Oophor: The Vital Root of Female Reproductive Health
Discover the significance of the root "oophor," derived from the Greek words "oion" (egg) and "phoros" (bearing). This root serves as a foundation for medical terms that highlight the importance of ovaries in reproductive health and beyond. From conditions like oophoritis to surgical procedures like oophorectomy, "oophor" captures the essence of ovarian functions.
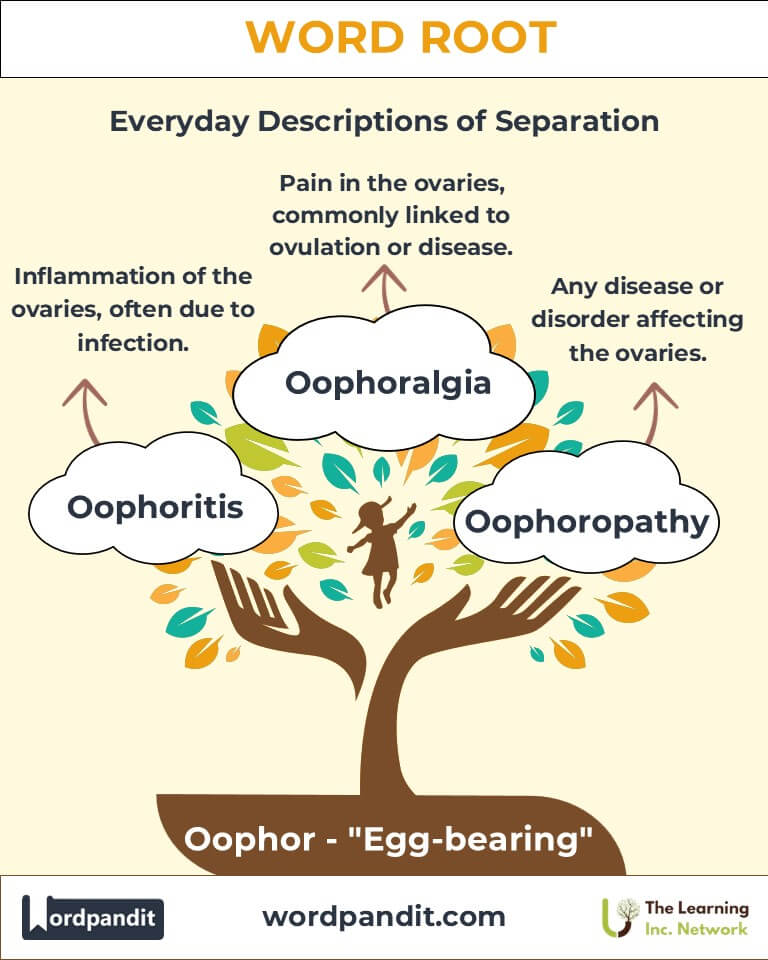
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Role of Oophor in Medicine
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Remembering Oophor
- Common Oophor-Related Terms
- Oophor Through Time
- Oophor in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Oophor in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Oophor Root
- The Oophor Family Tree
- FAQs About the Oophor Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Oophor Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Oophor
Introduction: The Role of Oophor in Medicine
Imagine the remarkable complexity of the human reproductive system, orchestrating the creation of life. At the heart of this system lies the ovary, responsible for producing eggs essential for reproduction. The root "oophor" (pronounced OH-uh-for) encapsulates this vital role, appearing in terms central to gynecology and reproductive medicine. Understanding "oophor" provides insight into how language captures the intricacies of biology and medicine.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "oophor" originates from Greek, combining "oion" (egg) and "phoros" (bearing or carrying). Historically, knowledge of the ovary’s function developed alongside advancements in medicine. Ancient Greek physicians recognized the ovary as central to fertility, and their terminology evolved to reflect its importance. With the rise of modern medical science, "oophor" became a cornerstone in clinical language.
Mnemonic: Remembering Oophor
Picture an egg being gently carried in a nest, symbolizing the ovary’s nurturing role.
Mnemonic Device:
"Oophor carries eggs, safeguarding life’s potential."
Common Oophor-Related Terms
- Oophoritis (OH-uh-for-ITE-is):
Definition: Inflammation of the ovaries, often due to infection.
Example: "The patient was treated with antibiotics for oophoritis, which was causing severe pelvic pain." - Oophorectomy (OH-uh-for-EK-toh-mee):
Definition: Surgical removal of one or both ovaries.
Example: "The surgeon performed an oophorectomy to prevent the spread of ovarian cancer." - Oophoralgia (OH-uh-for-AL-jee-uh):
Definition: Pain in the ovaries, commonly associated with ovulation or underlying conditions.
