Liter: The Root of Letters in Language and Literature
Discover the profound influence of the root "liter," meaning "letter," on the evolution of words and their significance in communication, storytelling, and scholarly pursuits. From literal meanings to the richness of literature, this root shapes our understanding of written language and its role in culture.
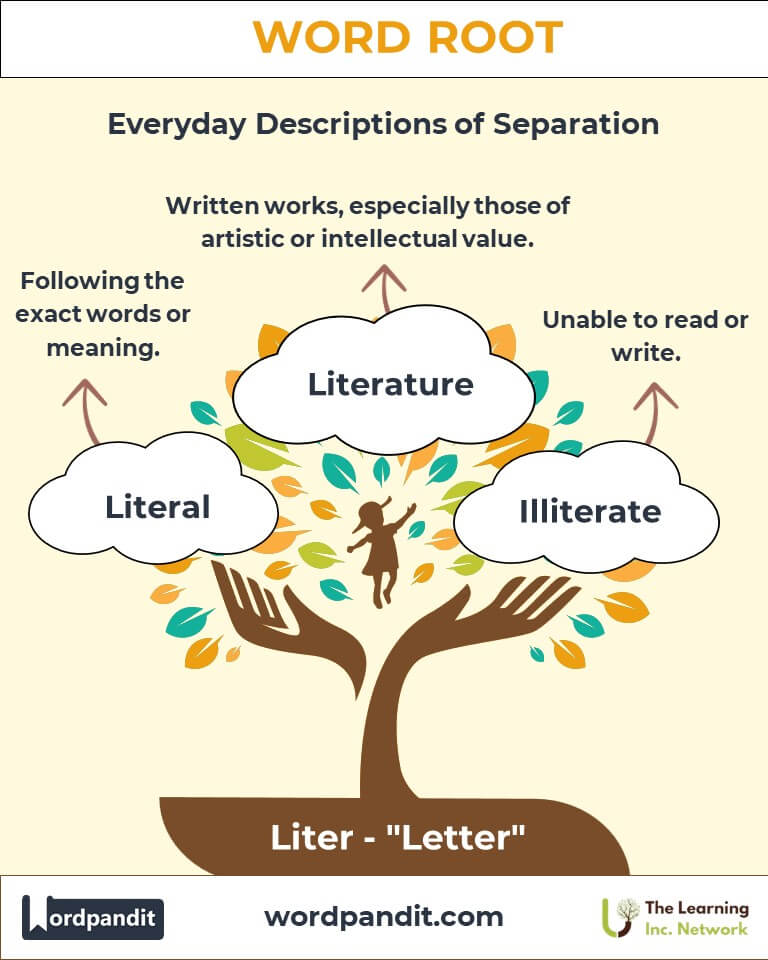
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of the Written Word
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Liter"
- Common "Liter"-Related Terms
- "Liter" Through Time
- "Liter" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Liter" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Liter"
- FAQs About the Liter Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Liter Word Root Quiz
- The "Liter" Family Tree
Introduction: The Power of the Written Word
Have you ever marveled at the power of words? From ancient manuscripts to modern novels, the root "liter," meaning "letter," forms the foundation of our written communication. Derived from the Latin "littera," this root underscores the essence of language, enabling us to document thoughts, preserve knowledge, and express creativity. Whether it’s a literal interpretation or the artistry of literature, "liter" weaves its influence across disciplines and cultures.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "liter" originates from the Latin "littera," meaning "letter" or "character." In ancient Rome, "littera" referred to the individual components of written language. Over centuries, it expanded to encompass the collective art of writing, giving rise to terms like "literature" (written works) and "literal" (adhering to exact words). With the spread of Latin through the Roman Empire and its influence on Romance and English languages, "liter" became integral to words reflecting the significance of written and recorded expression.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Liter"
To remember the root "liter," picture a letter (or "littera") transforming into a beautifully bound book. Imagine its words coming alive, telling stories or conveying truths.
Mnemonic Device: "Liter" leads to letters and literary treasures.
Common "Liter"-Related Terms
- Literal (LIT-er-uhl): Following the exact words or their original meaning.
