Aer: The Breath of Air in Language and Innovation
Discover the versatility and charm of the root "Aer," derived from Greek, meaning "air." From aviation to atmospheric science, this root has infused life into words and ideas that explore the realm above and beyond. Learn how "Aer" inspires innovation, imagination, and exploration across various fields.
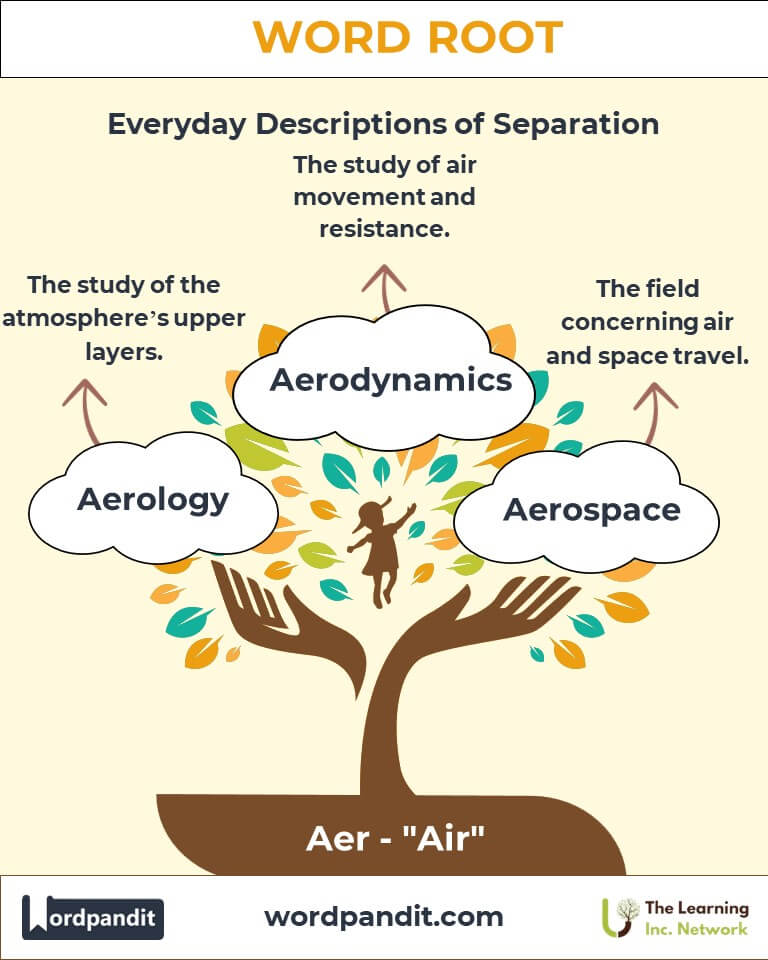
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Aer
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aer
- Common Aer-Related Terms
- Aer Through Time
- Aer in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Aer in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Aer Root
- The Aer Family Tree
- FAQs About the Aer Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Aer Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Aer
1. Introduction: The Essence of Aer
Imagine a world without air—a vital element for life and exploration. The root "Aer" (pronounced air) signifies air and its dynamic, omnipresent nature. Originating from Greek, it permeates words and concepts tied to flight, atmosphere, and innovation. Whether in aerial acrobatics or aeronautics, "Aer" lifts language into the skies, offering boundless possibilities.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Aer" comes from the Greek word aēr, meaning "air" or "atmosphere." Ancient civilizations revered air as a fundamental element, and Greek philosophers such as Aristotle associated it with life and the soul. Over centuries, "Aer" inspired advancements in meteorology, aviation, and even poetic expressions of freedom and flight.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aer
To remember "Aer," imagine a colorful hot air balloon floating gracefully through the sky. Its effortless rise embodies the lightness and movement of air.
Mnemonic Device:
“Aer lifts ideas into the atmosphere of possibilities.”
