Biosis, Biont, and Biotic: The Roots of Life and Vitality in Language
Byline: Explore the vibrant roots "Biosis," "Biont," and "Biotic," derived from the Greek bios, meaning "life." These roots shape our understanding of living systems, from biological terms like symbiosis to philosophical musings on the essence of life itself.
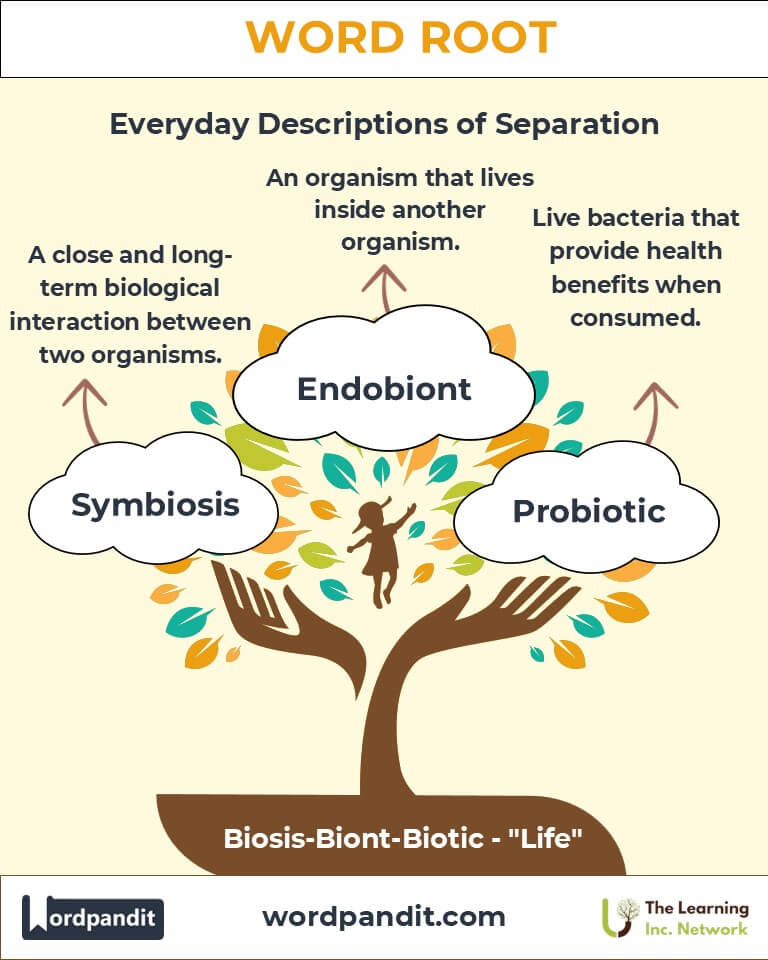
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Life Roots
- Common Terms Derived from Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
- The Roots Through Time
- Applications in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Life in Action
- Cultural Significance of Life Roots
- The Family Tree of Biosis and Related Roots
- FAQs about Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
- Test Your Knowledge: Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Biosis
1. Introduction: The Essence of Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
What ties the science of biology to the wonders of life on Earth? The roots "Biosis" (modes of living), "Biont" (a living being), and "Biotic" (related to life), derived from bios (life), highlight this connection. These roots emphasize the widespread relevance of life, from ecological interactions to healthcare innovations.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The roots trace their origins to ancient Greek:
- Biosis (βίωσις): Denotes life’s way or mode.
- Biont (βίων): Refers to a living entity.
- Biotic (βιωτικός): Pertaining to life.
Their influence spans scientific terminology, philosophical debates on existence, and ecological studies, shaping how we understand life’s processes and dynamics.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Life Roots
Visualize a thriving forest where life flourishes in balance. This imagery reflects "Biosis" as modes of living, "Biont" as living beings, and "Biotic" as the essence of life.
Mnemonic Device: “Biosis binds modes of life, Biont breathes life, and Biotic thrives in life’s essence.”
4. Common Terms Derived from Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
- Symbiosis: A mutualistic relationship between species.
