Xen: The Root of Foreign in Language and Thought
Discover the profound influence of the root "xen," derived from the Greek word "xenos," meaning "foreign" or "stranger." From the concept of xenophobia to the inert gas xenon, this root has left its mark on language, science, and social dynamics, encapsulating the idea of the unfamiliar or the other.
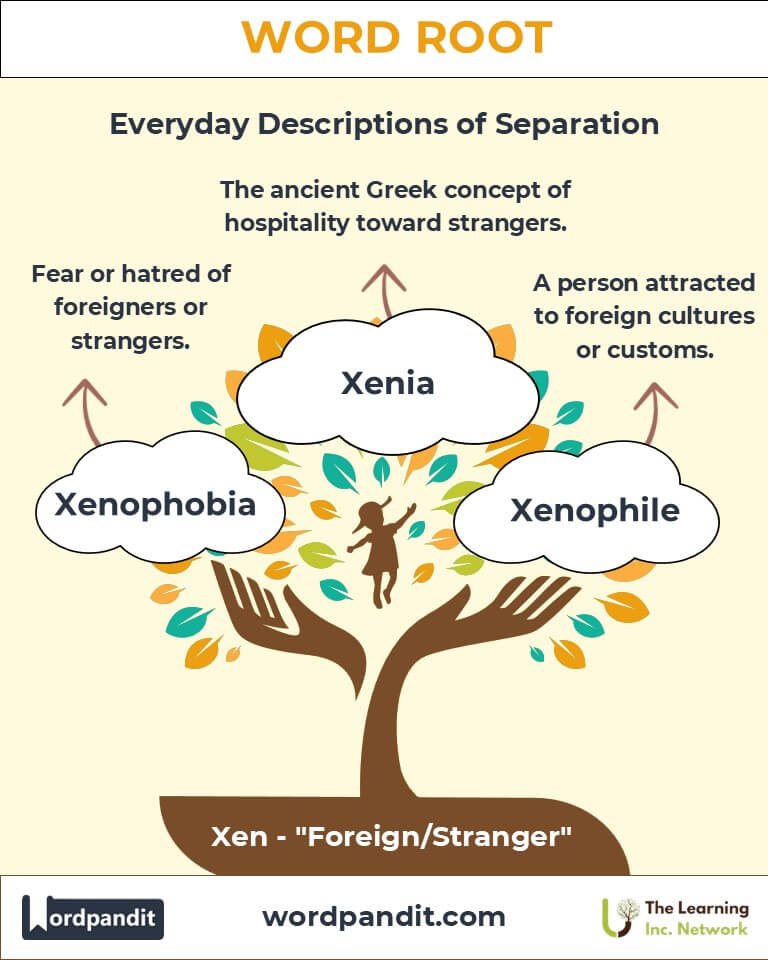
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Xen
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Xen
- Common Xen-Related Terms
- Xen Through Time
- Xen in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Xen in Action
- Cultural Significance of Xen
- The Xen Family Tree
- FAQs About the Xen Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Xen Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Xen
1. Introduction: The Essence of Xen
The root "xen" (pronounced zen) is a gateway to understanding our perceptions of the unfamiliar. Derived from the Greek word xenos, it represents "foreign," "stranger," or "guest." This root transcends language and culture, influencing fields as diverse as psychology, chemistry, and sociology. Whether discussing xenophobia (fear of the foreign) or xenon (a noble gas with unique properties), "xen" highlights the allure and challenge of encountering the unknown.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "xen" originates from ancient Greek, where xenos carried dual meanings of guest and stranger, reflecting the era's complex relationships with outsiders. The Greek tradition of xenia (hospitality) emphasized respect for strangers, a practice mirrored in Homer’s epics. Over centuries, "xen" retained its duality, shaping words that explore themes of hospitality, fear, and the unfamiliar.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Xen
To remember "xen," envision an alien visitor landing on Earth, symbolizing the ultimate "stranger" or "foreign entity." Imagine their welcome—or resistance—reflecting humanity’s varied reactions to the unfamiliar.
Mnemonic Device: "Xen marks the spot where the foreign becomes familiar."
4. Common Xen-Related Terms
- Xenophobia (zen-oh-foh-bee-uh)
- Definition: Fear or hatred of strangers or foreigners.
- Example: "The documentary explores the rise of xenophobia in modern societies."
- Xenophile (zen-oh-file)
- Definition: A person attracted to foreign cultures or customs.
- Example: "Her travels reflected her deep xenophilia for East Asian traditions."
