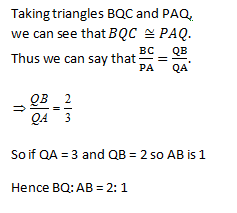- This is an assessment test.
- These tests focus on geometry and mensuration and are meant to indicate your preparation level for the subject.
- Kindly take the tests in this series with a pre-defined schedule.
Geometry and Mensuration: Test 14
Congratulations - you have completed Geometry and Mensuration: Test 14.You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.You correct answer percentage: %%PERCENTAGE%% .Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
The difference between the exterior and interior angles at a vertex of a regular polygon is 150o. The number of sides of the polygon is
10 | |
15 | |
24 | |
30 |
Question 1 Explanation:
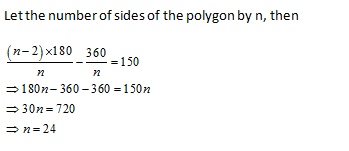
Question 2 |
The length of the diagonal BD of the parallelogram ABCD is 18 cm. If P and Q are the centroid of the ΔABC and ΔADC respectively then the length of the line segment PQ is
4 cm | |
6 cm | |
9 cm | |
12 cm |
Question 3 |
ABCD is a parallelogram where AB is parallel to CD. BC is produced to Q such that BC= CQ, where P is the point on DC
area Δ( BCP)= areaΔ ( DPQ) | |
area Δ( BCP) >areaΔ ( DPQ) | |
area Δ( BCP) | |
area Δ( BCP) +areaΔ( DPQ) |
Question 3 Explanation:
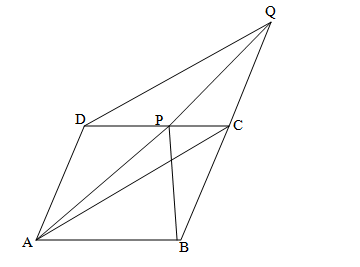
We know that: Triangles ΔAPC and ΔBCP have the common base PC.
Also, the two triangles ΔAPC and ΔBCP are located between the same two parallel lines: AB and PC
Thus, we can say: AD||CQ and AD=CQ……………………….i
From the above, we can conclude ADQC is a parallelogram.
Also, triangles ΔADC and ΔDAQ have the common base: AD
Also, the two triangles ΔADC and ΔDAQ are located between the same two parallel lines: AD and CQ.
Thus, we can conclude: Area of Δ( ADC)= Area of Δ( ADQ)
Let’s subtract area of ( DADP) from both sides: area of Δ( APC)= area of Δ( DPQ)……..(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we can conclude: area of Δ( BPC) = area of Δ( DPQ)
Question 4 |
ABCD is a rhombus. A straight line through C cuts AD produced at P and AB produced at Q. if DP= ½ AB, Then the ratio of the lengths of BQ and AB is
2: 1 | |
1: 2 | |
1: 1 | |
3: 1 |
Question 5 |
In a quadrilateral ABCD, with unequal sides if the diagonals AC and BD intersect at right angles, then
AB2 +BC2= DC2 +DA2 | |
AB2 +CD2 = BC2+ DA2 | |
AB2 +AD2= BC2+ CD2 | |
AB2+ BC2 =2(CD2 +DA2) |
Question 5 Explanation:

$ \begin{array}{l}Let\text{ }the\text{ }diagonals\text{ }intersect\text{ }at\text{ }O.\\A{{O}^{2}}+B{{O}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}~,~~\\B{{O}^{2}}+C{{O}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}~\\C{{D}^{2}}=O{{C}^{2}}+O{{D}^{2}}\\A{{D}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+A{{D}^{2}}\\From\text{ }the\text{ }equations\text{ }we\text{ }can\text{ }check\text{ }the\text{ }options\text{ }.\\A{{B}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+D{{A}^{2}}=B{{O}^{2}}+O{{D}^{2}}+A{{O}^{2}}+C{{O}^{2}}\\We\text{ }can\text{ }conclude\text{ }that\text{ }correct\text{ }option\text{ }is\text{ }\left( b \right)\end{array}$
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 5 questions to complete.
List |