Homo: The Root of Sameness in Language and Thought
Discover the rich significance of the root "Homo," originating from Greek, meaning "same." This versatile root is the cornerstone of words like "homogeneous" and "homosexual," bridging science, philosophy, and societal discourse to explore the concept of sameness and unity.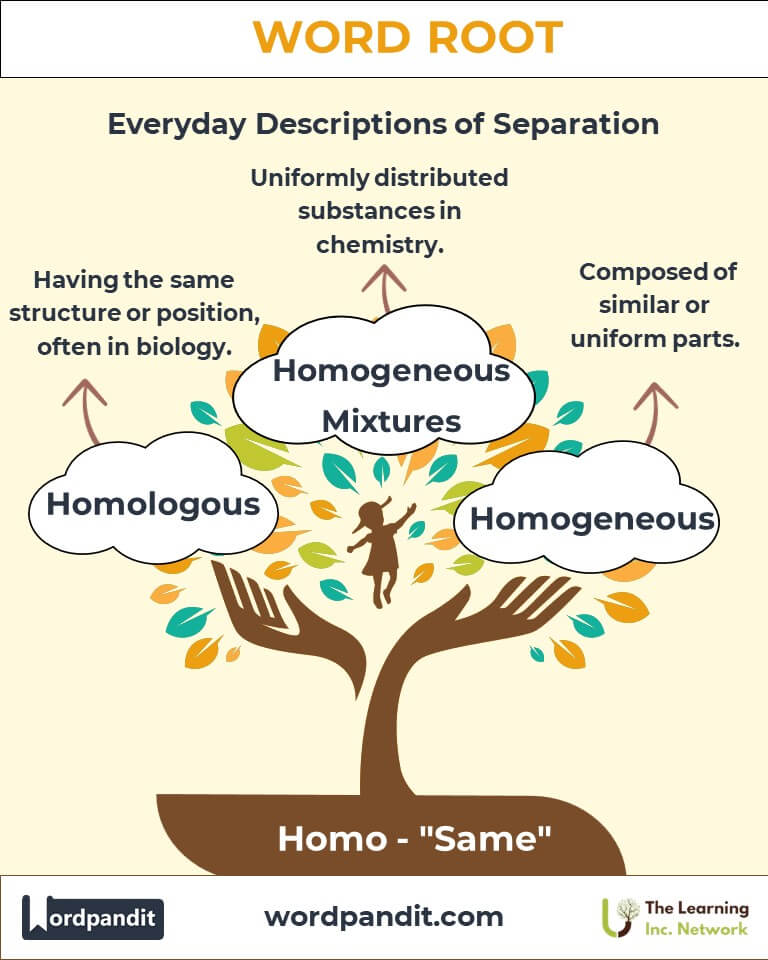
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Homo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Homo
- Common Homo-Related Terms
- Homo Through Time
- Homo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Homo in Action
- Cultural Significance of Homo
- The Homo Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Homo
Introduction: The Essence of Homo
When we hear words like "homogeneous" or "homosexual," we encounter the Greek root "Homo," pronounced "hoh-moh," which means "same." This root highlights the essence of similarity, uniformity, and shared characteristics across diverse contexts. It plays a pivotal role in scientific classification, social constructs, and philosophical discussions about unity and diversity.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Homo" originates from the Greek word homos, meaning "same" or "equal." Its use in the scientific lexicon dates back to ancient Greek philosophy, which emphasized categorization and comparison. Over centuries, "Homo" has been adapted into various fields such as biology, sociology, and linguistics, reflecting humanity's quest to understand and organize the world based on similarities.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Homo
Imagine a row of identical keys on a keyboard labeled "Homo." These keys symbolize sameness, with each representing uniformity in shape and function.
Mnemonic Device: “Homo is the key to sameness—same thoughts, same traits, same structure.”
Common Homo-Related Terms
- Homogeneous (hoh-muh-jee-nee-us): Composed of similar or uniform parts.
Example: "The mixture remained homogeneous, with all ingredients evenly distributed."
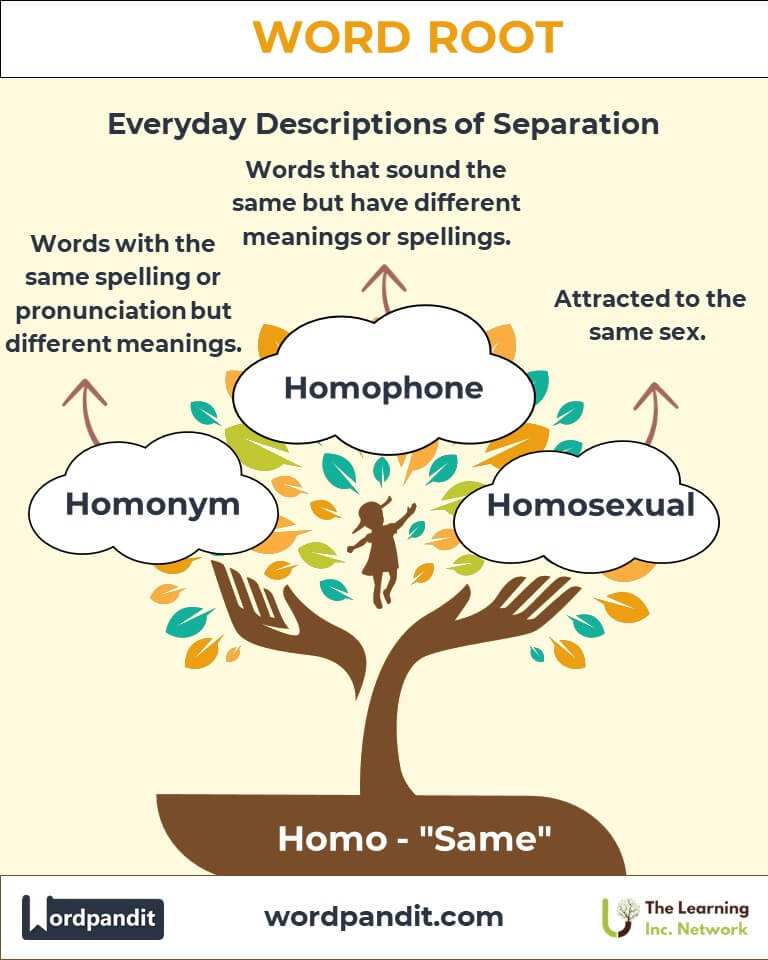
- Homosexual (hoh-muh-sek-shoo-uhl): Attracted to the same sex.
