Simil and Simul: The Roots of Resemblance and Imitation
Discover the linguistic journey of "simil" and "simul," roots that define similarity and simulation. From describing likeness in everyday life to simulating complex systems in technology, these roots are fundamental to our understanding of resemblance and imitation.
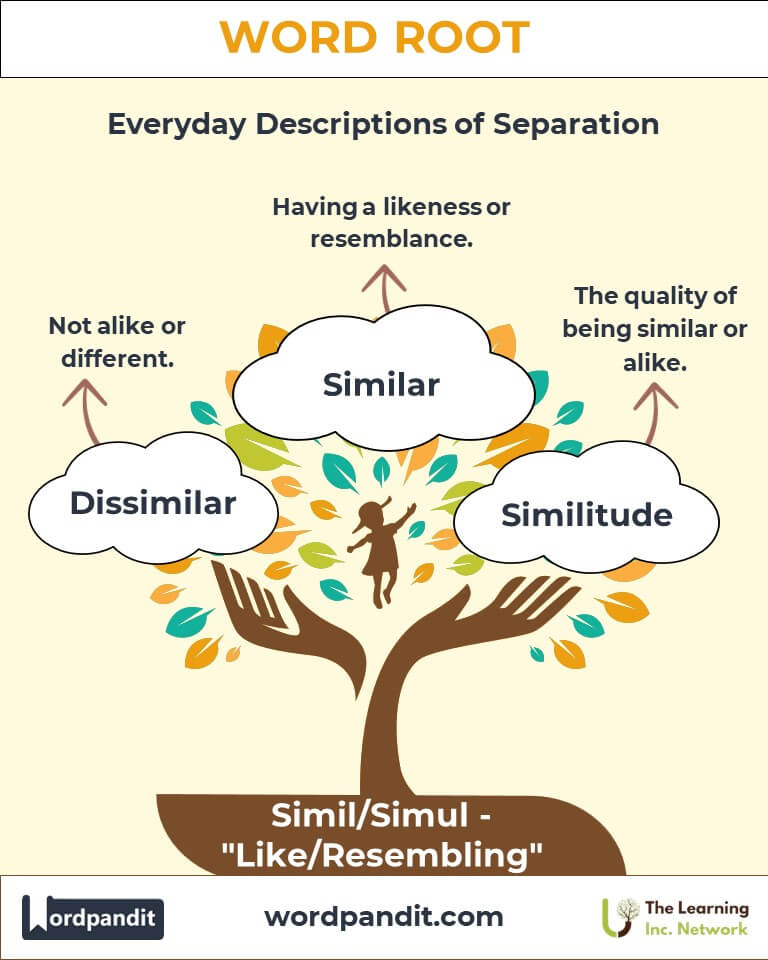
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Simil and Simul
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Simil and Simul
- Common Simil- and Simul-Related Terms
- Simil and Simul Through Time
- Simil and Simul in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Simul in Action
- Cultural Significance of Simil and Simul
- The Simil and Simul Family Tree
- FAQs About the Simil and Simul Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Simil and Simul Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of " Simil and Simul"
Introduction: The Essence of Simil and Simul
The roots "simil" (pronounced SIM-il) and "simul" (SIM-ul) derive from Latin and mean "like" or "resembling." These roots are the foundation of words that express similarity, imitation, and resemblance. Whether comparing two objects as similar or simulating real-world phenomena, "simil" and "simul" emphasize the importance of likeness in both everyday and technical contexts.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The roots trace back to the Latin words similis ("like" or "resembling") and simulare ("to imitate" or "to pretend"). Initially used in philosophical and rhetorical texts to describe analogy or resemblance, these roots expanded their influence through languages like French and English during the Middle Ages and Renaissance. They found new life in modern science and technology, where "simulation" became central to modeling and experimentation.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Simil and Simul
Mnemonic Device: "Simil" is like a mirror, reflecting resemblance. "Simul" adds an action—pretending or imitating.
Visualize a child imitating their parent in a playful simulation of adult life. This mental image captures the essence of both roots.
Common Simil- and Simul-Related Terms
- Similar (SIM-il-ar): Having a likeness or resemblance.
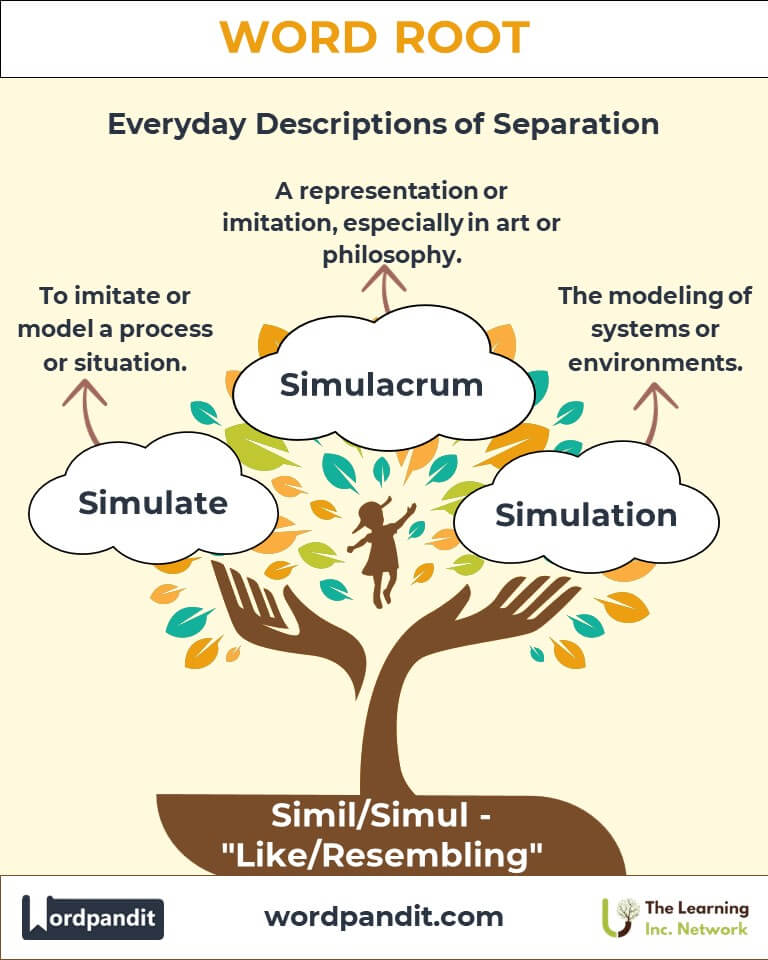
Example: "The twins look so similar that even their friends confuse them." - Simulate (SIM-yoo-late): To imitate or model a process or situation.
