Epistemo: The Root of Knowledge Across Disciplines
Discover the profound depth of the word root "Epistemo", derived from the Greek word episteme, meaning "knowledge." Explore its influence across philosophy, science, and linguistics, from epistemology to epistemic certainties.
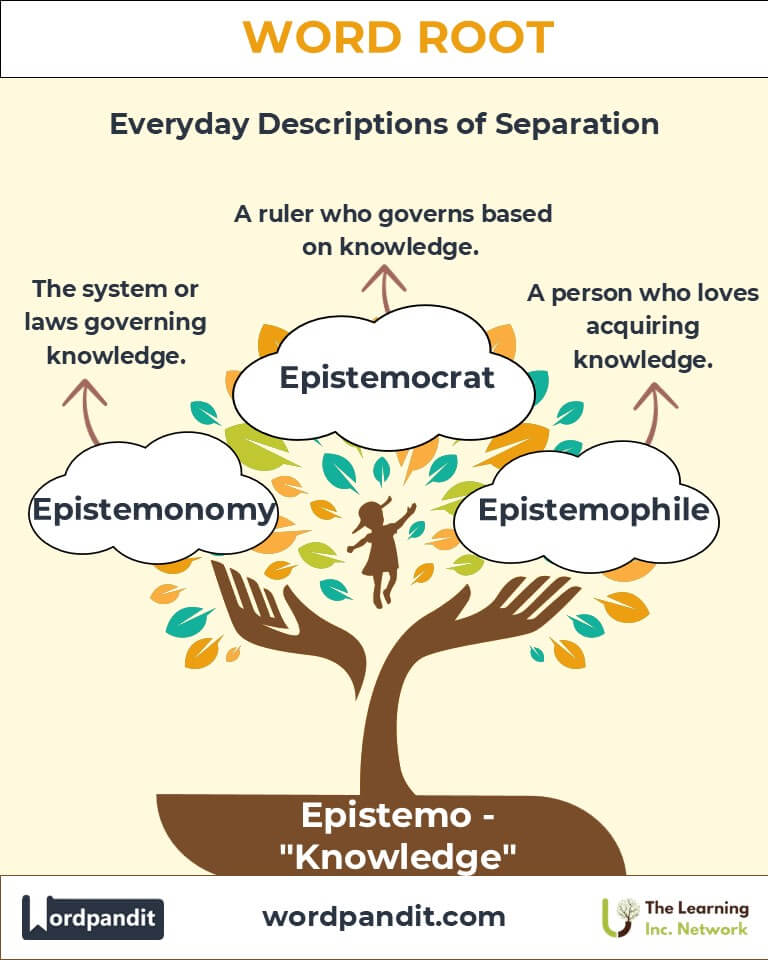
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Epistemo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Epistemo
- Common Epistemo-Related Terms
- Epistemo Through Time
- Epistemo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Epistemo in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Epistemo Root
- The Epistemo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Epistemo Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Epistemo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Epistemo
Introduction: The Essence of Epistemo
Imagine delving into the intricacies of human understanding or dissecting the fabric of what we consider "true." The root Epistemo—pronounced "eh-pis-teh-moh"—captures this pursuit of knowledge. Derived from the Greek word episteme (knowledge or understanding), it serves as a cornerstone for terms central to philosophy and science. Whether in epistemology (the study of knowledge) or epistemic (relating to knowledge), Epistemo reminds us of the endless quest to know and understand.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root Epistemo originates from the Greek episteme, meaning "knowledge," formed by combining epi- (upon, over) and histanai (to place or stand). In ancient Greek philosophy, episteme contrasted with doxa (opinion), emphasizing reasoned and justified understanding. The root gained prominence during the Enlightenment as thinkers like René Descartes and Immanuel Kant explored the nature of human knowledge, embedding Epistemo in the lexicon of philosophy and science.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Epistemo
Visualize a shining library labeled "Epistemo," with its shelves filled with books of ancient wisdom and modern discovery. This library symbolizes the treasure of knowledge, standing as a beacon for seekers of truth.
Mnemonic Device: “Epistemo is the vault of knowledge—unlock it, and truths abound.”
Common Epistemo-Related Terms
- Epistemology (eh-pis-teh-mol-uh-jee): The branch of philosophy concerned with the theory of knowledge.
Example: "Epistemology examines the nature, sources, and limits of human understanding." - Epistemic (eh-pis-teh-mik): Relating to knowledge or its validation.
Example: "The scientist discussed the epistemic implications of her findings." - Epistemicide (eh-pis-teh-mi-side): The destruction of knowledge systems or ways of knowing.
Example: "Colonialism often involved epistemicide, erasing indigenous knowledge." - Episteme (eh-pis-teh-mee): A foundational body of knowledge within a specific era or culture.
Example: "Foucault analyzed the shifting epistemes of history in his works." - Epistemophobia (eh-pis-teh-mo-foh-bee-uh): Fear of acquiring knowledge or learning.
