A/N: The Prefix of Absence and Negation in Language
Explore the transformative power of the root A/N, derived from Greek and Latin origins, symbolizing absence, negation, or lack. From ancient philosophy to modern science, this prefix negates concepts and flips meanings, highlighting its critical role in language and logic.
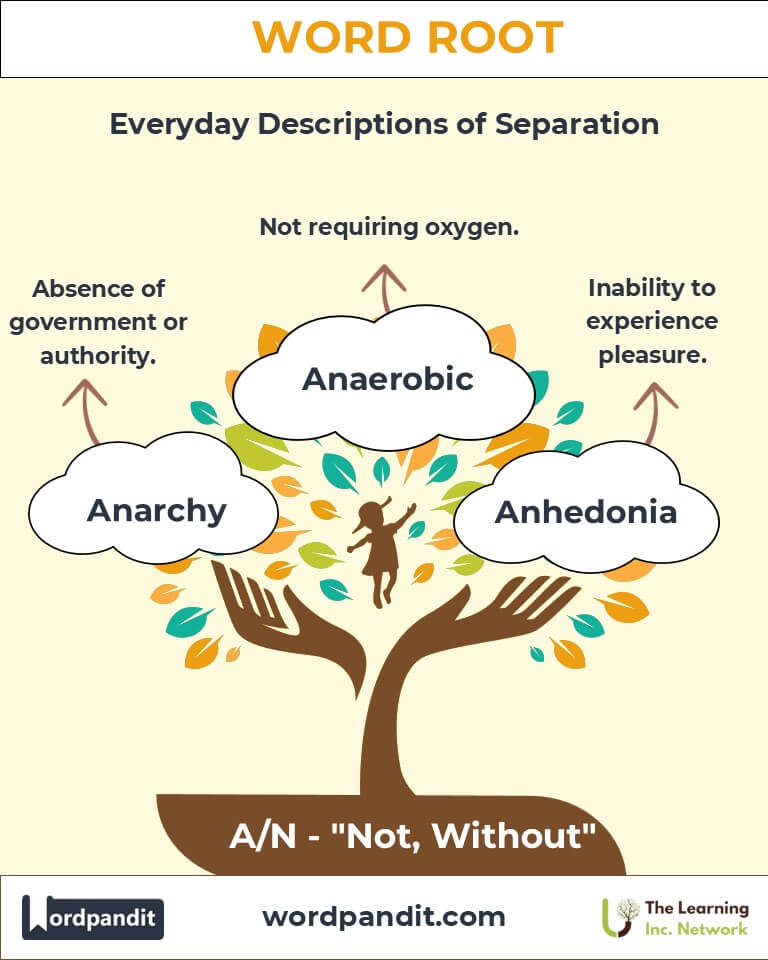
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of A/N
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of A/N
- Common A/N-Related Terms
- A/N Through Time
- A/N in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: A/N in Action
- Cultural Significance of A/N
- The A/N Family Tree
- FAQs about the A/N Prefix
- Test Your Knowledge: A/N Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Negating Legacy of A/N
1. Introduction: The Essence of A/N
The root A/N, pronounced "ay" or "an," serves as a linguistic marker of absence or negation. Whether describing the lack of faith (atheism) or the absence of rules (anarchy), this prefix forms the bedrock of terms across multiple disciplines. Derived from Greek and Latin, it transforms meanings, emphasizing the power of what is not.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
A/N stems from the Greek prefix a-/an-, meaning "not" or "without," and its Latin equivalent. It has a rich history in philosophical and scientific discourse, tracing back to Ancient Greece, where it shaped terms like atheos ("without gods") and anarchos ("without a ruler"). As language evolved, this prefix migrated into English, maintaining its negating essence.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of A/N
Imagine a door labeled "A/N" that opens to an empty room, symbolizing absence or lack.
Mnemonic Device: "A/N opens the door to absence, negating what once was."
4. Common A/N-Related Terms
- Atheism (AY-thee-iz-um): The lack of belief in deities.
