Mast: Exploring the Foundation of Breast-Related Terminology
Byline: Delve into the etymological significance and applications of the root "mast," derived from the Greek word mastós, meaning "breast." From medical procedures to anatomical structures, this root forms the basis of terms integral to understanding human biology and health.
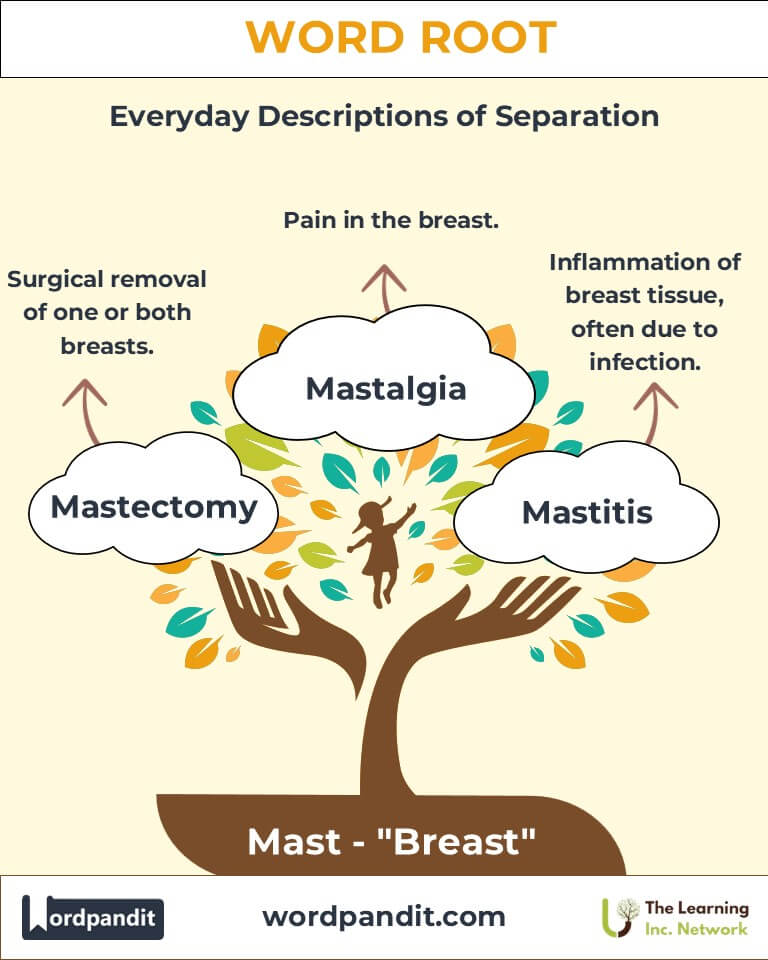
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Mast
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mast
- Common Mast-Related Terms
- Mast Through Time
- Mast in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Mast in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Mast Root
- The Mast Family Tree
- FAQs About the Mast Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Mast Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Kerat
Introduction: The Essence of Mast
The root "mast" (pronounced mast) originates from the Greek mastós, meaning "breast." This foundational term appears prominently in medical and anatomical language, symbolizing the breast's biological and symbolic importance. Words like mastoid and mastectomy draw upon this root, demonstrating its critical role in health sciences and everyday vocabulary.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The Greek root mastós served as the basis for terms related to the breast in ancient anatomy and medicine. With the rise of Latin as the language of science, the root "mast" integrated into medical terminology, influencing words that describe both normal breast anatomy and pathological conditions. Over centuries, "mast" became central to understanding conditions affecting the breast, as well as related surgical interventions.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mast
To remember the root "mast," think of a mast on a ship as a metaphor for support and structure—similar to the breast's role in nurturing life.
Mnemonic Device: "Mast carries life’s structure, just like a ship’s mast supports its journey."
Common Mast-Related Terms
- Mastoid (mas-toid):
- Definition: A bony prominence behind the ear, resembling a breast in shape.
- Example: "The doctor examined the mastoid area for signs of infection."
- Mastectomy (mas-tek-toh-mee):
- Definition: Surgical removal of one or both breasts, typically to treat or prevent cancer.
- Example: "After her diagnosis, she opted for a mastectomy to reduce future risks."
- Mastalgia (mas-tal-jee-uh):
- Definition: Pain in the breast.
- Example: "The patient reported experiencing mastalgia during her menstrual cycle."
- Mastitis (mas-tye-tis):
- Definition: Inflammation of breast tissue, often due to infection.
