Onto: The Essence of Being in Language and Philosophy
Discover the profound significance of the word root "onto," derived from the Greek ontos meaning "being." From its foundational use in the word ontology to its application in developmental biology with ontogenesis, this root unveils concepts central to existence, knowledge, and growth.
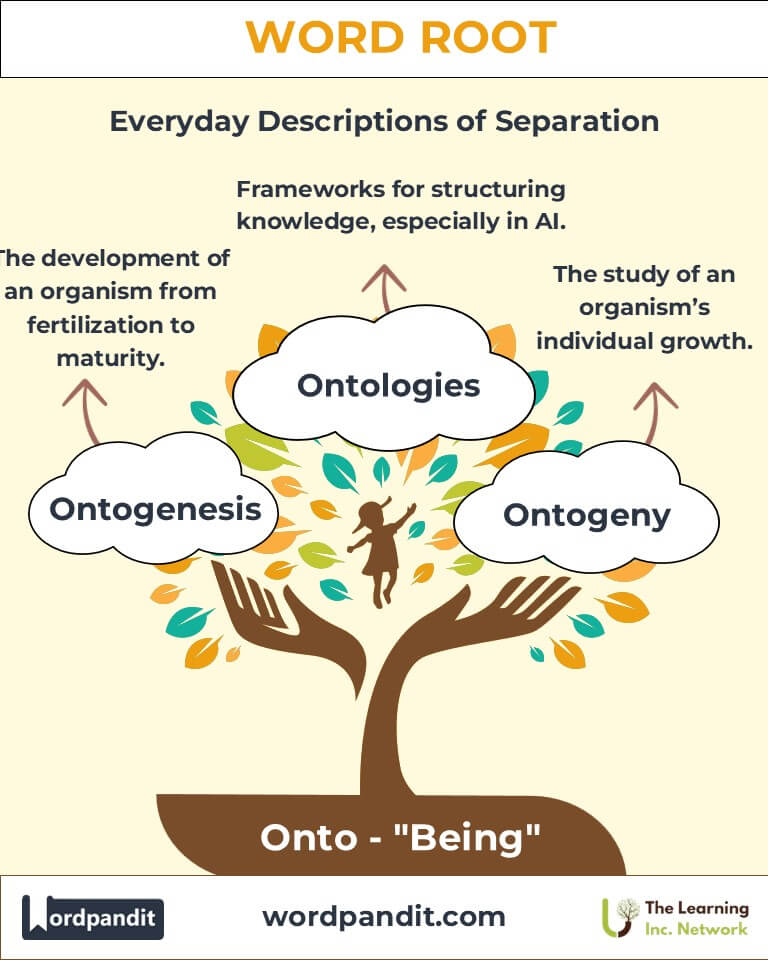
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Core of Onto
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Onto
- Common Onto-Related Terms
- Onto Through Time
- Onto in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Onto in Action
- Cultural Significance of Onto
- The Onto Family Tree
- FAQs About the Onto Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge:Onto Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Onto
Introduction: The Core of Onto
The root "onto" (pronounced on-toh) delves into questions of existence, being, and essence. It forms the basis of words that explore fundamental aspects of reality and life's processes, from philosophical discourse in ontology to biological phenomena in ontogenesis. This root connects fields as diverse as metaphysics and embryology, making it a cornerstone of intellectual inquiry.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "onto" stems from the Greek ontos, meaning "being" or "existence." First appearing in philosophical texts of Ancient Greece, it became integral to the metaphysical discussions of thinkers like Aristotle, who explored the nature of being. The root gained prominence during the Enlightenment with the emergence of ontology as a branch of philosophy. In the 19th and 20th centuries, it entered scientific domains like biology, where ontogenesis was coined to describe the development of an organism.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Onto
To remember "onto," imagine a tree growing from a seed, symbolizing the journey from potential to being.
Mnemonic Device:
"Onto is the root of being, from philosophy's questions to biology's beginnings."
Common Onto-Related Terms
- Ontology (on-tol-uh-jee):
Definition: The philosophical study of being and existence.
Example: "Ontology seeks to understand the nature of reality and existence." - Ontogenesis (on-toh-jen-uh-sis):
Definition: The biological process of an organism’s development from fertilization to maturity.
Example: "Ontogenesis traces the growth of an embryo into a fully formed individual." - Ontological (on-tuh-loj-i-kuhl):
Definition: Relating to the study of being.
