Dem: The Root of People Power in Words and Society
Discover the dynamic word root "Dem," originating from the Greek word "dēmos," meaning "people." From concepts like democracy to demographic trends, "Dem" forms the foundation of words that shape our understanding of collective governance and human populations.
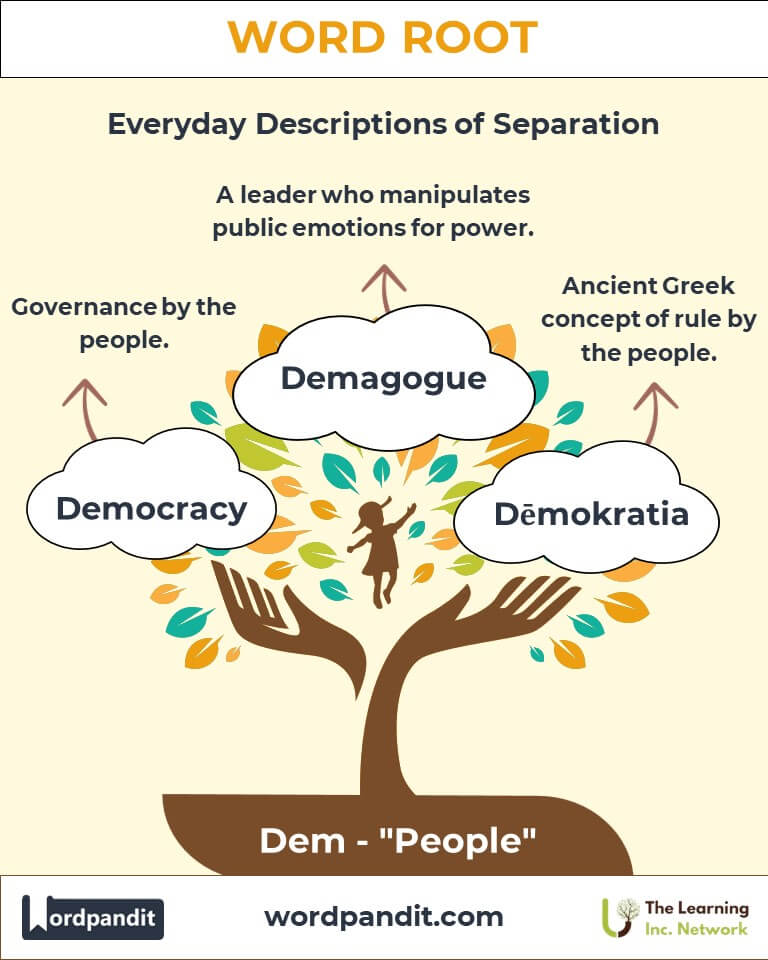
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Dem"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Dem"
- Common "Dem"-Related Terms
- "Dem" Through Time
- "Dem" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Dem" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Dem"
- The "Dem" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Dem" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Dem" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Dem"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Dem"
How do words unite people and communities? The root "Dem," pronounced "dehm", captures this essence. Derived from the Greek word dēmos, meaning "people," it lies at the heart of terms that describe governance, society, and population studies. Whether in democracy, where people rule, or demographic, where populations are studied, "Dem" symbolizes the power and complexity of human collectives.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Dem" originates from the Greek dēmos, which referred to the citizenry or populace of a city-state. This term gained prominence in Ancient Athens, where democracy—dēmokratia (people’s rule)—emerged as a revolutionary form of governance. Over centuries, "Dem" evolved to shape a vocabulary reflecting societal structures, political ideologies, and the study of human populations.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Dem"
Imagine a bustling city square filled with people united in shared purpose, their collective voice shaping the future. This visual connects "Dem" to its core meaning of "people."
Mnemonic Device:
"Dem is where democracy and demographics thrive among the people."
4. Common "Dem"-Related Terms
- Democracy (duh-mok-ruh-see): Governance by the people.
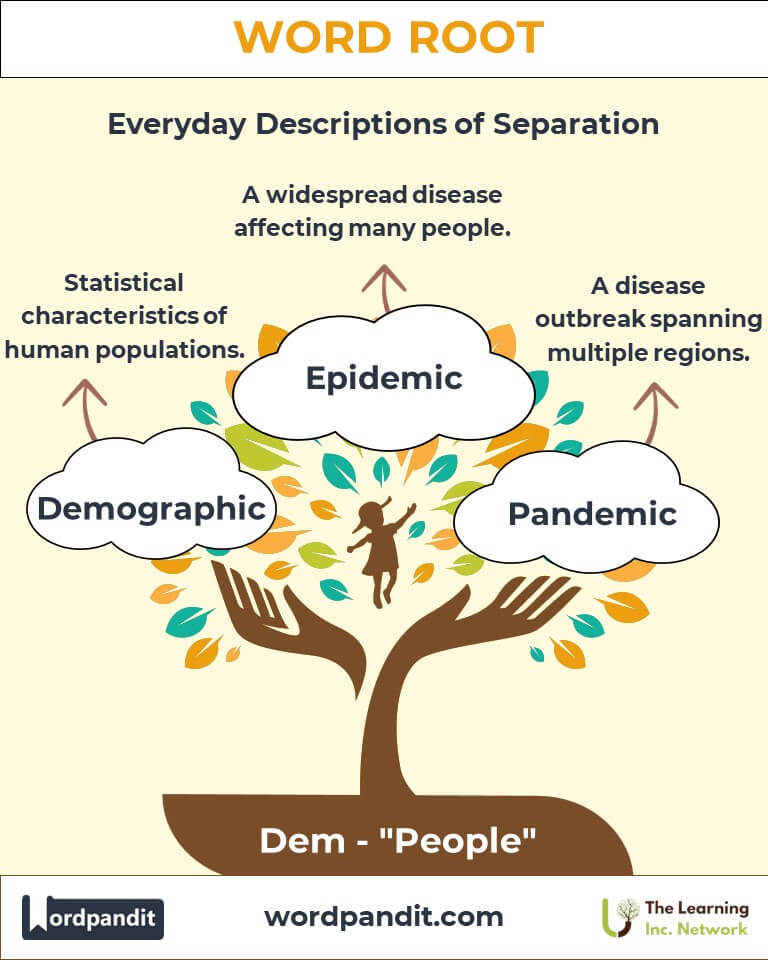
Example: "The citizens celebrated their democracy by voting in large numbers." - Demographic (deh-muh-graf-ik): Statistical characteristics of human populations.
