Olig: The Root of Few in Governance and Economics
Byline:
Discover the intriguing significance of "Olig," a root word derived from Greek, meaning "few." From oligarchy to oligopoly, this root shapes terms that explore the concentration of power and influence across governance and markets, enriching our understanding of societal structures.
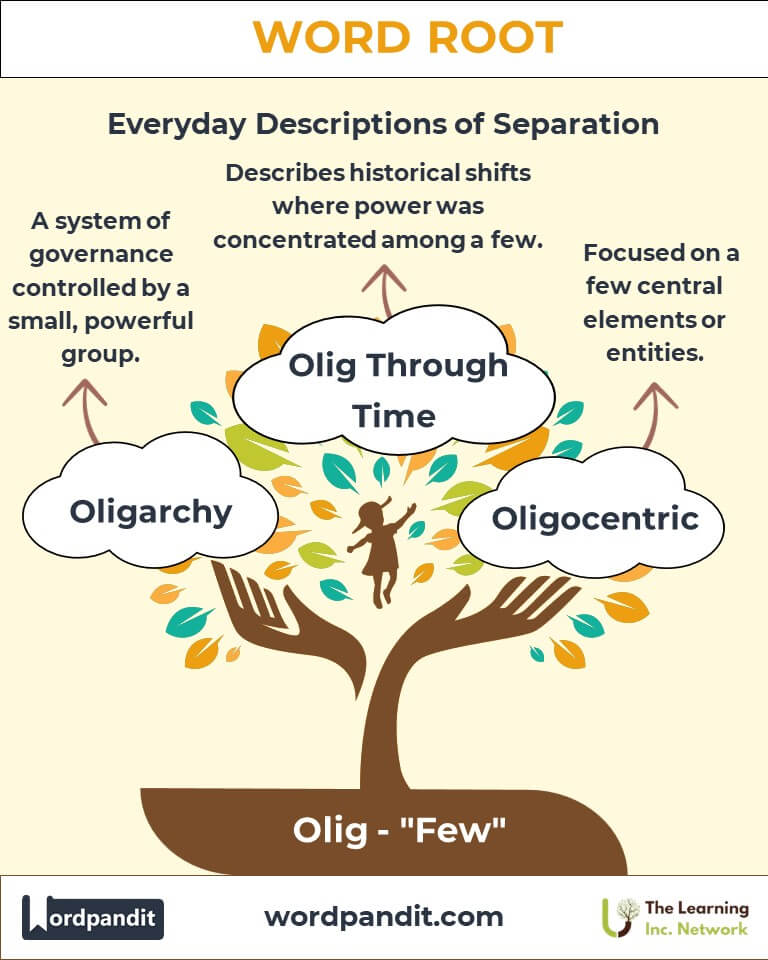
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Olig
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Olig
- Common Olig-Related Terms
- Olig Through Time
- Olig in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Olig in Action
- Cultural Significance of Olig
- The Olig Family Tree
- FAQs about the Olig Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Olig Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Olig
Introduction: The Essence of Olig
What do oligarchies and oligopolies have in common? They both stem from the Greek root "Olig," meaning "few." Pronounced AH-lig, this root underpins words that describe concentrated power or influence—whether among rulers, corporations, or resources. From politics to economics, understanding "Olig" helps us grasp systems where the few hold sway over the many.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Olig" originates from the Greek word oligos, meaning "few" or "small in number." In ancient Greece, oligoi referred to small, elite groups wielding power. The concept evolved to describe political systems like oligarchies, where a few individuals or families dominate governance. Similarly, in economics, oligopoly emerged to characterize markets controlled by a few large firms.
As societies and languages evolved, "Olig" terms gained broader applications, symbolizing limited access, exclusivity, and concentrated power.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Olig
Imagine a boardroom with only a few chairs, each occupied by powerful figures deciding the fate of an entire nation or market.
Mnemonic Device:
"Olig means only a few get a seat at the table."
Common Olig-Related Terms
- Oligarchy
Pronunciation: AH-lig-ar-kee
Definition: A system of governance controlled by a small, powerful group.
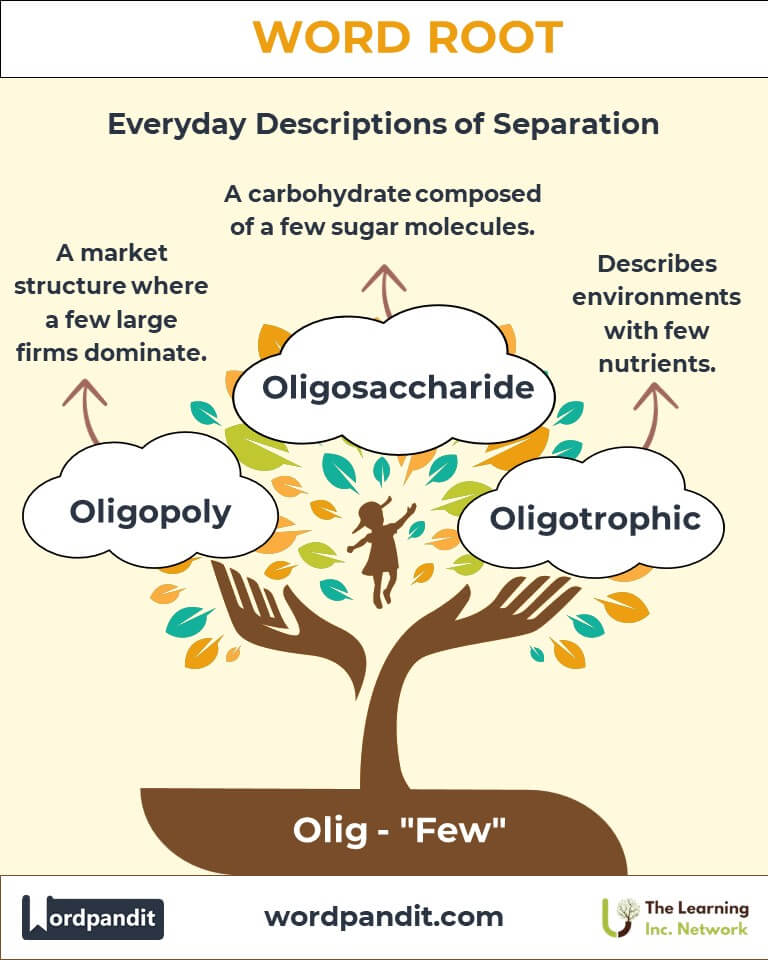
Example: "The country’s oligarchy suppressed public dissent to maintain its grip on power." - Oligopoly
Pronunciation: AH-lig-AH-puh-lee
Definition: A market structure where a few large firms dominate.
