in biology?
A: Actinomorphic refers to organisms, particularly flowers or animals, that exhibit radial symmetry, meaning their structure can be divided into similar halves along multiple planes. Examples include starfish and daisies.
Q: How is actinotherapy applied in medicine?
A: Actinotherapy is a treatment that uses light or radiation to address medical conditions. It is commonly applied in dermatology for treating skin conditions like psoriasis and in oncology as part of radiation therapy for cancer.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Actino " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "actino" mean?
2. Which instrument measures solar radiation?
3. What do actinomycetes produce?
4. What does actinomorphic describe in biology?
5. How is actinotherapy used in medicine?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Actino
The root "actino" embodies the essence of light, rays, and radiating forms. Its applications span meteorology, microbiology, and medicine, illustrating its versatility and relevance. As science advances, "actino" continues to illuminate new frontiers, reminding us of the radiant connections between knowledge, nature, and innovation.













