Trop: The Root of Turning Points in Language and Science
Byline: Dive into the fascinating world of the root "trop," derived from Greek, meaning "turn." From biological phenomena like tropism to complex concepts such as entropy, this versatile root marks pivotal transformations across disciplines.
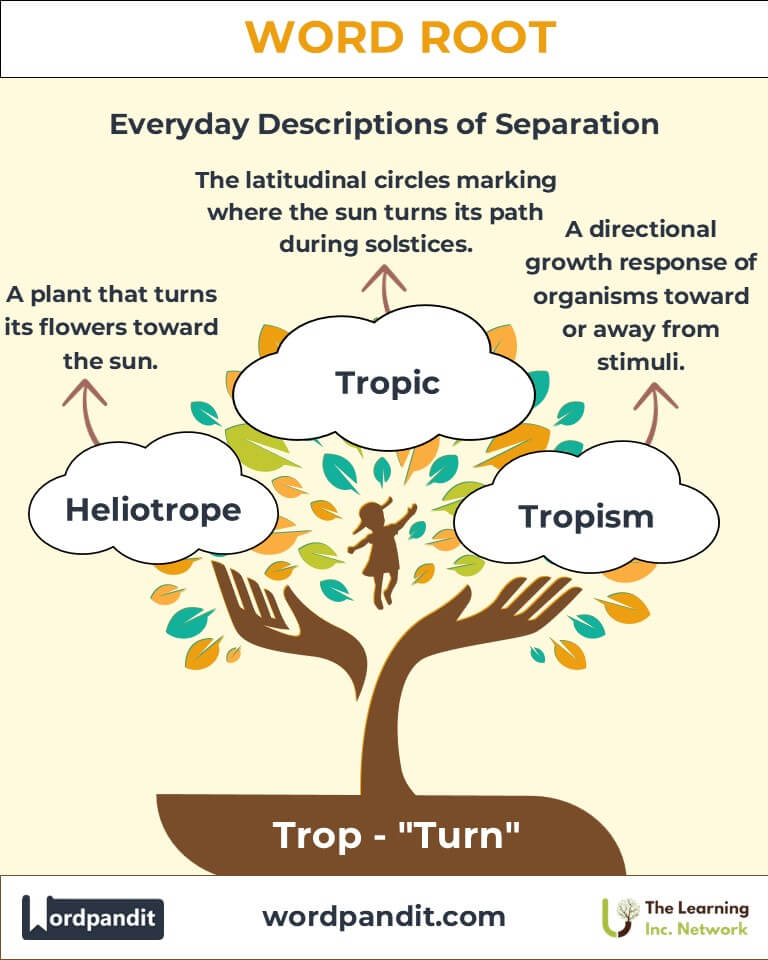
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Trop
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Trop
- Common Trop-Related Terms
- Trop Through Time
- Trop in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Trop in Action
- Cultural Significance of Trop
- The Trop Family Tree
- FAQs about the Trop Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge Trop Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Trop
1. Introduction: The Essence of Trop
What do plants bending toward light and the dispersal of energy in a system have in common? Both reflect the root "trop," pronounced "trohp," which means "turn" in Greek. This root connects words that describe physical, metaphorical, and scientific shifts. Its relevance spans biology, physics, literature, and more, embodying the idea of change and adaptation.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "trop" traces its origin to the Greek word tropos, meaning "turn" or "direction." In ancient Greek texts, it referred to shifts in thought, behavior, or celestial movements. Over time, "trop" influenced both scientific and artistic lexicons, symbolizing transitions and directional changes in natural and human-made systems.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Trop
Picture a sunflower turning its head to follow the sun’s arc across the sky—a vivid image of "trop" in action.
Mnemonic Device: “Trop turns toward the sun, showing change has begun.”
4. Common Trop-Related Terms
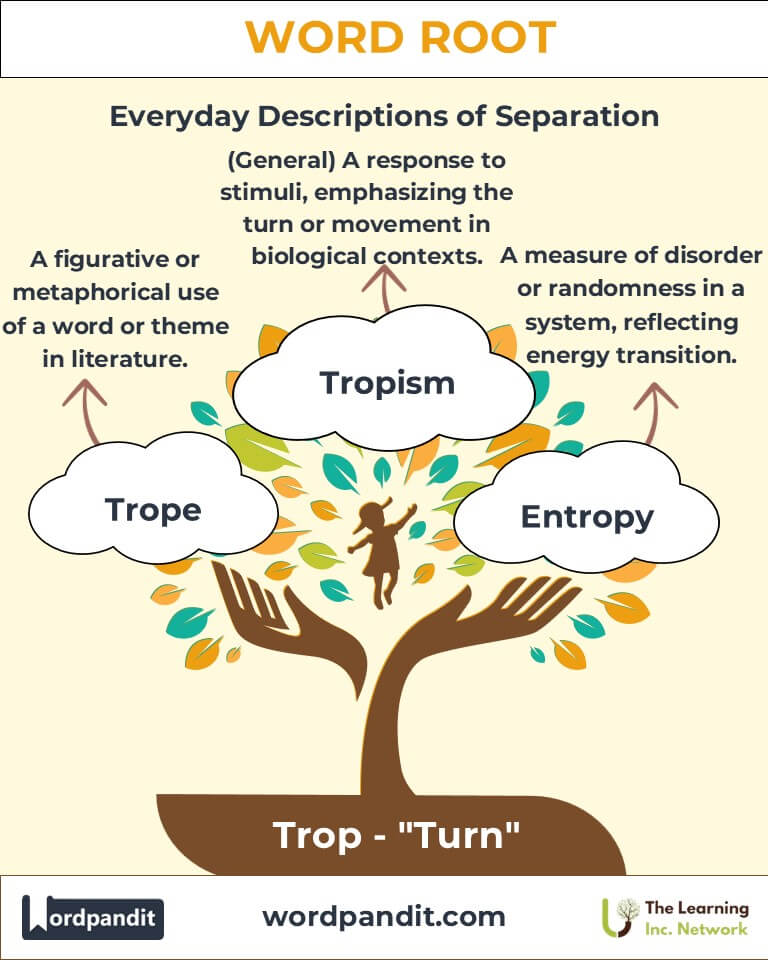
- Tropism (TROH-piz-um):
Definition: A biological response where organisms turn or grow toward or away from stimuli.