Example: "The airline industry is often considered an oligopoly due to limited competition." - Oligotrophic
Pronunciation: AH-lig-oh-TROH-fik
Definition: Referring to environments, particularly lakes, with few nutrients.
Example: "The crystal-clear waters of the oligotrophic lake attracted researchers." - Oligosaccharide
Pronunciation: AH-lig-oh-SAK-uh-ride
Definition: A carbohydrate composed of a few sugar molecules.
Example: "Oligosaccharides play a vital role in gut health." - Oligocentric
Pronunciation: AH-lig-oh-SEN-trik
Definition: Focused on a few central elements or entities.
Example: "The oligocentric strategy prioritized the most profitable markets."
Olig Through Time
- Oligarchy:
Historical context: In ancient Athens and Sparta, oligarchies often supplanted monarchies or democracies during political crises. - Oligopoly:
Modern relevance: Post-Industrial Revolution, industries like telecommunications and oil showcased oligopolistic tendencies as a few firms dominated these sectors.
Olig in Specialized Fields
- Political Science: Oligarchy: Analyzes governance by elites and its impact on democracy and inequality.
- Economics: Oligopoly: Studies market concentration and its effects on pricing, innovation, and consumer choice.
- Environmental Science: Oligotrophic: Focuses on ecosystems with limited nutrients and their unique biodiversity.
- Biochemistry: Oligosaccharides: Explores their function in cell signaling and digestion.
Illustrative Story: Olig in Action
In the bustling city of Metropolia, the power grid was controlled by three energy companies, forming an oligopoly. Despite their competition, they often collaborated to set high prices. Meanwhile, an oligarchy of city elites decided urban policies, prioritizing their interests over public needs. Grassroots movements began advocating for decentralization, striving to dismantle the dominance of the "few" in both governance and the market.
Cultural Significance of Olig
The concept of "Olig" underscores societal debates about equity, representation, and power dynamics. From ancient oligarchies to modern corporate oligopolies, the root reveals how the concentration of control shapes history, policy, and human lives. It also serves as a cautionary tale, reminding societies to balance power among the many rather than the few.

The Olig Family Tree
- Mono (one):
- Monopoly: A single entity controls an entire market.
- Monarchy: A single ruler governs.
- Poly (many):
- Polygamy: Marriage involving multiple partners.
- Polytheism: Belief in multiple gods.
- Arch (rule):
- Anarchy: Absence of governance.
- Patriarchy: Governance by male leaders.
FAQs About the "Olig" Word Root
Q: What does "Olig" mean?
A: "Olig" is a Greek root meaning "few" or "small in number." It appears in terms like oligarchy and oligopoly, describing concentrated power or influence in governance and markets.
Q: What is the difference between oligarchy and oligopoly?
A: Oligarchy refers to a political system where power is held by a small group, often leading to limited representation. Oligopoly describes a market dominated by a few large firms, reducing competition.
Q: What industries often exhibit oligopolistic characteristics?
A: Industries like airlines, telecommunications, oil, and technology often exhibit oligopolistic characteristics, with a few dominant firms influencing pricing, innovation, and consumer choices.
Q: What is an oligotrophic lake?
A: An oligotrophic lake has low nutrient levels, leading to clear water with limited algae growth. These lakes often support unique ecosystems adapted to nutrient-poor conditions.
Q: What is an oligosaccharide?
A: Oligosaccharides are carbohydrates composed of a few sugar molecules. They are found in foods like legumes and onions and play a crucial role in digestion by promoting healthy gut bacteria.
Test Your Knowledge: "Olig" Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Olig" signify?
2. Which system concentrates political power in a small group?
3. What does "oligotrophic" describe?
4. Which industry commonly exemplifies oligopoly?
5. What does "oligosaccharide" describe?
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Olig
The root "Olig" offers profound insights into the dynamics of concentration—whether of power, wealth, or resources. From ancient political systems to modern economic structures, it highlights the challenges of equity and representation in systems dominated by the few. Understanding "Olig" empowers us to recognize and address imbalances, fostering fairer and more inclusive societies.