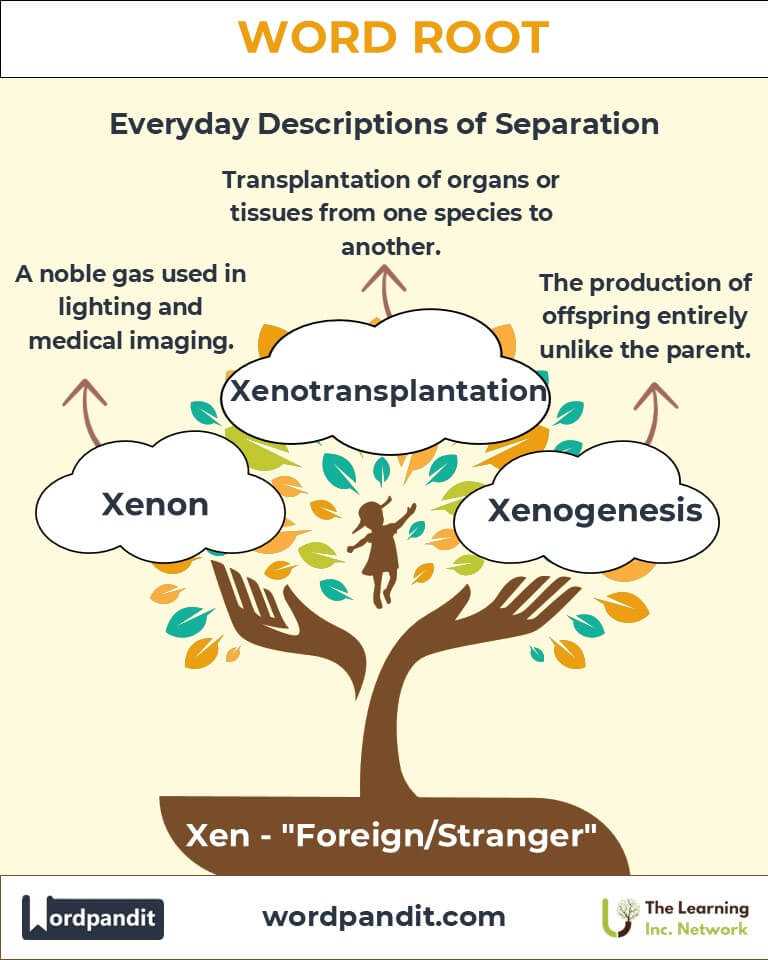
- Xenogenesis (zen-oh-jen-uh-sis)
- Definition: The production of offspring entirely unlike the parent.
- Example: "The sci-fi novel explored xenogenesis in intergalactic species."
- Xenon (zee-non)
- Definition: A noble gas used in lighting and medical imaging.
- Example: "Xenon headlights are popular for their brightness and efficiency."
- Xenotransplantation (zen-oh-trans-plan-tay-shun)
- Definition: Transplantation of organs or tissues from one species to another.
- Example: "The success of xenotransplantation could revolutionize medicine."
5. Xen Through Time
- Ancient Greece: The concept of xenia celebrated mutual respect between host and guest, showcasing the positive aspect of "xen."
- Modern Psychology: The term xenophobia emerged to describe societal fears and prejudices against immigrants and cultural outsiders.
- Contemporary Science: Xenon, discovered in 1898, showcases the root's adoption into the physical sciences.
6. Xen in Specialized Fields
- Psychology:
- Term: Xenophobia
- Relevance: Examines societal and individual responses to the unfamiliar, essential for understanding bias and promoting inclusivity.
- Medicine:
- Term: Xenotransplantation
- Impact: Holds promise for solving organ donor shortages.
- Chemistry:
- Term: Xenon
- Significance: A noble gas used in anesthesia and advanced lighting, demonstrating the versatility of inert gases.
7. Illustrative Story: Xen in Action
A village on the edge of a mysterious forest faced fear and wonder when a foreign traveler arrived. While some villagers shunned the visitor, calling them a "xenos," others welcomed them with curiosity. The traveler shared stories of distant lands, bridging gaps of misunderstanding. Over time, the village learned that embracing the "xen" could lead to growth and enrichment.
8. Cultural Significance of Xen
The duality of "xen" reflects humanity's complex relationship with the unfamiliar. From ancient Greek hospitality to modern debates on immigration, "xen" challenges us to balance fear with curiosity. It underscores cultural narratives about inclusion, diversity, and the value of encountering the unknown.

9. The Xen Family Tree
- Hosp- (Latin: Relating to hosting and strangers)
- Hospital: A place of care for guests or strangers.
- Hospitable: Welcoming to guests.
- Alien- (Latin: Relating to the other or foreign)
- Alienate: To make someone feel isolated.
- Alien: A being from another place.
10. FAQs About " Xen "
Q: What does the root "xen" mean?
A: The root "xen" originates from the Greek word "xenos," meaning "foreign" or "stranger." It embodies the idea of the unfamiliar or external, influencing words that describe relationships with outsiders or things that are rare and unknown.
Q: What is xenophobia?
A: Xenophobia refers to an intense fear, dislike, or prejudice against foreigners or strangers. This term highlights societal challenges surrounding diversity and inclusion, often reflecting underlying fears of change or competition.
Q: What is a xenophile?
A: A xenophile is someone who is fascinated by or loves foreign cultures, customs, or people. Unlike xenophobia, which represents fear or hatred, xenophilia celebrates diversity and the richness of experiencing unfamiliar traditions and ideas.
Q: What does xenogenesis mean?
A: Xenogenesis describes the creation of offspring that are entirely different from their parents. This term is commonly used in science fiction to explore themes of alien reproduction but is also applicable in biology when discussing certain unique evolutionary processes.
Q: What is xenon, and why is it significant?
A: Xenon is a noble gas discovered in 1898. Its name reflects its rarity (xenos, meaning "strange" or "rare"). It has significant applications in advanced technology, including lighting, medical imaging, and space propulsion systems.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Xen " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "xen" mean?
2. Which term describes fear of the foreign?
3. What is xenon used for?
4. What does xenotransplantation involve?
5. What does xenophile mean?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Xen
The root "xen" invites us to explore the unfamiliar with both caution and curiosity. Its presence in language and science reflects humanity’s evolving relationship with the "other." By understanding "xen," we embrace a broader worldview, fostering empathy and innovation. Let "xen" inspire you to discover the beauty of the unknown.