Example: “Phototropism explains how plants grow toward light for photosynthesis.” - Entropy (EN-troh-pee):
Definition: A measure of disorder or randomness in a system, often linked to the dispersal of energy.
Example: “As entropy increases, systems tend to move toward equilibrium.” - Heliotrope (HEE-lee-uh-trohp):
Definition: A plant named for its tendency to turn toward the sun.
Example: “The heliotrope’s flowers align with the sun’s path across the sky.” - Trope (trohp):
Definition: A figurative or metaphorical use of a word or phrase.
Example: “The author’s use of the hero’s journey trope made the story relatable.” - Tropic (TROP-ik):
Definition: Either of the two circles of latitude where the sun turns its path during solstices.
Example: “The Tropic of Cancer marks the sun’s northernmost point.”
5. Trop Through Time
- Heliotrope in Ancient Botany: Greek botanists observed plants like heliotropes following the sun, coining the term based on their turning behavior.
- Entropy in Modern Physics: Introduced in thermodynamics in the 19th century, it redefined the concept of "turn" as energy transitions within systems.
6. Trop in Specialized Fields
- Biology:
- Tropism: Explains directional growth responses, such as phototropism (light) and gravitropism (gravity).
- Impact: Critical in understanding plant behavior and environmental adaptation.
- Physics:
- Entropy: A cornerstone of thermodynamics, used to study energy transformations and system randomness.
- Relevance: Integral to engineering, cosmology, and statistical mechanics.
- Literature:
- Trope: Used to describe recurring themes or devices in storytelling.
- Significance: Shapes narratives, making them resonate culturally and emotionally.
7. Illustrative Story: Trop in Action
In a lush botanical garden, a curious child noticed that the flowers turned toward the sunlight. Their parent explained phototropism, sparking the child’s interest in science. Decades later, that child—now a physicist—used the concept of entropy to develop sustainable energy systems. The turning of flowers had inspired a lifetime of exploration into energy transformations.
8. Cultural Significance of Trop
The root "trop" is embedded in cultural narratives of change and transformation. From philosophical discussions of entropy as a metaphor for chaos to artistic tropes that define genres, it underscores humanity's fascination with the dynamics of turning points.

9. The Trop Family Tree
- Vert (Latin: turn)
Example: Convert (to change direction or form). - Clin (Greek/Latin: lean or bend)
Example: Incline (to tilt or lean toward something). - Vers (Latin: turn)
Example: Revert (to turn back to a previous state).
10. FAQs About " Trop "
Q: What does the root "Trop" mean?
A: The root "Trop" comes from the Greek word tropos, meaning "turn" or "change." It appears in words like "tropic," "entropy," and "troposphere," all associated with turning, transformation, or directional movement.
Q: What are the tropics?
A: The tropics are the regions of Earth near the equator, defined by the Tropic of Cancer in the north and the Tropic of Capricorn in the south. The name "tropics" reflects the idea of turning, as it relates to the apparent movement of the sun during solstices.
Q: What is the troposphere?
A: The troposphere is the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, where most weather occurs. The name is derived from the root "Trop," signifying constant change or turning, as the weather is dynamic and always shifting in this layer.
Q: How is "Trop" used in biology?
A: In biology, "Trop" appears in terms like "tropism," which describes the turning or growth of an organism in response to a stimulus, such as plants growing toward light (phototropism) or roots growing toward gravity (gravitropism).
Q: What is entropy?
A: Entropy, derived from "Trop," measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It reflects transformation and change, especially in physics and thermodynamics, where systems naturally move toward greater entropy.
Q: What does "tropical" signify?
A: "Tropical" relates to the tropics, areas near the equator characterized by warm climates and seasonal changes associated with the sun’s position. The term reflects the root "Trop," indicating cyclical changes or turning points.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Trop " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Trop" mean?
2. Where are the tropics located?
3. What happens in the troposphere?
4. What does "tropism" describe in biology?
5. What does entropy measure?
10. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Trop
The root "trop" captures the essence of transformation, from literal turns in nature to metaphorical shifts in art and science. It reminds us of the beauty in change, growth, and movement. As we explore "trop," we uncover the dynamic forces that shape our world and inspire continuous discovery.














