Neg: The Root of Denial and Negotiation Across Language
Discover the profound influence of the root "neg," originating from Latin, meaning "deny." From everyday words like "negative" to complex processes like "negotiate," this root plays a critical role in shaping language and thought.
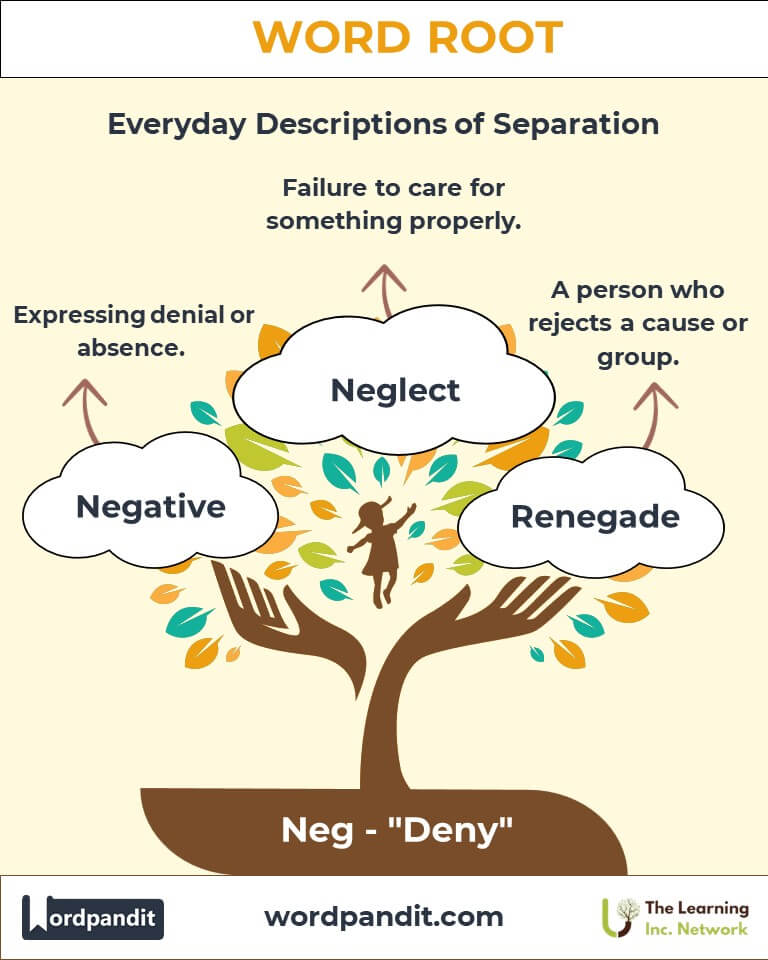
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Neg
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Remembering Neg with Ease
- Common Neg-Related Terms
- Neg Through Time
- Neg in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Neg in Action
- Cultural Significance of Neg
- The Neg Family Tree
- FAQs about the Neg Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Neg Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of Neg
Introduction: The Power of Neg
The root "neg," pronounced "neg," encapsulates the concept of denial and contradiction. Derived from the Latin word negare, meaning "to deny," this root has developed into a cornerstone of numerous words in English. Whether discussing opposites in mathematics or finding common ground in a negotiation, "neg" is integral to expression across various disciplines.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "neg" originates from the Latin negare, which itself stems from nec (not) + aio (I say), literally meaning "I do not say." Over centuries, this root has influenced the formation of words in Romance languages and English. The rise of negotiation during the Renaissance period, driven by trade and diplomacy, cemented "neg" as a critical linguistic element.
Mnemonic: Remembering Neg with Ease
To remember "neg," visualize a stop sign with the words "NEG" boldly printed on it, symbolizing denial or refusal.
Mnemonic Device: “NEG is the sign to say no, block, or oppose.”
Common Neg-Related Terms
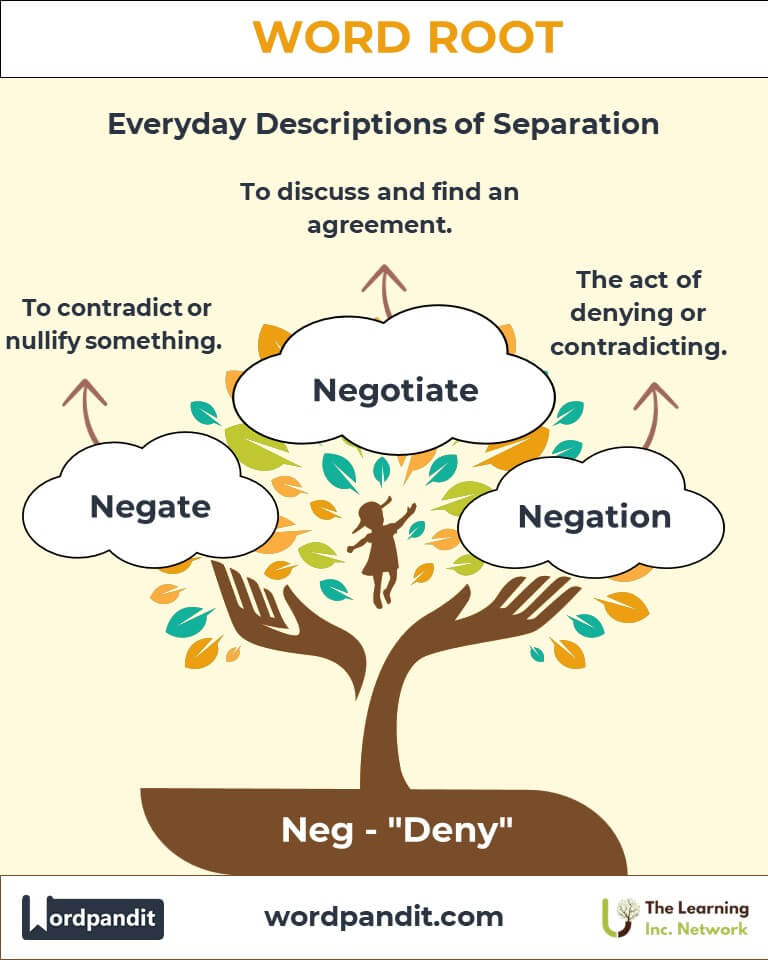
- Negative
Pronunciation: neg-uh-tiv
Definition: Expressing denial or absence.
