Fid: The Root of Faith and Trust in Language
Delve into the Latin-rooted "fid," a linguistic foundation representing faith and trust. From everyday words like "confident" to specialized terms like "fidelity," discover how "fid" builds connections in language and life.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Fid"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Fid"
- Common Fid-Related Terms
- "Fid" Through Time
- "Fid" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Fid" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Fid"
- The "Fid" Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Fid"
Introduction: The Essence of "Fid"
The word root "fid," derived from Latin fides (faith, trust), underpins a rich vocabulary that speaks to the essence of belief and confidence. Whether expressing personal assurance in "confident" or unwavering loyalty in "fidelity," "fid" forms the backbone of terms that resonate across personal, social, and professional realms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
Rooted in the Latin fides, meaning "faith" or "trust," "fid" first entered English during the Middle Ages through Old French. It carried connotations of both spiritual belief and interpersonal reliability. With the Renaissance's linguistic expansion, "fid" found its way into legal, musical, and literary contexts, solidifying its versatility.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Fid"
Imagine a trusted bridge labeled "FID," spanning two sides of a river. It represents faith and trust, holding strong under the weight of belief.
Mnemonic Device: “FID forms a bridge of trust, connecting hearts and minds.”
Common Fid-Related Terms
- Confident (kon-fi-dent): Having strong belief in oneself or someone else.
Example: "She felt confident about her ability to deliver the speech."
- Fidelity (fi-del-i-tee): Faithfulness to a person, cause, or belief, demonstrated through loyalty and support.
Example: "His fidelity to the team was unwavering, even during difficult times."
- Infidel (in-fi-del): A person who does not believe in a particular religion or set of beliefs.
Example: "During the era, infidels were often viewed with suspicion."
- Perfidy (pur-fi-dee): Deceitfulness or unfaithfulness.
Example: "The spy’s perfidy was exposed when his betrayal was discovered."
- Confide (kon-fide): To trust someone with a private matter or secret.
Example: "She confided her deepest fears to her closest friend."
"Fid" Through Time
- Fides (Ancient Rome): In Roman culture, fides symbolized a cardinal virtue tied to honesty and mutual respect, foundational to societal and legal frameworks.
- Fidelity (Renaissance): The Renaissance period extended "fidelity" to music, referring to the faithful reproduction of sound, a usage still relevant today in "high-fidelity audio."
"Fid" in Specialized Fields
- Law:
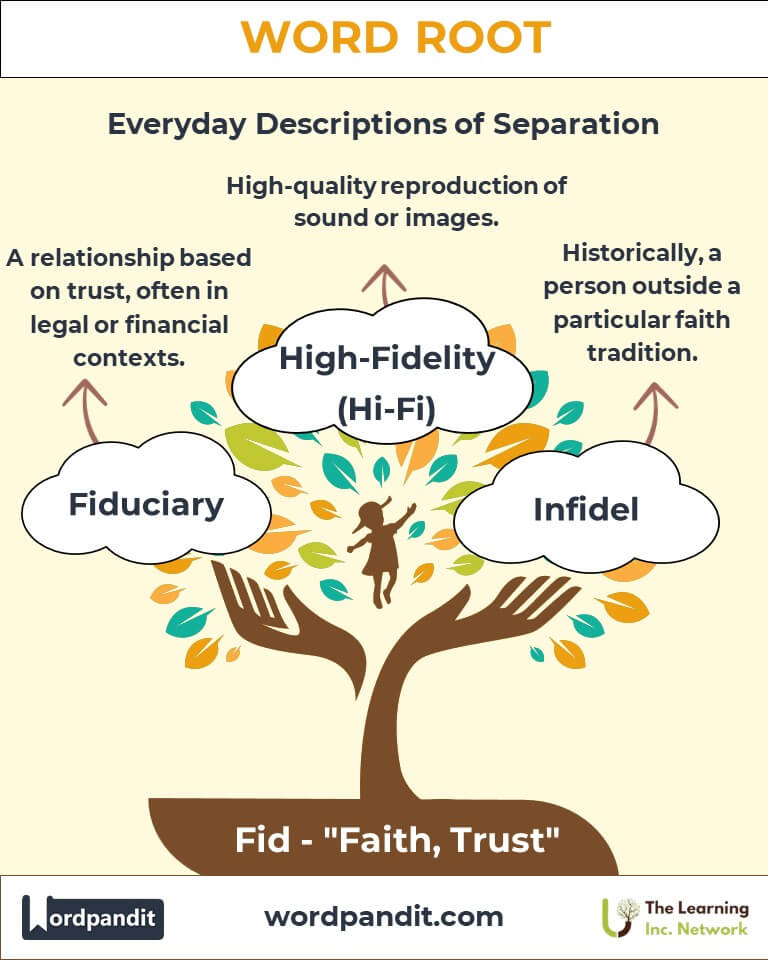
- Fiduciary: Refers to a relationship based on trust, often used in legal and financial contexts.