Example: "The LGBTQ+ community embraces individuals of diverse sexual orientations, including homosexual people."
- Homonym (hoh-muh-nim): Words with the same spelling or pronunciation but different meanings.
Example: "The word 'lead' as a metal and 'lead' as in to guide are homonyms."
- Homophone (hoh-muh-fohn): Words that sound the same but differ in meaning or spelling.
Example: "The words 'bare' and 'bear' are homophones."
- Homologous (hoh-mol-uh-guhs): Having the same structure or position, often in biology.
Example: "Homologous chromosomes carry genes for the same traits."
Homo Through Time
- Homogeneous:
- Historical Use: Initially used in ancient Greek science to describe uniformity in elements.
- Modern Usage: Now central to discussions in chemistry, materials science, and even social cohesion.
- Homosexual:
- Historical Use: The term emerged in the late 19th century in medical and psychological literature.
- Modern Usage: A widely recognized identity within LGBTQ+ discourse.
Homo in Specialized Fields
- Biology:
Homologous: Essential in genetics for studying evolutionary relationships.
Application: "Homologous structures help scientists trace ancestry across species."
- Linguistics:
Homonym: Highlights the complexity of language in semantics and phonetics.
Application: "Homonyms challenge learners to understand context in communication."
- Chemistry:
Homogeneous Mixtures: Crucial in material sciences and chemical engineering.
Example: "Solutions like saltwater are homogeneous at the molecular level."
Illustrative Story: Homo in Action
In a small lab, Dr. Elena used homologous structures to trace the evolutionary link between two bird species. At the same time, a linguist in the adjacent room marveled at homonyms in Shakespearean texts, revealing hidden puns. Despite their different fields, both researchers celebrated the root "Homo" as the foundation for understanding sameness in life and language.
Cultural Significance of Homo
The root "Homo" resonates deeply in culture and society. Philosophically, it fosters discussions about unity and shared humanity. Socially, it underscores inclusivity, as in terms like "homosexual," reflecting shifts toward equality and acceptance. In literature, it enriches language through homonyms and homophones, enhancing creativity and interpretation.

The Homo Family Tree
- Hetero (Different):
- Heterogeneous: Composed of diverse parts.
Example: "A heterogeneous group fosters creative problem-solving."
- Iso (Equal):
- Isothermal: Maintaining the same temperature.
Example: "The experiment required isothermal conditions."
- Auto (Self):
- Autonomous: Self-governing or independent.
Example: "Autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing transportation."
FAQs About the "Homo" Word Root
Q: What does "Homo" mean?
A: The root "Homo" means "same" and originates from the Greek word homos. It emphasizes similarity, uniformity, or equality, forming the basis of many words related to sameness in science, language, and society.
Q: How does "Homogeneous" differ from "Heterogeneous"?
A: "Homogeneous" refers to something that is uniform in composition or structure, while "heterogeneous" describes diversity or variety within a system. For example, a cup of saltwater is homogeneous because the salt dissolves evenly, but a salad is heterogeneous due to its varied ingredients.
Q: What is the significance of "Homologous" in biology?
A: "Homologous" describes structures or features that share a common evolutionary origin. For example, the forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales are homologous—they differ in function but have a shared anatomical blueprint, indicating evolutionary links.
Q: What are homophones and homonyms?
A:
- Homophones: Words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings (e.g., "bare" and "bear").
- Homonyms: Words that share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings (e.g., "lead" as a metal and "lead" as in to guide). Homophones can also be homonyms if they share the same pronunciation.
Q: Why is "Homosexual" significant in modern discussions?
A: The term "homosexual" describes individuals who are sexually attracted to members of the same sex. It is widely used in conversations about identity, equality, and inclusivity, particularly within LGBTQ+ contexts, highlighting the root’s role in societal discourse.
Q: How does "Homo" relate to mixtures in chemistry?
A: In chemistry, "homogeneous" mixtures are those where the components are uniformly distributed. Examples include solutions like sugar dissolved in water. The opposite is "heterogeneous," where components remain distinct, such as oil and water.
Q: What is the idea behind "Homogeneous Societies"?
A: A homogeneous society refers to a group of people with shared cultural, ethnic, or social traits, promoting unity and collective identity. However, such societies might lack diversity, which can also limit innovation and adaptability.
Test Your Knowledge: Homo Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Homo" signify?
2. Which word means uniform in composition?
3. What does "Homologous" refer to in biology?
4. What is the definition of "Homophone"?
5. Which term describes attraction to the same sex?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Homo
The root "Homo" serves as a testament to the interconnectedness of language, science, and culture. From fostering inclusivity to enabling scientific discovery, its impact is profound and far-reaching. As society evolves, the legacy of "Homo" continues to inspire unity, understanding, and exploration of sameness in all its forms.














