Adeno: The Root of Life in Glands and Medicine
Discover the depth of "adeno," a word root derived from Greek meaning "gland." From the essential adenoids in your throat to medical conditions like adenoma, this root anchors key vocabulary in biology, anatomy, and medicine.
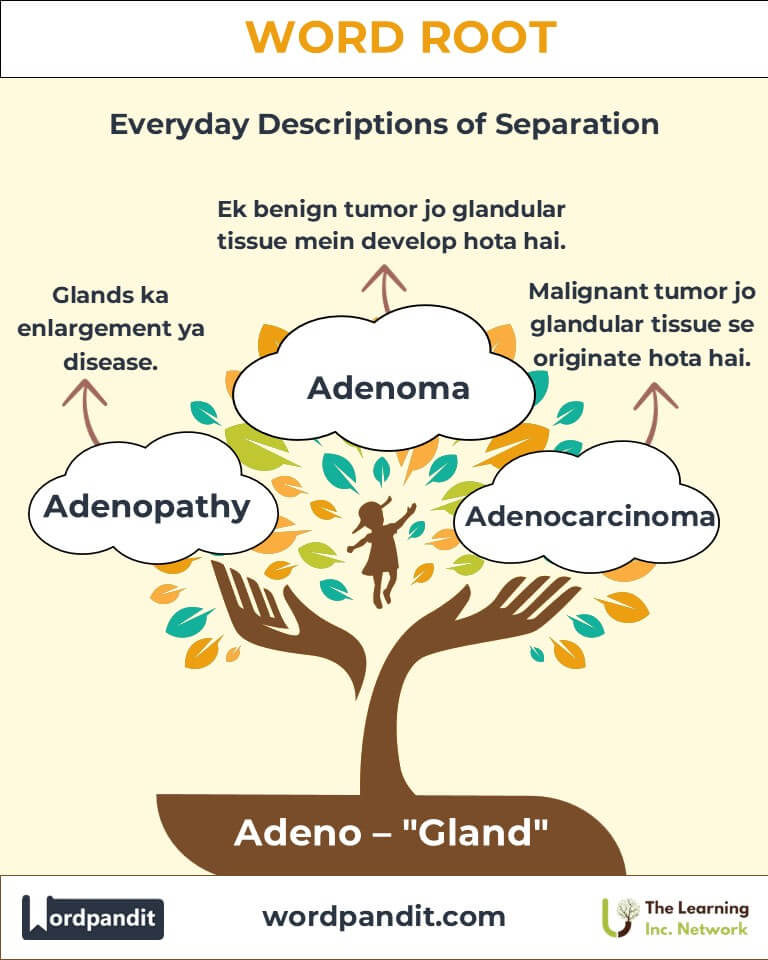
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Adeno"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Adeno"
- Common Adeno-Related Terms
- Adeno Through Time
- Adeno in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Adeno" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Adeno Root
- The Adeno Family Tree
- FAQs about the Adeno Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Adeno Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Adeno"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Adeno"
Have you ever pondered the role glands play in maintaining the body’s harmony? The word root "adeno", pronounced "uh-DEE-noh", originates from the Greek word "aden," meaning "gland." Glands, such as the adenoids in the throat or endocrine glands like the thyroid, are vital to regulating bodily functions and sustaining life. Understanding "adeno" enriches our appreciation of these essential biological components.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "adeno" traces back to ancient Greek, where "aden" described structures responsible for secreting or regulating fluids. Over centuries, medical science adopted the term to name and categorize gland-related structures and conditions. By the Renaissance, as anatomical studies expanded, "adeno" found its way into modern medicine to describe both healthy and pathological aspects of glands.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Adeno"
To remember "adeno," visualize a bustling factory producing life-essential products, symbolizing the glands' role in the body.
Mnemonic Device: “Adeno: The gland is the body’s factory, working endlessly to maintain balance.”
4. Common Adeno-Related Terms
- Adenoids (AD-uh-noids):
- Definition: Lymphatic tissues located in the throat, critical for immune defense in children.
- Example: "Enlarged adenoids can cause breathing difficulties in children."
- Adenoma (AD-uh-NO-muh):
- Definition: A benign tumor originating in glandular tissue.
