Funct: The Root That Drives Performance and Purpose
Discover the origins, meanings, and applications of the Latin root "Funct," meaning "to perform" or "to execute." From words like "function" to "malfunction," this root embodies the essence of tasks, roles, and operational efficiency. Understanding "Funct" enriches vocabulary by connecting it to ideas of functionality, purpose, and effectiveness.
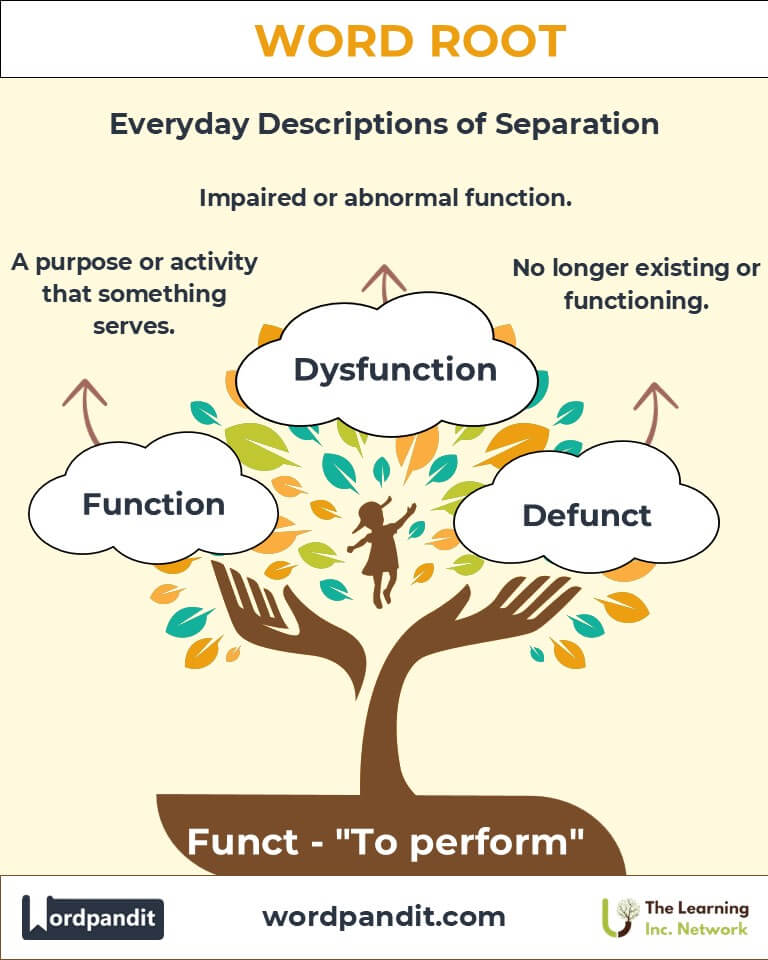
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Performing Power of Funct
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Funct
- Common Funct-Related Terms
- Funct Through Time
- Funct in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Funct in Action
- Cultural Significance of Funct
- The Funct Family Tree
- FAQs about the Funct Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Funct Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Ever-Relevant Nature of Funct
1. Introduction: The Performing Power of Funct
Every object, system, or person serves a purpose—this is the essence of the Latin root "Funct," meaning "to perform" or "to execute." Found in words like function, functional, and malfunction, it emphasizes action, purpose, and the consequences of inefficiency. Funct connects us to the mechanics of how things work and why they matter.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root Funct originates from the Latin word functus, the past participle of fungi, meaning "to perform" or "to execute." It initially described duties and roles, later evolving into terms signifying operational efficiency and purpose. The word entered English in the Middle Ages, becoming integral to technical, mechanical, and philosophical vocabulary.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Funct
Imagine a clock performing its function of keeping time. Each gear plays a role, representing the essence of Funct.
Mnemonic Device: "Funct is about functioning—everything has a role to perform!"
4. Common Funct-Related Terms
- Function (funk-shun): The purpose or activity for which something is designed.
Example: "The primary function of a car is to transport people." - Functional (funk-shun-uhl): Serving a practical and useful purpose.
Example: "The office space is both functional and stylish." - Malfunction (mal-funk-shun): A failure to work as intended.
Example: "The machine malfunctioned during the experiment." - Functionary (funk-shuh-ner-ee): A person performing official duties.
Example: "The functionary ensured the ceremony ran smoothly." - Nonfunctional (non-funk-shun-uhl): Not serving its intended purpose.
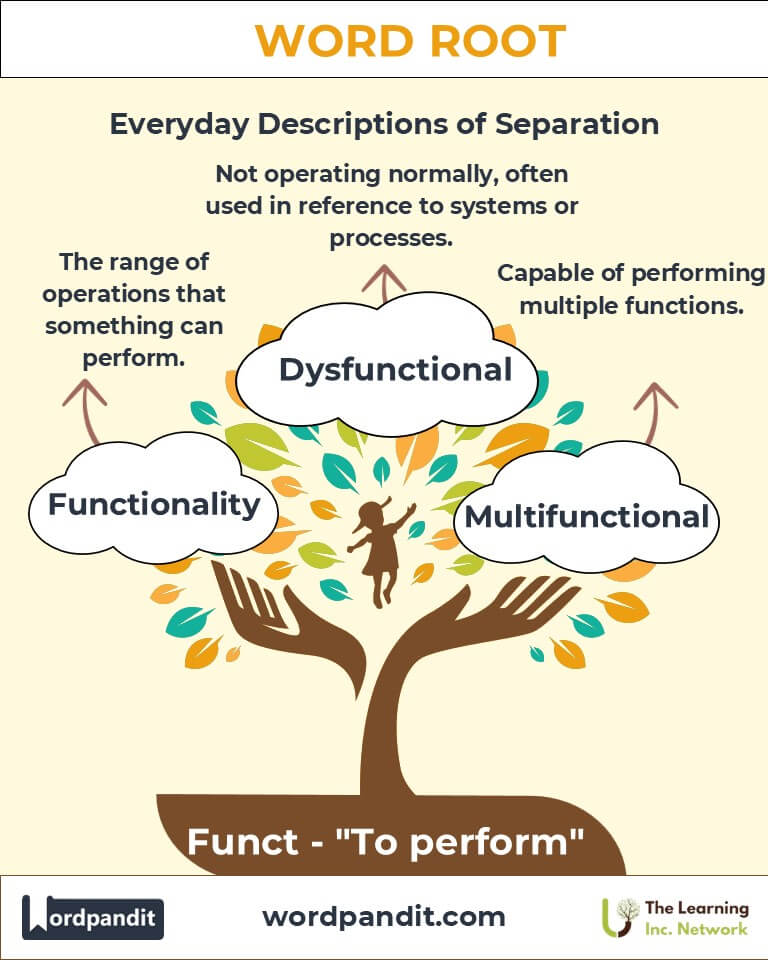
Example: "The nonfunctional light bulb was promptly replaced." - Multifunction (mul-tee-funk-shun): Capable of performing many functions.