4. Common Aer-Related Terms
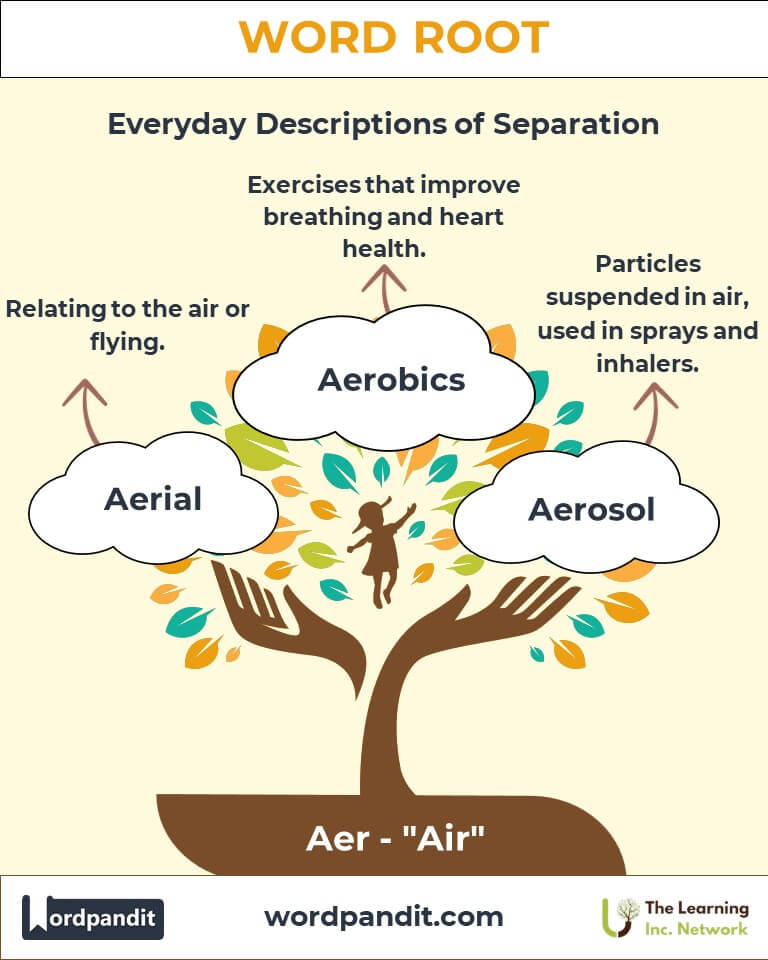
- Aerial (air-ee-uhl): Relating to the air or flying.
Example: The aerial view of the city from the drone was breathtaking. - Aeronautics (air-oh-naw-tiks): The science or art of flying aircraft.
Example: Advances in aeronautics have revolutionized air travel. - Aerobics (air-oh-biks): Exercises that improve cardiovascular efficiency through air breathing.
Example: She attends aerobics classes to stay fit and active. - Aerodynamic (air-oh-dye-nam-ik): Designed to reduce air resistance.
Example: The car’s aerodynamic shape improves fuel efficiency. - Aerospace (air-oh-space): The industry concerned with air and space travel.
Example: Aerospace engineers are developing next-generation rockets.
5. Aer Through Time
The root "Aer" has evolved, reflecting humanity's expanding understanding of air and flight:
- Ancient Times: Philosophical discussions linked "Aer" to life and the heavens.
- Renaissance: The study of flight began with pioneers like Leonardo da Vinci exploring the concept of aerial machines.
- Modern Era: "Aer" forms the basis of technological breakthroughs in aviation and space exploration.
6. Aer in Specialized Fields
The root "Aer" also plays a vital role in various specialized fields:
- Meteorology: The study of the atmosphere, including aerology, which focuses on upper atmospheric layers.
Example: Aerological data helps predict weather patterns. - Medicine: The development of aerosols for treatments like inhalers.
Example: Asthma patients rely on aerosol inhalers for relief. - Engineering: Advancements in aerodynamics to design efficient vehicles and aircraft.
Example: Engineers optimized the jet’s aerodynamics for speed. - Sports and Fitness: Aerobic exercises that enhance lung capacity and heart health.