Example: "The symbiosis between bees and flowers benefits both species." - Abiotic: Non-living environmental factors.
Example: "Sunlight and water are abiotic factors essential for plant growth." - Microbiont: A microorganism in an ecosystem.
Example: "Microbionts play a crucial role in nutrient cycling." - Probiotic: Living microbes beneficial for health.
Example: "Probiotics support a healthy gut microbiome."
5. The Roots Through Time
Key terms reflect historical shifts in understanding life:
- Symbiosis: Introduced in ecological studies to describe interspecies relationships.
- Biotic Factors: A foundational concept in environmental science, distinguishing living components from abiotic influences.
6. Applications in Specialized Fields
- Ecology: Exploring abiotic and biotic factors in ecosystems.
- Medicine: Studying probiotics to enhance gut health and immunity.
- Philosophy: Examining biosis in existential debates on life and being.
7. Illustrative Story: Life in Action
In a thriving rainforest, a tiny microbiont (fungus) lived symbiotically with tree roots. Despite harsh abiotic stresses like drought, their biotic connection enabled mutual survival. This tale highlights the delicate interplay of biosis and life’s resilience.
8. Cultural Significance of Life Roots
The roots "Biosis," "Biont," and "Biotic" reflect humanity’s enduring curiosity about life. From Greek metaphysical explorations of bios to modern environmental ethics, these roots emphasize life’s complexity and interconnectivity.

9. The Family Tree of Biosis and Related Roots
- Bio (Life): Biology, biography.
- Vita (Life, Latin): Vitality, vitamin.
- Anim (Soul, Life): Animate, animal.
10. FAQs About Biosis, Biont, and Biotic
Q: What does "biosis" mean?
A: Biosis refers to modes or ways of living. It captures how organisms interact with their environments and sustain life, whether through symbiosis, parasitism, or other relationships.
Q: What is the difference between biotic and abiotic?
A: Biotic pertains to living organisms in an ecosystem, like plants, animals, and microbes. Abiotic refers to non-living elements like sunlight, water, and temperature that influence life. Together, they shape ecosystems.
Q: How is "biont" used in scientific contexts?
A: Biont denotes a living entity, particularly in ecology or microbiology. For example, in studies of lichens, the algal and fungal components are termed microbionts due to their symbiotic relationship.
Q: What does "biotic factor" mean in ecology?
A: A biotic factor is any living component in an ecosystem that affects other organisms. Examples include predators, prey, and decomposers. They influence growth, reproduction, and survival.
Q: Are "biotic" and "biosis" interchangeable?
A: No, "biotic" describes anything related to life, such as biotic factors in ecology. "Biosis" is more specific, describing a mode of living or life-sustaining processes, such as mutualism in symbiosis.
Q: What is the significance of symbiosis in ecosystems?
A: Symbiosis is a form of biosis where organisms interact for mutual, commensal, or parasitic benefit. It is essential for nutrient cycling, ecosystem stability, and evolutionary adaptation.
Q: How do probiotics relate to "biotic"?
A: Probiotics are live microorganisms that positively affect health by improving gut flora. The term derives from "biotic," emphasizing their role as life-sustaining agents in the human body.
Q: What role does abiotic stress play in ecosystems?
A: Abiotic stress, such as drought or extreme temperatures, challenges biotic organisms. Studying abiotic factors helps us understand ecosystem resilience and adaptability.
Q: How do "biotic" and "biosis" appear in philosophical discussions?
A: In philosophy, "biosis" examines the essence of life and existence, while "biotic" can pertain to ethical debates on life forms, conservation, and the interconnectedness of living systems.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Biosis, Biont, and Biotic Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "biosis" mean?
2. Which term is used for non-living environmental factors?
3. What is a biont?
4. Which of the following best describes symbiosis?
5. How do biotic factors differ from abiotic factors?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Biosis
The roots "Biosis," "Biont," and "Biotic" encapsulate the essence of life in language and science. From symbiotic ecosystems to philosophical musings on existence, these roots illuminate life’s complexity and beauty. As we explore and protect life on Earth, these terms remind us of our interconnected world and the vitality of all living systems.