Example: "The patient reported oophoralgia during her mid-cycle ultrasound." - Oophorocystectomy (OH-uh-for-oh-sis-TEK-toh-mee):
Definition: Surgical removal of a cyst from an ovary.
Example: "The laparoscopic oophorocystectomy successfully removed the benign ovarian cyst." - Oophoropathy (OH-uh-for-OP-uh-thee):
Definition: Any disease or disorder affecting the ovaries.
Example: "Endocrinologists specialize in managing oophoropathy linked to hormonal imbalances."
Oophor Through Time
- Ancient Understanding: Early anatomists observed ovarian structures but lacked knowledge of their functions.
- Modern Advances: With the advent of microscopy, the discovery of ovarian follicles revolutionized reproductive biology.
- Contemporary Innovations: Today, treatments for ovarian disorders reflect cutting-edge research in genetics and endocrinology.
Oophor in Specialized Fields
- Gynecology:
Oophorectomy: Critical in managing conditions like ovarian cancer or endometriosis. - Endocrinology:
Oophoropathy: Involves hormonal disorders impacting fertility and overall health. - Oncology:
Focuses on diagnosing and treating cancers affecting the reproductive system. - Reproductive Medicine:
Techniques like egg freezing hinge on understanding ovarian biology.
Illustrative Story: Oophor in Action
Dr. Mira Patel, a gynecologic surgeon, faced a challenging case: a young woman diagnosed with an ovarian tumor. Balancing her patient’s fertility aspirations with the need for intervention, Dr. Patel opted for a unilateral oophorectomy. The patient’s remaining ovary preserved her chances of motherhood, highlighting the delicate balance between medical necessity and personal dreams—a testament to the root "oophor’s" profound significance in life’s journey.
Cultural Significance of the Oophor Root
In many cultures, fertility and the ovary are celebrated as symbols of life and renewal. The linguistic heritage of "oophor" reflects this reverence, connecting ancient beliefs with modern medical practices.

The Oophor Family Tree
- Ov- (Latin: "egg"):
- Ovum: A single egg cell.
- Ovulation: The release of an egg from the ovary.
- Phor- (Greek: "to bear or carry"):
- Metaphor: Carrying meaning beyond the literal.
- Semaphore: A system for carrying messages through signals.
- Gonad- (Greek: "seed, sexual gland"):
- Gonadotropin: A hormone stimulating gonadal activity.
- Gonadectomy: Surgical removal of gonads.
FAQs About the Oophor Word Root
Q: What does "oophor" mean?
A: "Oophor" means "egg-bearing" and is derived from the Greek words "oion" (egg) and "phoros" (bearing). It refers to the ovaries, which are responsible for producing eggs in the female reproductive system.
Q: What is an oophorectomy, and when is it performed?
A: An oophorectomy is the surgical removal of one or both ovaries. It is often performed to treat conditions such as ovarian cancer, endometriosis, ovarian torsion, or large ovarian cysts. In some cases, it is also done preventively for individuals with a high genetic risk of ovarian cancer.
Q: What causes oophoritis?
A: Oophoritis is inflammation of the ovaries, commonly caused by bacterial infections such as those associated with pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). It can also occur due to autoimmune conditions, where the body’s immune system attacks ovarian tissue.
Q: Can a person live without ovaries, and what happens if they are removed?
A: Yes, a person can live without ovaries, but their body will no longer produce ovarian hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This can lead to symptoms of menopause, including hot flashes, mood changes, and bone loss. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often prescribed to manage these effects after an oophorectomy.
Q: What is the difference between oophoralgia and oophoritis?
A: Oophoralgia refers to pain in the ovaries, which might occur during ovulation or due to cysts. Oophoritis, on the other hand, specifically refers to inflammation of the ovaries, often accompanied by infection-related symptoms like fever, pelvic pain, and tenderness.
Q: How is oophoritis diagnosed and treated?
A: Oophoritis is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, pelvic examination, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes laboratory tests to identify infectious agents. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to address bacterial infections and pain relief medications.
Q: What is the role of the ovaries in the endocrine system?
A: The ovaries play a dual role in the reproductive and endocrine systems. They produce eggs for reproduction and secrete essential hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle, maintain pregnancy, and influence secondary sexual characteristics.
Test Your Knowledge: Oophor Word Root Quiz
1. What does "oophor" mean?
2. What is the surgical removal of an ovary called?
3. Which term refers to inflammation of the ovaries?
4. What is oophoralgia?
5. What does "oophoropathy" describe?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Oophor
The root "oophor" embodies the essence of life, reflecting the crucial role of the ovaries in reproduction and health. From ancient medical theories to cutting-edge treatments, this root underscores humanity’s enduring quest to understand and nurture life’s beginnings. As we delve deeper into the science of reproduction, "oophor" continues to inspire innovation and compassion.