Example: "Some critics labeled his rejection of new theories as epistemophobia."
Epistemo Through Time
- Ancient Greece: Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle emphasized episteme as rational, systematic knowledge.
- Enlightenment Era: The term evolved to address epistemic certainty in scientific and philosophical discourse.
- Modern Usage: Epistemo informs debates in artificial intelligence, cognitive science, and post-colonial studies.
Epistemo in Specialized Fields
- Philosophy: Examines what constitutes justified belief and knowledge.
- Science: Refers to scientific methods and the reliability of knowledge claims.
- Linguistics: Focuses on epistemic modality, indicating certainty in statements.
- Sociology: Explores the systemic erasure of knowledge systems (epistemicide).
- Technology: Applies epistemic logic in AI to model reasoning and belief systems.
Illustrative Story: Epistemo in Action
Amara, a philosophy professor, challenged her students with a thought experiment: "How do you know what you know?" Intrigued, the class debated epistemology, tracing its principles to AI's ability to "learn." By the semester's end, they had not only unraveled the mysteries of human knowledge but also designed an epistemic model to help computers reason like humans, blending ancient wisdom with cutting-edge technology.
Cultural Significance of the Epistemo Root
The Epistemo root has deep cultural resonance, influencing philosophy, education, and societal structures. From debates on what defines "truth" to the preservation of indigenous epistemologies, it underscores the power dynamics inherent in knowledge systems. In literature and art, Epistemo themes often explore the tension between ignorance and enlightenment.

The Epistemo Family Tree
- Logos (Greek): "Word, reason" — Example: Epistemology
- Sophia (Greek): "Wisdom" — Example: Philosophy
- Gnosis (Greek): "Knowledge" — Example: Diagnosis
- Epi- (Greek): "Upon, over" — Example: Episteme
FAQs About the Epistemo Root
Q: What does "Epistemo" mean?
A: "Epistemo" is a Greek root meaning "knowledge" or "understanding." It comes from episteme, which emphasizes rational, justified knowledge. Unlike casual or intuitive beliefs, it refers to structured and systematic understanding, often explored in philosophy and science.
Q: What is epistemology?
A: Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that studies the nature, origin, and limits of knowledge. It asks questions like "What can we know?" and "How do we justify our beliefs?" For instance, epistemology helps differentiate between knowledge gained through observation versus inference.
Q: How is "Epistemic" used in everyday language?
A: The term "epistemic" relates to knowledge or the validation of beliefs. For example, in debates, someone might say, "That’s an epistemic claim," meaning the argument concerns what we can know or prove. In daily conversations, it might appear in discussions about certainty, such as "epistemic uncertainty," which describes doubts about what is known.
Q: What is epistemicide?
A: Epistemicide refers to the destruction or suppression of knowledge systems, often linked to colonialism or cultural dominance. For instance, during colonization, many indigenous ways of knowing, such as oral histories and herbal medicine practices, were erased or devalued, constituting epistemicide.
Q: What are epistemic modals in language?
A: Epistemic modals are words or expressions that indicate the speaker's level of certainty about a statement. For example, "might," "must," and "could" show varying degrees of confidence. Saying, "She might come to the party," conveys less certainty than, "She must come to the party."
Q: How does epistemology relate to AI?
A: Epistemology guides AI development by defining how machines acquire and validate knowledge. For example, epistemic logic helps AI reason about what it "knows" or "believes" to be true, such as determining whether to rely on certain data inputs for decision-making.
Q: What’s the difference between episteme and doxa?
A: Episteme refers to structured, rational knowledge, while doxa means opinion or belief. In ancient Greek thought, episteme was considered superior, as it stemmed from reason and evidence, whereas doxa was seen as subjective or unreliable.
Q: Can "Epistemo" apply to emotions or intuition?
A: While "Epistemo" primarily concerns rational knowledge, some modern thinkers argue that it can include intuitive understanding. For example, tacit knowledge—such as knowing how to ride a bike—can be seen as a type of epistemic understanding.
Q: What’s an example of epistemic logic?
A: Epistemic logic is a system used to model reasoning about knowledge and beliefs. For instance, in a game theory scenario, epistemic logic helps predict how players will act based on what they know about others' strategies. It’s also applied in AI to simulate reasoning processes.
Test Your Knowledge: Epistemo Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root Epistemo mean?
2. What is epistemology?
3. Which term refers to fear of knowledge?
4. What’s an example of an epistemic modal?
5. What does epistemicide describe?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Epistemo
The root Epistemo bridges ancient wisdom and modern inquiry, shaping our understanding of knowledge across fields. Its relevance spans philosophy, science, and language, inspiring us to question, learn, and grow. As the quest for knowledge evolves, Epistemo continues to illuminate paths to discovery, reminding us that understanding is both a journey and a treasure.