- Example: "The adenoma was surgically removed to prevent complications."
- Adenopathy (ad-uh-NOP-uh-thee):
- Definition: Enlargement or disease of the lymph nodes or glands.
- Example: "The doctor noted adenopathy during the patient's examination."
- Adenitis (ad-uh-NY-tis):
- Definition: Inflammation of a gland.
- Example: "Adenitis is commonly treated with antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medication."
- Adenocarcinoma (ad-uh-noh-kar-sih-NOH-muh):
- Definition: A malignant tumor originating in glandular tissue.
- Example: "Adenocarcinoma is one of the most common forms of lung cancer."
5. Adeno Through Time
- Ancient Use: Early Greek physicians used "aden" to describe glandular swellings or masses in the body.
- Modern Medicine: Terms like "adenoma" and "adenopathy" became integral to diagnostics, especially in oncology and immunology.
6. Adeno in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Adenocarcinoma: Key in oncology, highlighting malignant transformations in glands.
- Significance: Early detection improves outcomes in cancers like pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
- Immunology:
- Adenoids: Study focuses on their role in immune system development and related disorders.
- Surgery:
- Adenectomy: Refers to the surgical removal of glandular tissue.
- Application: Common in cases of obstructive or cancerous glands.
7. Illustrative Story: "Adeno" in Action
Dr. Claire, an oncologist, was puzzled by a patient's persistent symptoms. A biopsy revealed an adenoma in the adrenal gland. Collaborating with a surgeon, she ensured its successful removal. Meanwhile, her colleague in pediatrics treated a young boy whose enlarged adenoids caused snoring and breathing issues. Through their expertise, they showcased the pivotal role of glands—and "adeno"—in health and healing.
8. Cultural Significance of the Adeno Root
Throughout history, glands symbolized balance and vitality in ancient medical traditions. From Ayurveda’s focus on bodily fluids to Western medicine’s exploration of lymphatic tissues, "adeno" remains central to understanding human health.

9. The Adeno Family Tree
- Lymph (Latin): Refers to fluid and immune nodes.
- Example: Lymphoma – Cancer of lymphatic tissue.
- Endo (Greek, "within"): Indicates internal systems, often paired with gland terms.
- Example: Endocrine – Hormone-secreting glands.
- Karyo (Greek, "nucleus"): Relates to cellular functions.
- Example: Karyotype – Chromosome mapping.
10. FAQs About " Adeno "
Q: What does "adeno" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Adeno" means "gland" and originates from the Greek word "aden." It is used in biology and medicine to describe structures or conditions related to glands, such as adenoids or adenomas. Glands are vital organs responsible for secreting hormones or fluids that regulate various bodily functions.
Q: What are adenoids, and what do they do?
A: Adenoids are lymphatic tissues located in the upper part of the throat behind the nose. They help protect the body from infection by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose or mouth. While prominent in children, adenoids shrink as we age and are less critical to the immune system in adults.
Q: What is the difference between adenoma and adenocarcinoma?
A: An adenoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that forms in glandular tissue, while adenocarcinoma is a malignant (cancerous) tumor originating from the same type of tissue. Adenomas can sometimes develop into adenocarcinomas if not treated or monitored appropriately.
Q: What is adenopathy, and how is it treated?
A: Adenopathy refers to the swelling or disease of glands, particularly lymph nodes. It is often caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or, in some cases, cancer. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medication, or further diagnostic tests to rule out serious conditions.
Q: Are adenoids and tonsils the same thing?
A: No, adenoids and tonsils are different. Both are part of the lymphatic system and help fight infections, but they are located in separate areas. Tonsils are visible at the back of the throat, while adenoids are situated higher up, behind the nasal cavity.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Adeno " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "adeno" mean?
2. What are adenoids?
3. Which term describes a benign tumor in glandular tissue?
4. What is adenopathy?
5. What is adenocarcinoma?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Adeno"
The root "adeno" underscores the significance of glands in maintaining health and vitality. From ancient diagnostics to modern oncology, it bridges our understanding of essential biological functions. As science progresses, "adeno" continues to illuminate the complexities of the human body, inspiring innovations in medicine and care.