Example: "The map gives the literal route to the treasure." - Literature (LIT-er-uh-cher): Written works, especially those with artistic or intellectual value.
Example: "Classic literature like Shakespeare's plays enriches our understanding of humanity." - Illiterate (ih-LIT-er-it): Unable to read or write.
Example: "The charity aims to reduce the number of illiterate adults worldwide." - Alliteration (uh-lit-uh-RAY-shun): The repetition of the same initial letter or sound in closely connected words.
Example: "‘Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers’ is an example of alliteration." - Literati (lit-er-AH-tee): Well-educated individuals interested in literature.
Example: "The literati gathered at the annual literary festival to discuss emerging trends in fiction."
"Liter" Through Time
- Literal (Early Use): Initially used to emphasize exactness, "literal" has maintained its precision but is also used metaphorically (e.g., "literally amazing").
- Literature (Evolving Definition): Once limited to written works of high culture, it now embraces diverse genres, from graphic novels to digital storytelling.
"Liter" in Specialized Fields
- Linguistics:
- Alliteration: Used in analyzing patterns of sounds in poetry and prose.
- Application: Explores how sound repetition affects rhythm and mood.
- Education:
- Illiterate: A term central to literacy campaigns and initiatives.
- Application: Combating illiteracy is key to global educational goals.
- Cultural Studies:
- Literature: Examines how written works reflect societal values and histories.
- Example: Literature from the Renaissance reveals cultural shifts toward individualism.
Illustrative Story: "Liter" in Action
In a quiet village, a teacher named Rosa dedicated her life to helping illiterate adults learn to read and write. One day, her student, Emilio, who had never written more than his name, composed a heartfelt letter to his daughter. Tears of joy welled up in Rosa’s eyes as she realized the transformative power of literacy. From that moment, Emilio became a voracious reader, eventually sharing his favorite literature with his granddaughter, ensuring the gift of "liter" continued to inspire future generations.
Cultural Significance of "Liter"
The root "liter" is a cornerstone of cultural identity. Literature, from sacred texts to modern novels, preserves and disseminates the essence of civilizations. Illiteracy, conversely, highlights inequalities in access to education and opportunity. Across history, movements to promote literacy have empowered individuals, fueling intellectual and creative growth worldwide.

The "Liter" Family Tree
- Litera- (Latin):
- Literal: Exact meaning.
- Literature: Artistic written works.
- Graph- (Greek, "write"):
- Autograph: A person’s handwritten signature.
- Typography: The art of arranging text in print.
- Log- (Greek, "word"):
- Logic: Reasoning conducted according to strict principles.
- Dialogue: A conversation or exchange of ideas.
FAQs About the "Liter" Word Root
Q: What does "liter" mean?
A: The root "liter" means "letter" or "character," originating from the Latin "littera." It is the basis of many words related to written language and communication.
Q: What is the difference between "literal" and "literature"?
A: "Literal" refers to adhering to the exact meaning of words, while "literature" refers to creative or intellectual written works valued for their artistic merit and cultural significance.
Q: What is alliteration?
A: Alliteration is a literary device involving the repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely connected words, enhancing rhythm and auditory appeal.
Q: How does "illiterate" relate to "liter"?
A: "Illiterate" describes someone who is unable to read or write, highlighting the absence of literacy or connection to letters ("liter").
Q: What are the "literati"?
A: The term "literati" refers to well-educated individuals deeply interested in literature or intellectual pursuits.
Test Your Knowledge: "Liter" Mastery Quiz
1. What does "liter" mean?
2. What is an example of alliteration?
3. Who are the "literati"?
4. What does "illiterate" mean?
5. What does "literal" emphasize?
Conclusion: The Everlasting Legacy of "Liter"
From the precision of "literal" meanings to the artistry of "literature," the root "liter" bridges practicality and imagination. It highlights the fundamental role of written language in preserving knowledge, expressing ideas, and shaping cultures. As literacy rates rise and literature diversifies, the influence of "liter" continues to grow, celebrating the written word's timeless significance.