Example: "Her negative attitude affected the team's morale." - Neglect
Pronunciation: nuh-glekt
Definition: To fail to care for something properly.
Example: "The abandoned house showed signs of neglect." - Negotiate
Pronunciation: nuh-goh-shee-ate
Definition: To discuss and find an agreement.
Example: "The countries negotiated a peace treaty after years of conflict." - Negation
Pronunciation: nuh-gay-shun
Definition: The contradiction or denial of something.
Example: "His argument relied on the negation of false claims." - Renegade
Pronunciation: ren-uh-gade
Definition: A person who rejects a cause or group.
Example: "The renegade soldier joined the opposing side."
Neg Through Time
- Negare (Latin): Originally used to signify refusal or denial in ancient Roman texts.
- Negotiate (15th Century): From Latin negotiatus, meaning to carry on business; evolved into finding resolutions between parties.
- Negative (Modern): The term adapted to mathematics, electronics, and general speech to denote absence or opposition.
Neg in Specialized Fields
- Mathematics: The term "negative" defines values less than zero, critical in equations and functions.
- Business: Negotiation serves as a fundamental process in conflict resolution, deal-making, and contracts.
- Logic: "Negation" is a primary operator used in formal logic to express contradiction or the denial of a statement.
Illustrative Story: Neg in Action
In a bustling city, Mia, a seasoned diplomat, faced a high-stakes negotiation between two rival companies. Despite initial negativity from both sides, she skillfully identified common goals and facilitated a historic agreement. Her mastery of navigating "neg" terms—negotiation, negation of false assumptions, and renegotiation—showed the transformative power of this root in action.
Cultural Significance of Neg
The root "neg" symbolizes a universal aspect of human interaction: the necessity to oppose, refuse, or find common ground. From ancient philosophies debating moral opposites to modern discussions on negative feedback in psychology, "neg" reflects humanity's effort to understand and reconcile contradictions.

The Neg Family Tree
- Nec (Latin: "not"):
- Necessary: From nec + cessarius: not avoidable.
- Nega (Deny):
- Abnegate: To renounce or deny oneself something.
- No/Non (English/Latin: "not"):
- Nonfiction: Not fiction.
FAQs About the "Neg" Word Root
Q: What does the root "neg" mean?
A: The root "neg" means "deny" or "refuse." It originates from the Latin word negare, which translates to "to say no." This concept underpins many English words related to denial, contradiction, or refusal.
Q: What is the historical origin of "neg"?
A: The root "neg" comes from Latin negare (to deny) and nec (not). Over time, it influenced words in various Romance languages and eventually English, maintaining its core meaning of opposition or denial.
Q: Is "negative" always a bad thing?
A: While "negative" often carries a sense of something undesirable, such as negative emotions or outcomes, it is neutral in contexts like mathematics or science. For instance, a negative number is simply a value below zero, and negative feedback in biology helps maintain homeostasis.
Q: How does "negate" differ from "deny"?
A: "Negate" implies formal contradiction or nullification of something, often in logical or philosophical contexts (e.g., "negating an argument"). In contrast, "deny" is a broader term for refusing or rejecting something (e.g., "denying an accusation").
Q: What is the relationship between "neg" and "negotiate"?
A: "Negotiate" stems from the Latin negotiari, meaning "to carry on business." It evolved from the concept of managing opposing interests or resolving refusals, highlighting how negotiation often involves reconciling disagreements or denial.
Test Your Knowledge: "Neg" Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "neg" signify?
2. Which word means "to discuss to reach an agreement"?
3. What is the term for failure to care for something?
4. Which word derived from "neg" means "absence or opposition"?
5. What does "renegade" describe?
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of Neg
The root "neg" provides a lens to explore the complexities of denial and resolution in human language. From its historical roots in Latin to its modern applications in negotiation and logic, "neg" remains a vital tool for understanding contradiction and compromise. By appreciating its depth, we enrich our grasp of language and its power to bridge opposites.