Example: "This multifunction printer is also a scanner and copier."
5. Funct Through Time
- Defunction (Archaic): A term meaning "death" or cessation of function.
Historical Note: Common in old texts describing the end of life or operation. - Perfunctory (Modern): Performing an action with minimal effort or attention.
Current Usage: Often used in critiques of mechanical or careless actions. - Functionary (Evolving): From minor official roles to encompassing broader administrative functions.
6. Funct in Specialized Fields
- Technology:
Functionality: The range of operations a system can perform.
Example: "The app’s functionality improved with the latest update." - Medicine:
Dysfunction: Abnormal or impaired functioning of an organ or system.
Example: "Kidney dysfunction can have serious health implications." - Mathematics:
Function: A relationship between variables where one depends on another.
Example: "A quadratic function forms a parabola on a graph." - Sociology:
Functionalist: A scholar who views social systems in terms of their roles and stability.
Relevance: Highlights the importance of societal roles in maintaining order.
7. Illustrative Story: Funct in Action
Alex, a tech-savvy problem solver, was tasked with fixing a recurring malfunction in a company’s server. By analyzing its functionality and redesigning its outdated script, Alex transformed the system into a multifunctional tool. His innovative solution not only restored the system but optimized its performance, showcasing the enduring relevance of Funct.
8. Cultural Significance of Funct
The concept of "function" has been central to societal roles throughout history. Ancient civilizations assigned functional roles to individuals to maintain balance. Today, functionality drives design, technology, and organizational efficiency, reflecting the timeless importance of purpose and execution.

9. The Funct Family Tree
Related Roots:
- Oper (Latin: "to work"):
Operate: To control the functioning of something.
Operation: The process of functioning. - Techn (Greek: "art, skill"):
Technical: Relating to a specific skill or craft.
Technician: An expert skilled in a particular technical area. - Erg (Greek: "work"):
Energy: The capacity for performing work.
Ergonomics: The study of optimizing work environments.
FAQs About the Funct Word Root
Q: What does the root “Funct” mean?
A: The root Funct comes from the Latin word functus, meaning "to perform" or "to execute." It forms the basis of words that highlight roles, purposes, and actions. Its meaning extends to concepts of efficiency, operation, and even the failure to perform (e.g., malfunction).
Q: How does “Function” differ from “Functionality”?
A: Function refers to a specific role or purpose of an object, system, or action. For example, “The function of a thermostat is to regulate temperature.” Functionality, on the other hand, describes the range of tasks or capabilities something can perform, such as an app's scheduling features.
Q: What does “Malfunction” mean, and how does it occur?
A: Malfunction refers to a failure in performing a role or task properly. For example, "The machine malfunctioned due to a power surge." It often results from technical issues, design flaws, or external disturbances, emphasizing operational reliability.
Q: What is the origin of the word “Perfunctory,” and what does it signify?
A: Perfunctory comes from Latin perfunctorius, meaning "careless" or "superficial." It describes performing a task with minimal effort or attention to detail, often out of routine or obligation.
Q: What is a “Multifunction” device? How is it advantageous?
A: A multifunction device performs multiple roles, such as a printer that also scans, faxes, and copies. These devices save space, reduce costs, and improve convenience by consolidating several functionalities into one machine.
Q: What role does the term “Functionary” play in modern usage?
A: A functionary is someone who performs official duties, often within a bureaucratic or administrative setting. It emphasizes defined roles within an organization, such as a registrar or event coordinator.
Q: What is the relationship between “Dysfunction” and “Malfunction”?
A: Dysfunction typically refers to abnormal functioning in biological, psychological, or social systems, such as "Family dysfunction." Malfunction is more commonly used for technical or mechanical failures, like "The malfunctioning car."
Q: What is the importance of “Functionality” in technology?
A: In technology, functionality determines the usefulness and efficiency of a system, software, or device. It describes how well it meets user needs through its features, like AI-powered cameras in smartphones.
Test Your Knowledge: Funct Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root “Funct” mean?
2. Which word describes a failure to operate correctly?
3. What does “Perfunctory” mean?
4. What is a “Multifunctional” device?
5. Which word refers to the range of operations a system can perform?
12. Conclusion: The Ever-Relevant Nature of Funct
The root Funct captures the essence of performance and purpose. From understanding technical systems to appreciating human roles, it reminds us of the significance of functionality in a dynamic world. Embrace the Funct legacy to enhance efficiency and purpose in every endeavor!















Thanks for enriching our vocabulary
Love it