Ethno: The Root of Identity and Culture
Discover the significance of the root "Ethno," meaning "race," and its profound influence on language, sociology, and history. From "ethnicity" to "ethnography," this root provides insights into human diversity and the shared stories of cultures worldwide.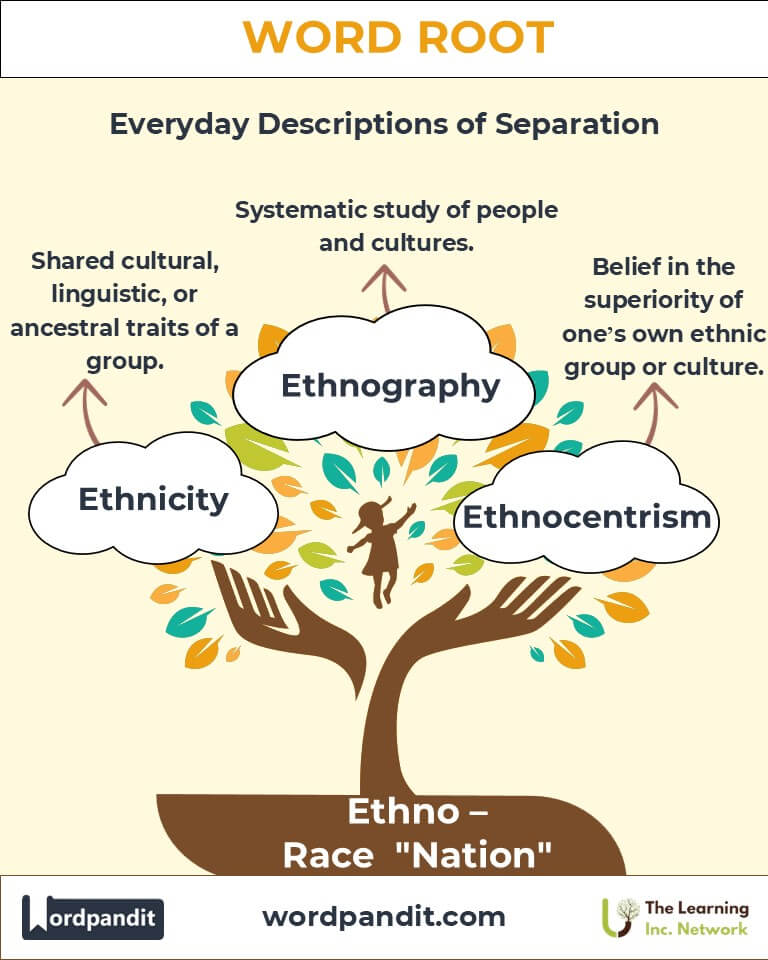
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Ethno"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Ethno
- Common Ethno-Related Terms
- Ethno Through Time
- Ethno in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Ethno in Action
- Cultural Significance of Ethno
- The Ethno Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Ethno
Introduction: The Essence of "Ethno"
What ties together the study of culture, identity, and traditions? The answer lies in the root "Ethno," derived from the Greek word ethnos, meaning "race" or "nation." Pronounced eth-noh, this root helps us understand words and concepts that explore cultural identity and diversity, making it essential in anthropology, sociology, and history.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Ethno" stems from the Greek ethnos, originally meaning "people" or "nation." Over time, its usage expanded beyond denoting specific groups to exploring cultural characteristics and collective identities. The word entered English in the 19th century, coinciding with the growth of anthropology and the academic study of human societies.
Notable influences on the development of "Ethno" include the works of early anthropologists and sociologists, who sought to classify and study the cultural and social practices of different communities worldwide.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Ethno
To remember "Ethno," imagine a colorful tapestry woven from the threads of many cultures, symbolizing the diversity of races and nations.
Mnemonic Device: “Ethno ties us to our roots, stitching stories of race and culture.”
Common Ethno-Related Terms
- Ethnicity (eth-NISS-uh-tee): The shared cultural, linguistic, or ancestral traits of a group.
Example: "Her ethnicity is reflected in the traditional recipes passed down through generations."
- Ethnography (eth-NOG-ruh-fee): The systematic study of people and cultures.
Example: "The ethnography detailed the daily rituals of the indigenous tribe."
- Ethnocentrism (eth-noh-SEN-triz-um): The belief in the inherent superiority of one's own ethnic group or culture.
Example: "Ethnocentrism often leads to misunderstanding and conflict between communities."