Example: "The demographic report revealed shifts in the city's age distribution." - Epidemic (eh-puh-dem-ik): A widespread outbreak affecting many people.
Example: "The epidemic required immediate public health interventions." - Demagogue (dem-uh-gog): A leader who gains power by exploiting the emotions and prejudices of the people.
Example: "The demagogue’s rhetoric divided the community." - Pandemic (pan-dem-ik): A disease affecting people across a wide geographical area.
Example: "Global cooperation was essential to combat the pandemic."
5. "Dem" Through Time
Ancient Usage:
- Dēmokratia: The concept of democracy, introduced in Ancient Athens, laid the foundation for modern governance.
- Significance: Demonstrated the power of collective decision-making.
Modern Developments:
- Demographics: In the 19th century, "Dem" expanded into population studies, enabling nuanced insights into societal trends.
- Evolution: This shift highlights the root’s adaptability in addressing emerging disciplines.
6. "Dem" in Specialized Fields
Politics:
Democracy: Focuses on systems where people participate directly or through representatives in governance.
Example: Parliamentary democracies balance representation and decision-making.
Medicine:
Epidemic/Pandemic: Terms derived from "Dem" address public health crises impacting large populations.
Example: The pandemic reinforced the importance of global health infrastructure.
Sociology:
Demographic Analysis: Examines population dynamics like age, ethnicity, and income.
Example: Policymakers use demographic studies to plan urban development.
7. Illustrative Story: "Dem" in Action
In the vibrant town of Polistia, citizens eagerly prepared for an upcoming referendum—an exercise in direct democracy. Among them was Sofia, a demographer tasked with analyzing voter trends. While the mayor emphasized collective decision-making, a local demagogue stirred emotions with divisive speeches. Ultimately, the town united to reaffirm their shared commitment to democracy, demonstrating the enduring relevance of "Dem" as a root of unity and progress.
8. Cultural Significance of "Dem"
The root "Dem" underscores humanity’s emphasis on collective governance and community well-being. From Ancient Greek practices to modern democratic ideals, it has shaped cultures worldwide. Additionally, terms like "epidemic" and "pandemic" highlight the interconnectedness of people, emphasizing collective responsibility in addressing global challenges.

9. The "Dem" Family Tree
- Popul (Latin: "people"):
Example: Population, Popularity. - Civ (Latin: "citizen"):
Example: Civilian, Civilization. - Soci (Latin: "companion"):
Example: Society, Social. - Anthrop (Greek: "human"):
Example: Anthropology, Philanthropy.
10. FAQs About the "Dem" Word Root
Q: What does the root "Dem" mean?
A: "Dem" originates from the Greek word dēmos, meaning "people." It forms the basis of words related to society, population, and governance, highlighting the role and power of people in collective systems.
Q: What is democracy?
A: Democracy, derived from dēmokratia (Greek for "rule by the people"), is a system of governance where power rests with the populace. Citizens participate either directly or through elected representatives, embodying the principle of collective decision-making.
Q: What is the meaning of demographics?
A: Demographics involve the statistical study of populations. This includes analyzing characteristics such as age, income, ethnicity, and education to understand societal trends and inform policies, business strategies, or planning.
Q: How are "epidemic" and "pandemic" different?
A: Both words describe the spread of diseases among people. An epidemic refers to a localized outbreak affecting a specific region or community. In contrast, a pandemic describes a disease outbreak that spans countries or continents, impacting a large global population.
Q: What does a demagogue do?
A: A demagogue is a leader who manipulates people's emotions, prejudices, or fears to gain power. Historically, such leaders have used divisive rhetoric to sway public opinion, often prioritizing personal or political agendas over collective well-being.
Q: How is the root "Dem" relevant in modern contexts?
A: "Dem" remains vital in words like democracy, emphasizing governance by the people, and demographics, which analyze societal structures. These terms are crucial in addressing contemporary challenges, such as equitable governance and population management.
Q: What is the historical significance of "Dēmokratia"?
A: Dēmokratia emerged in Ancient Athens as one of the first systems of people-powered governance. It introduced ideas like citizen participation and equality before the law, influencing modern democratic frameworks worldwide.
Q: Why is understanding demographics important?
A: Demographics provide insights into population trends and societal changes. For example, businesses use demographic data to target audiences, while governments rely on it for urban planning, healthcare, and resource allocation.
11. Test Your Knowledge: "Dem" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Dem" signify?
2. Which word means "governance by the people"?
3. What is demographic analysis?
4. What does "pandemic" mean?
5. What term describes a manipulative leader?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Dem"
The root "Dem" continues to shape our understanding of people and society. From governance to health and sociology, it reflects humanity’s collective journey and challenges. As we face an interconnected future, "Dem" reminds us of the strength in unity and the importance of putting people at the heart of progress. Let this powerful root inspire your exploration of words and the stories they tell.