- Example: "Lactating mothers are at risk for mastitis if milk ducts become blocked."
- Mastopexy (mas-toh-pek-see):
- Definition: Surgical lifting of sagging breasts.
- Example: "The cosmetic surgeon performed a mastopexy to improve breast contour."
Mast Through Time
- Mastitis (Ancient to Modern):
Originally documented in ancient Greek medical texts, mastitis was a common affliction among nursing mothers. Over time, treatments have evolved from herbal remedies to antibiotics.
- Mastectomy (19th Century to Present):
Historically a last resort, mastectomy has become a highly sophisticated procedure, often accompanied by reconstructive surgery to restore form and function.
Mast in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Mastalgia: Critical in diagnosing conditions like hormonal imbalances or cysts.
Mastoiditis: Infections of the mastoid bone, requiring timely medical intervention.
- Surgery:
Mastectomy and Mastopexy: Central to oncological and cosmetic breast surgery.
- Anthropology:
Mastoid Process: Key in studying human evolution, as the size and shape vary among species.
Illustrative Story: Mast in Action
Dr. Elena, a seasoned oncologist, specialized in breast cancer surgeries. One morning, she encountered a patient, Maria, who was apprehensive about undergoing a mastectomy. Dr. Elena explained how the procedure, combined with reconstructive options, could restore her health and confidence. Post-surgery, Maria felt empowered by her journey, grateful for advancements in mast-related medicine that prioritized both health and self-image.
Cultural Significance of the Mast Root
The breast holds profound cultural and symbolic significance, representing life, nourishment, and femininity. The root "mast" underpins this importance, influencing not only medical vocabulary but also societal perceptions of health and beauty.

The Mast Family Tree
- Mammo- (Breast):
- Mammogram: Imaging technique for breast health.
- Gyn- (Woman):
- Gynecomastia: Enlargement of male breast tissue.
- Lacto- (Milk):
- Lactation: The process of producing milk.

FAQs About the Mast Word Root
Q: What does the root "mast" mean?
A: The root "mast" originates from the Greek word mastós, which means "breast." It forms the foundation for numerous medical and anatomical terms related to the breast, its anatomy, and conditions affecting it.
Q: Is "mastoid" related to the breast?
A: The term "mastoid," while referring to a bony prominence located behind the ear, is named for its resemblance to the shape of a breast. The mastoid process is critical in cranial anatomy and provides attachment points for muscles.
Q: What is a mastectomy, and why is it performed?
A: A mastectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of one or both breasts, usually to treat or prevent breast cancer. It may also be performed in cases of significant risk factors (such as genetic predispositions) or as part of gender-affirming surgery.
Q: What causes mastitis, and who is most affected?
A: Mastitis is an inflammation of breast tissue, often caused by blocked milk ducts or bacterial infections. It most commonly affects lactating women but can occur in non-lactating individuals due to injury or infections.
Q: What is the difference between mastalgia and mastitis?
A:
- Mastalgia: Refers to breast pain, which can be cyclical (linked to hormonal changes) or non-cyclical (caused by injuries, cysts, or other conditions).
- Mastitis: Refers to inflammation of the breast tissue, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and fever.
Q: Are there cosmetic procedures involving the root "mast"?
A: Yes, the term "mast" appears in cosmetic procedures such as mastopexy, which refers to the surgical lifting of sagging breasts. This procedure is often performed for aesthetic purposes or to address physical discomfort.
Q: What role does the mastoid process play in anatomy?
A: The mastoid process is a part of the temporal bone in the skull, located just behind the ear. It provides attachment points for muscles involved in head and neck movement and contains air cells connected to the middle ear, playing a role in hearing and balance.
Q: How has the term "mast" evolved in medical science?
A: Initially rooted in Greek and Latin, "mast" evolved to describe a wide range of conditions, anatomical structures, and procedures associated with the breast. Its use expanded with advancements in medicine to include diagnostics, surgical techniques, and even cosmetic procedures.
Test Your Knowledge: Mast Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "mast" signify?
2. What is mastitis?
3. Which term refers to breast pain?
4. What is the mastoid process?
5. Which procedure lifts sagging breasts?
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Mast
The root "mast" is a cornerstone of anatomical and medical terminology, highlighting the breast's multifaceted roles in health and culture. By understanding its applications and history, we gain insights into the interconnectedness of language, medicine, and humanity’s enduring pursuit of knowledge and care.