- Ethnology (eth-NOL-uh-jee): The comparative study of different cultures.
Example: "The museum's exhibit on ethnology showcased artifacts from around the world."
- Ethnobotany (eth-noh-BAH-nee): The study of how people use plants in their cultures.
Example: "Ethnobotany revealed how local herbs were traditionally used as medicine."
Ethno Through Time
- Ethnography: Originally focused on field studies of "exotic" cultures, it has expanded to include urban and globalized communities.
- Ethnicity: Once a term for broad racial categories, it now emphasizes cultural identity and self-perception.
Ethno in Specialized Fields
- Anthropology:
- Ethnography: Integral to field research, documenting societal structures and practices.
- Sociology:
- Ethnocentrism: Analyzed to understand biases and promote cultural relativism.
- Medicine:
- Ethnomedicine: Explores traditional healing practices across cultures.
- Ecology:
- Ethnobotany: A key discipline in sustainable resource management.
Illustrative Story: Ethno in Action
In a remote village in Southeast Asia, Dr. Elena, an ethnographer, immersed herself in the community’s way of life. She documented their rituals, cuisine, and oral histories, uncovering a deep connection between their identity and the surrounding environment. Her research not only preserved their traditions but also educated others on the importance of cultural diversity.
Cultural Significance of Ethno
The root "Ethno" highlights the richness of human cultures and the need to celebrate diversity. From festivals that showcase ethnic pride to academic research that bridges cultural gaps, "Ethno" serves as a foundation for fostering mutual understanding and respect.

The Ethno Family Tree
- Gen (Birth or Origin):
- Genealogy: The study of family ancestries.
- Genocide: The deliberate destruction of an ethnic group.
- Anthro (Human):
- Anthropology: The study of humanity.
- Anthropocentric: Viewing humans as the most important entity.
- Civ (Citizen or City):
- Civilization: Advanced stage of social development.
- Civil: Relating to citizens.
FAQs About the "Ethno" Word Root
Q: What does "Ethno" mean?
A: "Ethno" originates from the Greek word ethnos, meaning "race" or "nation." It refers to the cultural and social characteristics that define a group of people, such as traditions, language, and shared history.
Q: How is ethnicity different from race?
A: Ethnicity refers to shared cultural traits, such as language, traditions, and ancestry, while race is primarily based on physical characteristics like skin color and facial features. Ethnicity emphasizes cultural identity, while race focuses on biological factors.
Q: What is ethnography, and why is it important?
A: Ethnography is the detailed study and systematic recording of cultures and societies, often conducted through immersive fieldwork. It helps document and preserve cultural practices, provides insights into human behavior, and fosters cross-cultural understanding.
Q: What is ethnocentrism, and how does it affect societies?
A: Ethnocentrism is the belief that one's own culture or ethnic group is superior to others. This mindset can lead to prejudice, discrimination, and misunderstandings between cultures, hindering cooperation and mutual respect.
Q: How does ethnobotany contribute to science and culture?
A: Ethnobotany studies how people use plants in their cultures, including for food, medicine, and rituals. It helps preserve traditional knowledge, supports sustainable practices, and fosters innovations in areas like pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
Q: What is ethnology, and how does it differ from ethnography?
A: Ethnology is the comparative study of cultures to identify patterns and differences, often using data collected through ethnography. While ethnography focuses on documenting a single culture, ethnology compares multiple cultures to draw broader conclusions.
Q: How has the term "ethnicity" evolved over time?
A: Historically, "ethnicity" was used to categorize broad racial groups. Over time, it has evolved to focus on shared cultural characteristics, self-identification, and social cohesion within a group.
Q: Why is studying "Ethno"-related topics relevant today?
A: Understanding ethnicity, ethnography, and related topics helps address issues like multiculturalism, social integration, and cultural preservation. In a globalized world, it fosters empathy and collaboration across diverse communities.
Test Your Knowledge: Ethno Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Ethno" signify?
2. What is the focus of ethnography?
3. What is ethnocentrism?
4. How does ethnobotany contribute to sustainability?
5. What does ethnology study?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Ethno
The root "Ethno" is a testament to humanity's shared and diverse heritage. From the study of ethnicity to the documentation of cultures, it enriches our understanding of identity and belonging. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the lessons of "Ethno" remind us to celebrate diversity while seeking common ground. Let this root inspire you to explore and embrace the beauty of cultural differences.