Example: "The philosopher presented an ontological argument for the existence of God." - Ontogeny (on-toj-uh-nee):
Definition: The development and growth of an individual organism.
Example: "The scientist studied ontogeny to understand evolutionary patterns." - Ontic (on-tik):
Definition: Pertaining to the nature of being as it exists in reality.
Example: "The discussion shifted from ontological theories to ontic realities."
Onto Through Time
- Ontology in Ancient Greece: Coined by early philosophers like Parmenides and Aristotle, who debated the essence of being.
- Modern Ontology: Expanded by philosophers like Martin Heidegger, focusing on existential questions.
- Ontogenesis in Biology: Introduced in the 19th century, it revolutionized the understanding of life’s developmental stages.
Onto in Specialized Fields
- Philosophy:
Ontology: Explores foundational questions about reality and existence.
Example: "What does it mean to exist?" - Biology:
Ontogenesis: Studies developmental processes from a single cell to complex organisms.
Example: "Ontogenesis reveals how genetic codes shape life forms." - Artificial Intelligence:
Ontologies: Frameworks to represent knowledge structures.
Example: "Ontologies are essential for machine learning and semantic web development." - Psychology:
Ontological Insecurity: Describes a state of existential uncertainty.
Example: "The patient’s ontological insecurity stemmed from a crisis of identity."
Illustrative Story: Onto in Action
Dr. Elaine Thomas, a developmental biologist, examined the ontogenesis of a rare amphibian species. Using advanced imaging, she traced its growth from a single-cell zygote to a fully developed adult. Meanwhile, her philosopher friend, Daniel, grappled with an ontological debate on the nature of identity. In a lively discussion, they realized their work shared a common thread: the root "onto" tied their pursuits of understanding life’s essence, from cells to souls.
Cultural Significance of Onto
The root "onto" resonates across cultures, reflecting humanity’s enduring quest to understand existence. Whether in ancient Greek metaphysics or contemporary debates in AI ethics, "onto" symbolizes a bridge between abstract thought and tangible reality. It informs religious, philosophical, and scientific narratives, uniting diverse fields under a shared inquiry into being.

The Onto Family Tree
- Bio- (Life):
Example: Biogenesis – The origin of life. - Logy- (Study):
Example: Anthropology – The study of humans. - Gen- (Origin):
Example: Genetics – The study of heredity.
FAQs About the Onto Word Root
Q: What does "onto" mean?
A: "Onto" means "being" or "existence," derived from the Greek word ontos. It is a foundational root in philosophy and science, helping us explore what it means to exist or grow.
Q: What is ontology?
A: Ontology is the branch of philosophy that studies the nature of being, existence, and reality. Philosophers use ontology to address fundamental questions such as "What exists?" and "What does it mean to be?"
Q: How does ontology differ from ontogenesis?
A: Ontology focuses on the philosophical aspects of existence, while ontogenesis is a biological term describing an organism's development from a single cell to maturity.
Q: What is an ontological argument?
A: An ontological argument is a reasoning used in philosophy, particularly in theology, to prove the existence of God. It asserts that the very concept of a perfect being implies its existence.
Q: How is "onto" used in artificial intelligence (AI)?
A: In AI, ontologies are structured frameworks that represent knowledge about a domain. They help machines understand and process information in a meaningful way, such as in semantic search and natural language processing.
Q: What is ontogeny, and why is it important?
A: Ontogeny refers to the entire process of an organism’s growth and development from fertilization to adulthood. It is crucial in biology because it reveals how genetic and environmental factors interact during development.
Q: Why is the root "onto" significant in science?
A: In science, "onto" is pivotal because it bridges the study of individual development (ontogenesis) with broader evolutionary patterns, helping scientists understand how life forms adapt and grow.
Test Your Knowledge: Onto Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "onto" mean?
2. What field studies ontogenesis?
3. Which term describes the study of being?
4. Ontological arguments are part of:
5. Ontologies in AI are:
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Onto
The root "onto" anchors our understanding of being and existence. From metaphysical debates to the marvels of embryonic development, it offers insights into the essence of life and reality. As we advance in philosophy, science, and technology, "onto" will continue to shape our exploration of what it means to exist. Embrace this root as a gateway to profound knowledge across disciplines.














