Pneum: The Breath of Life in Language and Science
Discover the power and depth of the root "Pneum," derived from the Greek word for "breath." From life-sustaining air to cutting-edge technologies, this root permeates fields as diverse as medicine, engineering, and linguistics.
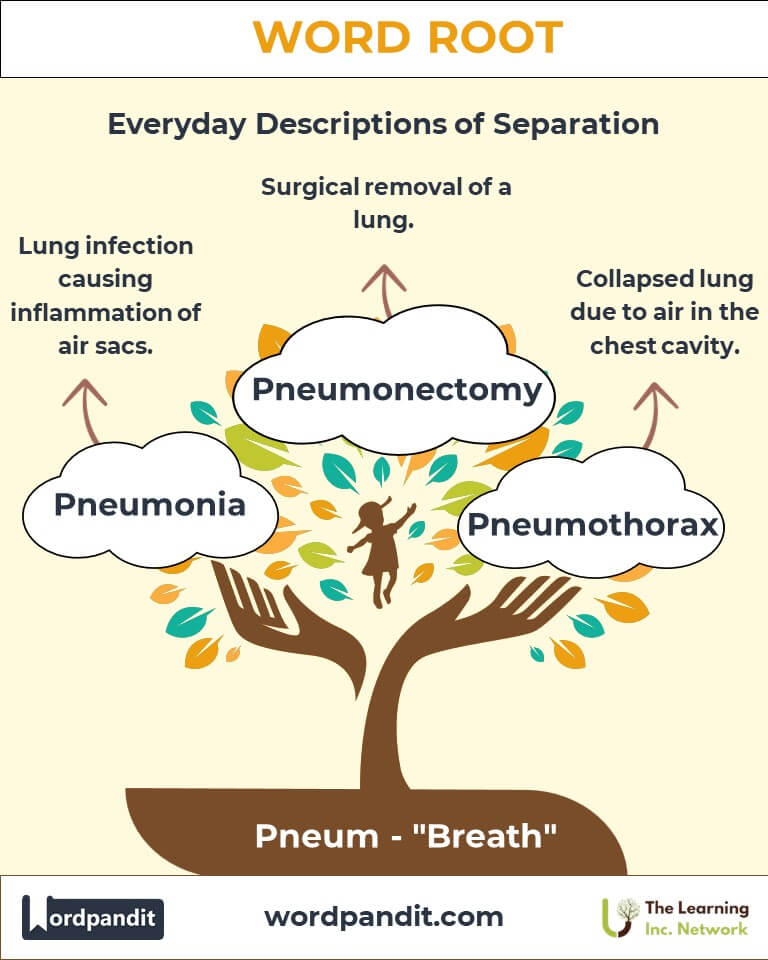
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Pneum
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Pneum
- Common Pneum-Related Terms
- Pneum Through Time
- Pneum in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Pneum in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Pneum Root
- The Pneum Family Tree
- FAQs about the Pneum Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Pneum Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Pneum
1. Introduction: The Essence of Pneum
When we think of "breath," we think of life itself. The root "Pneum," pronounced "noom," traces back to the Greek word pneuma, meaning "breath" or "spirit." This linguistic cornerstone is foundational to a wealth of terms across science, medicine, and everyday language, encompassing everything from respiratory health to pneumatic tools.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Pneum" originates from the Greek pneuma, referring to breath, wind, or spirit. Ancient Greek philosophers, such as Aristotle, saw pneuma as the vital essence of life. As the term traveled through Latin into English, it retained its life-giving connotations, becoming integral to words describing respiratory functions and air-based technologies.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Pneum
To remember "Pneum," imagine a powerful gust of wind filling a pair of lungs, symbolizing the essence of life.
Mnemonic Device: "Pneum fills the room with breath and spirit."
4. Common Pneum-Related Terms
- Pneumonia (noo-moh-nyuh): A serious lung infection that inflames the air sacs.
Example: "Her pneumonia required immediate treatment to improve her breathing." - Pneumatic (noo-mat-ik): Operated by compressed air.
Example: "The mechanic used a pneumatic drill to fix the car." - Pneumothorax (noo-moh-thor-aks): A collapsed lung caused by air in the chest cavity.