Example: "The flight simulator helps pilots train for emergencies." - Assimilate (uh-SIM-uh-late): To absorb or integrate into a larger system.
Example: "New immigrants assimilate into their host culture over time." - Facsimile (fak-SIM-uh-lee): An exact copy, especially of a document.
Example: "The museum displayed a facsimile of the ancient manuscript." - Similitude (si-MIL-i-tood): The quality of being similar or alike.
Example: "The similitude between the two stories was striking." - Dissimilar (dis-SIM-il-ar): Not alike or different.
Example: "Despite their dissimilar appearances, they shared the same personality traits."
Simil and Simul Through Time
- Simulacrum (Latin): Originally describing a likeness or image, this term evolved to describe representations or imitations, particularly in art and philosophy.
Example: "The simulacrum of the city in the video game felt incredibly real." - Simulation (Modern): Once referring to imitation, it now signifies the modeling of systems or environments in fields like computing and science.
Example: "The weather simulation accurately predicted the hurricane’s path."
Simil and Simul in Specialized Fields
- Technology:
Simulation: Used in virtual reality to create immersive experiences or model real-world systems.
Example: "Engineers rely on simulations to test new designs." - Medicine:
Simulated Training: Essential for preparing doctors and nurses for real-life scenarios.
Example: "Simulated surgeries improve precision and confidence." - Psychology:
Assimilation: A cognitive process where new information is integrated with existing knowledge.
Example: "Children assimilate new words into their vocabulary through context."
Illustrative Story: Simul in Action
In a bustling hospital, Dr. Elena trained her interns using a sophisticated simulation room. The simulated environment mimicked emergencies, testing their quick thinking. One day, a real emergency mirrored the simulation almost exactly. Because of their training, the interns handled the crisis seamlessly, proving the power of similitude between practice and reality.
Cultural Significance of Simil and Simul
From literature to technology, "simil" and "simul" shape how we perceive and create likeness. Fables and metaphors rely on similarity to convey morals, while advanced simulations in video games and virtual reality push the boundaries of imitation. These roots highlight humanity’s innate desire to understand the world through resemblance and replication.

The Simil and Simul Family Tree
- Simil (Latin: like):
Example: Similar, simile (a literary comparison). - Simul (Latin: together, at the same time):
Example: Simultaneous, simulate. - Pseudo (Greek: false):
Example: Pseudonym, pseudoscience.
10. FAQs About " Simil" and "Simul "
Q: What do "simil" and "simul" mean?
A: The roots "simil" and "simul" mean "like" or "resembling." Derived from the Latin words similis and simulare, these roots have been integral in shaping terms that express likeness, imitation, or resemblance. For instance, "similar" denotes having a likeness, while "simulate" involves creating an imitation.
Q: How is "simulate" different from "similar"?
A: "Similar" describes objects, ideas, or concepts that have a likeness or are alike in certain ways, whereas "simulate" involves the act of imitating, modeling, or pretending. For example, a painting may look similar to a photograph, but a flight simulator actively imitates the experience of flying an airplane.
Q: What is the role of "simulation" in modern technology?
A: Simulation is widely used in technology to create models of real-world systems, processes, or environments. For example, weather simulations predict climate changes, and virtual reality simulations immerse users in realistic experiences for entertainment or training purposes.
Q: What is the meaning of "similitude"?
A: Similitude refers to the quality of being similar or a likeness between two things. It’s often used in artistic or philosophical contexts to discuss the resemblances between ideas, appearances, or even abstract concepts.
Q: What does "assimilate" mean in different contexts?
A:
- Cultural context: Assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt the customs, language, or culture of another group.
- Cognitive context: In psychology, assimilation is the process of integrating new information into existing frameworks of understanding.
- Biological context: Assimilation can also describe how organisms absorb and utilize nutrients.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Simil" and "Simul " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "simulate" mean?
2. Which term describes a likeness or resemblance?
3. What is "assimilation" in psychology?
4. Which word relates to imitation?
5. What does "simultaneous" mean?
Conclusion: The Legacy of Simil and Simul
The roots "simil" and "simul" shape our language and understanding of likeness and imitation. From comparing objects to simulating complex systems, they remain vital in both everyday language and advanced fields. As technology and creativity evolve, these roots will continue to define how we perceive and recreate the world around us.