Example: "A fiduciary must act in the best interest of their client."
- Fiduciary: Refers to a relationship based on trust, often used in legal and financial contexts.
- Technology:
- High-Fidelity (Hi-Fi): Denotes high-quality reproduction of sound or images.
Example: "Audiophiles seek high-fidelity equipment for the best experience."
- High-Fidelity (Hi-Fi): Denotes high-quality reproduction of sound or images.
- Religion:
- Infidel: Historically used to denote someone outside a particular faith tradition.
Example: "Medieval texts often debated the treatment of infidels."
- Infidel: Historically used to denote someone outside a particular faith tradition.
Illustrative Story: "Fid" in Action
Amira, a young violinist, poured her heart into preparing for a high-fidelity music competition. Her confidence in her abilities grew with each practice session. On the day of the event, she confided in her mentor about her nervousness. With faith in her fidelity to the art, she delivered a breathtaking performance, proving that trust in oneself and one’s craft can bridge challenges.
Cultural Significance of "Fid"
The concept of "fid" has shaped human values, symbolizing trustworthiness in friendships, relationships, and societal institutions. Religious practices emphasize fidelity as a cornerstone of moral behavior, while modern culture celebrates personal confidence as a pathway to success.

The "Fid" Family Tree
- Cred (Believe, trust):
- Incredible: Something beyond belief.
- Credence: Acceptance as true.
- Faith (Derived from fides):
- Faithful: Loyal and reliable.
- Faithless: Lacking trust or belief.
- Trust (Old Norse origin, related to fides):
- Trustworthy: Deserving of trust.
- Distrust: To doubt or suspect.
FAQs About the Fid Word Root
Q: What does "fid" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Fid" comes from the Latin root fides, meaning "faith" or "trust." It appears in words like "confident" (having trust in oneself) and "fidelity" (faithfulness or loyalty). Its influence extends to fields such as law, technology, and everyday language.
Q: How is "fid" used in legal contexts?
A: In legal terminology, "fid" forms the basis of "fiduciary," describing a relationship built on trust. For example, a fiduciary is someone, like a trustee, who must act in the best interests of another party, emphasizing loyalty and faithfulness in fulfilling duties.
Q: What’s the difference between "confidence" and "fidelity"?
A: While both derive from "fid," they carry different nuances. Confidence refers to belief or trust in oneself or another, often tied to self-assurance. Fidelity, on the other hand, emphasizes loyalty or faithfulness to a cause, person, or principle, such as marital fidelity or fidelity to a contract.
Q: What does "infidel" mean, and how has its usage evolved?
A: Historically, "infidel" was used to describe someone who did not believe in a particular religion, especially in religious conflicts. Over time, its use has declined in polite discourse, and it is now seen as a dated or even pejorative term.
Q: What does "high-fidelity" mean in modern technology?
A: High-fidelity, often abbreviated as "hi-fi," refers to the accurate reproduction of sound or images. It signifies that the output remains faithful to the original source, ensuring minimal distortion and high-quality results, commonly used in audio systems.
Q: Why does "fid" signify both trust and deceit (as in "perfidy")?
A: "Fid" generally denotes trust and faith, but in words like "perfidy" (from Latin perfidia, meaning betrayal), it highlights the breach of trust. This duality reflects how trust is central to human interactions, and its violation can have profound consequences.
Q: How does "fid" appear in financial terms?
A: In finance, "fiduciary" relationships are common. For example, financial advisors have a fiduciary duty to prioritize their clients’ interests over their own, ensuring trust and ethical behavior in financial dealings.
Q: What is the cultural significance of "fid"?
A: The root "fid" has shaped cultural values by symbolizing the importance of trust and loyalty in relationships, religion, and governance. In literature and history, fidelity often represents the highest moral standards, such as in tales of faithful lovers or trusted warriors.
Test Your Knowledge: Fid Word Root Quiz
1. What term describes a relationship based on trust?
2. What does "fid" mean?
3. What does "perfidy" mean?
4. What is the modern use of "high-fidelity"?
5. What is the origin of "confident"?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Fid"
The root "fid" endures as a symbol of trust and faith in relationships, language, and culture. From ancient virtues to modern technologies, it continues to shape how we connect, believe, and inspire confidence. By embracing "fid," we strengthen the bonds that unify us in an ever-changing world.















This was really cool never done it before or used any thing like it it was really cool and saved my a lot of time.