Example: "The doctor treated the pneumothorax to restore normal lung function." - Pneumonectomy (noo-moh-nek-tuh-mee): Surgical removal of a lung.
Example: "A pneumonectomy was necessary to remove the damaged tissue." - Pneumatology (noo-mah-tol-uh-jee): The study of spiritual beings or phenomena, often linked to breath or spirit.
Example: "The theologian’s research in pneumatology explored ancient beliefs about the soul."
5. Pneum Through Time
- Ancient Roots: The term pneuma was integral to ancient Greek philosophy, symbolizing the life force or soul.
- Modern Medicine: By the 19th century, "pneum" became associated with medical terms describing lung health, reflecting advances in respiratory science.
- Technology: The advent of industrial tools expanded "pneum" into pneumatic technologies, emphasizing the utility of compressed air.
6. Pneum in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Pneumonia and pneumothorax highlight respiratory health's critical nature.
- Engineering: Pneumatic systems power tools and machinery using compressed air.
- Theology: Pneumatology examines spiritual connections to breath and life.
7. Illustrative Story: Pneum in Action
Lila, a young doctor, found her calling treating respiratory illnesses. One day, she encountered a patient with severe pneumonia, their lungs struggling for every breath. Using advanced diagnostic tools and a ventilator powered by a pneumatic system, she stabilized the patient. Later, during her studies in theology, Lila marveled at how "Pneum" symbolized both breath and spirit, tying her medical practice to humanity's deeper connection to life.
8. Cultural Significance of the Pneum Root
Across cultures, breath has symbolized life, spirit, and vitality. In Greek philosophy, pneuma was the soul's essence. Eastern practices like yoga and meditation emphasize breath control (pranayama) as a path to spiritual enlightenment. This universal reverence for breath underscores the enduring importance of the root "Pneum."

The "Pneum" Family Tree
- Spir- (Latin: breath):
- Spirit: The essence of life or soul.
- Respiration: The process of breathing.
- Vent- (Latin: wind):
- Ventilate: To provide fresh air.
- Ventilator: A machine aiding breathing.
- Aer- (Greek: air):
- Aerobic: Requiring air or oxygen.
- Aerospace: Related to the Earth's atmosphere and beyond.

FAQs About the "Pneum" Word Root
Q: What does "Pneum" mean?
A: "Pneum" means "breath" or "air," derived from the Greek word pneuma. In ancient Greek, pneuma referred to both physical breath and the spiritual essence of life, tying it to vital functions and philosophical ideas about the soul.
Q: What is Pneumonia?
A: Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that inflames the air sacs, potentially filling them with fluid or pus. This condition can make breathing difficult and often requires medical intervention. The term reflects the root "Pneum" as it involves the lungs, which are essential for breathing.
Q: How do Pneumatic tools work?
A: Pneumatic tools, such as drills and hammers, are powered by compressed air. This air creates force, allowing the tools to function efficiently in industrial or mechanical applications. The "Pneum" root underscores the reliance on air as a key energy source.
Q: What is Pneumothorax?
A: Pneumothorax refers to a collapsed lung caused by air leaking into the space between the lungs and chest wall. This condition prevents the lung from expanding properly, leading to difficulty breathing. The term illustrates how "Pneum" relates to air and its interaction with the respiratory system.
Q: What does Pneumatology study?
A: Pneumatology is the theological study of spiritual beings or the "breath" of life. It explores the role of the Holy Spirit in Christian theology and investigates ancient philosophical ideas about the vital essence of breath or spirit in human existence.
Test Your Knowledge: "Pneum" Word Root Quiz
1. Which condition involves inflamed lung air sacs?
2. How do pneumatic tools work?
3. What does Pneumatology explore?
4. What is Pneumothorax?
5. What does the root "Pneum" signify?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Pneum
The root "Pneum" connects breath, spirit, and innovation. From life-saving medical interventions to technologies shaping our future, it bridges ancient philosophy and modern science. As we continue to innovate and explore, "Pneum" will remain a testament to the vitality of language and life.