Example: "Her atheism sparked deep philosophical debates." - Anarchy (AN-ar-kee): The absence of government or order.
Example: "After the collapse of the regime, the country descended into anarchy." - Atypical (AY-tip-uh-kul): Not typical or usual.
Example: "His atypical approach to the problem yielded innovative solutions." - Anonymous (uh-NON-uh-muhs): Without a known name or identity.
Example: "The letter was signed by an anonymous sender." - Agnostic (ag-NOS-tik): One who believes the existence of God or the supernatural is unknowable.
Example: "Her agnostic perspective left her open to many possibilities."
5. A/N Through Time
- Anathema: In early Christianity, this term described something cursed or detested.
Evolution: Today, it broadly refers to anything strongly disliked. - Anemia: Originating in ancient medicine, it initially described a lack of blood.
Modern Use: Now refers to a deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin.
6. A/N in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Anesthesia – The absence of sensation, typically induced for medical procedures.
Example: "The dentist administered local anesthesia before the procedure." - Philosophy: Agnosticism – The belief that ultimate knowledge (e.g., of God) is unattainable.
- Biology: Asexual – Lacking sexual reproduction or characteristics.
- Sociology: Anomie – A societal state without norms or moral guidance.
Example: "Periods of rapid change can lead to anomie in communities."
7. Illustrative Story: A/N in Action
Dr. Elena’s team discovered an anonymous donor funding an experimental treatment for anemic patients. Despite facing anarchy in their supply chain, they delivered hope to patients previously thought untreatable. Their story exemplifies the transformative power of addressing absence—be it of resources, order, or health.
8. Cultural Significance of A/N
The A/N prefix permeates language and culture, highlighting humanity's fascination with absence and negation. From theological debates (atheism) to existential philosophy (anomie), it shapes our understanding of absence as a force of definition and transformation.

9. The A/N Family Tree
- Un- (English): Examples: Uncertain, unbelievable.
- Dis- (Latin): Examples: Disorder, disbelief.
- In-/Im- (Latin): Examples: Inactive, impossible.
- Non- (Latin): Examples: Nonexistent, nonessential.
FAQs About the A/N Prefix
Q: What does A/N mean?
A: The prefix A/N means "without" or "not." It originates from Greek and Latin roots, symbolizing absence or negation. For instance, "atheism" refers to the lack of belief in gods, while "anarchy" describes the absence of government or order.
Q: How is A/N different from Un- or Dis-?
A: While Un- and Dis- also signify negation, A/N conveys a more fundamental or complete absence. For example, "anonymous" (A/N) means completely nameless, whereas "unknown" (Un-) refers to something not yet known.
Q: What is the origin of the prefix A/N?
A: A/N comes from the Greek prefix a-/an-, meaning "not" or "without," and its Latin equivalent. These roots have been used for centuries to form words expressing negation in science, philosophy, and everyday language.
Q: What does Anomie mean?
A: Anomie refers to a societal state where norms, values, and moral guidance are absent or eroded. Coined by sociologist Émile Durkheim, it often describes societal instability during rapid change or crises.
Q: Why is A/N significant in philosophy and theology?
A: A/N articulates profound concepts of absence and negation. In philosophy, "agnosticism" expresses the belief that the existence of God or the divine is unknowable. Similarly, "atheism" negates belief in deities, shaping centuries of debate.
Test Your Knowledge: A/N Mastery Quiz
1. What does the prefix A/N signify?
2. What does Anonymous mean?
3. Which field uses Anesthesia frequently?
4. What is the meaning of Anarchy?
5. What does Atypical mean?
12. Conclusion: The Negating Legacy of A/N
The A/N prefix remains a powerful linguistic tool, shaping expressions of absence, negation, and neutrality. Its influence spans languages, disciplines, and cultures, emphasizing the importance of what is not. As language evolves, A/N continues to challenge perceptions and redefine concepts. Embrace its negating potential to deepen your understanding of language and life.