Example: Aerobics sessions are a fun way to exercise in groups.
7. Illustrative Story: Aer in Action
Sophie, an aeronautical engineer, had always dreamed of flying. She designed drones capable of reaching high altitudes to collect aerological data. During a storm, one of her drones helped predict its path, saving lives. Sophie’s journey demonstrated how "Aer" symbolizes not just air but also innovation and resilience.
8. Cultural Significance of the Aer Root
The root "Aer" connects to humanity's fascination with flight and freedom. From Icarus’s mythical wings to modern-day drones and planes, "Aer" reflects our desire to explore the skies. Its presence in poetry, art, and music captures our yearning to soar above the ordinary.

9. The Aer Family Tree
Explore related roots and their connections to "Aer":
- Vent (Latin: "wind")
- Ventilation: Circulation of fresh air.
Example: Good ventilation is essential for healthy indoor spaces.
- Ventilation: Circulation of fresh air.
- Pneuma (Greek: "breath, spirit")
- Pneumatic: Powered by air pressure.
Example: Pneumatic tools simplify construction tasks.
- Pneumatic: Powered by air pressure.
- Spir (Latin: "breathe")
- Respiration: The act of breathing.
Example: Proper respiration is key during physical activities.
- Respiration: The act of breathing.
10. FAQs About the Ac and Acr Word Roots
Q: What do "ac" and "acr" mean?
A: "Ac" and "acr" are derived from the Latin root "acer," which means sharp, bitter, or pointed. These roots are used to describe intensity or sharpness, whether in physical sensations, smells, tastes, or intellectual qualities. For instance, "acrid" refers to a sharp or bitter smell, while "acumen" describes sharpness of intellect.
Q: What is the origin of "acrimonious"?
A: The word "acrimonious" comes from the Latin term "acrimonia," which refers to sharpness or severity. It entered English to describe bitterness in speech or behavior. Acrimonious exchanges often convey hostility or sharp criticism, commonly seen in heated debates or arguments.
Q: How is "acute" used in medicine?
A: In medical terminology, "acute" describes conditions or diseases that arise suddenly and with significant intensity or severity. For example, "acute appendicitis" refers to a rapid onset of severe symptoms requiring immediate attention. It contrasts with "chronic," which refers to long-lasting conditions.
Q: Are "acrid" and "acerbic" synonyms?
A: While both words share the root meaning sharp or bitter, they differ in usage: "Acrid" typically refers to unpleasant smells or tastes, like the acrid odor of smoke. "Acerbic" describes sharpness or harshness in tone or behavior, such as acerbic remarks in a conversation.
Q: What does "acumen" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Acumen" refers to sharpness of insight, judgment, or understanding. It’s commonly used in professional contexts to praise someone's ability to make quick, effective decisions. For example, "Her financial acumen helped the company navigate a challenging market."
Q: What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
A: Acute describes something intense or severe that occurs suddenly, like an acute illness or acute pain. Chronic refers to conditions that develop over time and persist for a long duration, such as chronic back pain.
Q: How does "acrimonious" relate to interpersonal dynamics?
A: "Acrimonious" describes bitterness or hostility in interactions. Acrimonious disputes often arise in legal battles, political debates, or personal conflicts, characterized by sharp criticism and harsh tones.
Q: Can "acerbic" be positive?
A: While "acerbic" typically has a negative connotation, describing harsh or biting remarks, it can be positive in specific contexts. For example, an acerbic wit might be appreciated for its sharp humor or cleverness, especially in satire.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Ac and Acr Mastery Quiz
1. What does "acute" mean?
2. Which word describes a sharp smell?
3. What is "acrimony"?
4. What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
5. Which word best describes sharpness in tone?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Aer
The root "Aer" breathes life into our language, embodying innovation and exploration. From ancient philosophies to cutting-edge technologies, it inspires humanity to reach new heights. As we continue to innovate, "Aer" remains a timeless reminder of the boundless possibilities in the air and beyond.














